Vitamin B12: Essential Insights for Chemists
Dec 27,2024
Introduction to Vitamin B12
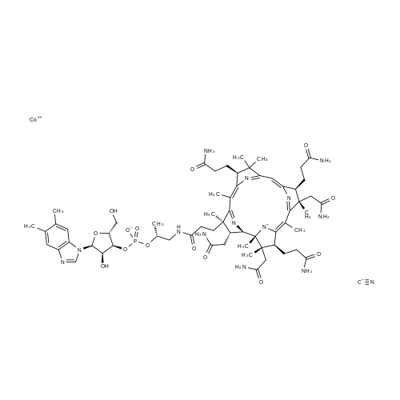
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is an organic molecule. It is a water-soluble vitamin that plays a crucial role in red blood cell formation, neurological function, and DNA synthesis. It contains a cobalt ion at its center, which is key to its biological activity. Vitamin B12 is naturally found in animal products, including meat, fish, and dairy, and is essential for maintaining healthy nerve cells and producing red blood cells.
Vitamin B12 is important for the proper functioning of the brain and nervous system. It is commonly used to treat vitamin B12 deficiency, which can lead to symptoms such as fatigue, memory problems, and nerve damage. It is also used in the management of conditions like pernicious anemia, where the body is unable to absorb enough B12 from food. In addition to its medical uses, Vitamin B12 is also added to energy drinks and supplements for its role in boosting energy and enhancing cognitive function.
Vitamin B12 should be stored in a cool, dry place away from direct light to maintain its stability. It is important to follow dosing recommendations, as excessive intake can lead to side effects such as skin rashes or gastrointestinal issues. When handling Vitamin B12 in medical settings, proper protective equipment should be worn to avoid any direct exposure during preparation or administration.

Figure 1 Characteristics of Vitamin B12
Preparation of Vitamin B12
There are usually two methods for producing vitamin B12: one is to ferment bacteria (such as certain streptococcal bacteria) to produce vitamin B12; Another method is to use chemical synthesis.
The properties of Vitamin B12
Deep red crystal or crystalline powder. Bromine free, odorless. Not melting at 300 ℃. The color darkens at 210-220 ℃. It has hygroscopicity and can absorb 12% moisture in the air. Its aqueous crystals are stable in the air. Soluble in water and alcohol, insoluble in acetone, chloroform, and ether. It is water-soluble and neutral and is most stable at pH 4.5-5. It can slowly hydrolyze in alkaline or strongly acidic solutions.
The preparation method of Vitamin B12
Produced by fermentation of grey Streptomyces, the fermentation broth is acidified, adsorbed, eluted, purified, converted with 1% cyanide, and then repeatedly extracted, concentrated, chromatographed, and crystallized with solvent and water. Vitamin B12 deficiency can cause anemia and nervous system disorders. It can be used in infant foods, used amount is 10~30μg/kg; use in strengthening drink liquid and the amount is 2~6μg/kg.2. Mainly used to treat megaloblastic anemia, poor nutrition, blood loss anemia, neuralgia and obstructive disorders. As the feed nutrition fortifier, with anti-anemia effects of pernicious anemia, nutritional anemia, parasites and anemia and effective dosage is 15-30mg/t.4.
Vitamin B12 is essential for the metabolism of the human body. The average total amount of vitamin B12 in the human body is 2-5mg, 50-90% of which is stored in the liver, which the body needs to release into the blood in the formation of red blood cells. Chronic lack of B12 can cause pernicious anemia. B12 and folic acid are important fear of enzymes during cell nucleic acid synthesis, involved in the synthesis of purines, pyrimidines, nucleic acids, and methionine; and allow methyltransferase to promote the synthesis of the base; at the same time to increase the synthesis of sugar yuan, thus eliminating the role of liver fat. Clinical often as a drug for the treatment of liver diseases. Humans need vitamin B121 micrograms per day, every day foods provide 2 micrograms, to ensure normal needs.
Hydroxocobalamin in Vitamin B12 reacts with cyanide to generate Vitamin B12, to eliminate cyanide toxicity. Therefore, the lack of vitamin B12 for cyanide sensitivity is higher than the average person. Thus, vitamin B12 deficiency sensitivity to cyanide is higher than the average person. Vitamin B12 is mainly used to treat pernicious anemia, megaloblastic anemia, antifolate drugs starting from anemia, and multiple neuritis.
![]() References
References
[1] Smith A D, Warren M J, Refsum H. Vitamin B12[J]. Advances in food and nutrition research, 2018, 83: 215-279.
[2] Brown K L. Chemistry and enzymology of vitamin B12[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2005, 105(6): 2075-2150.
References:
[1] EVA GREIBE. Dietary Intake of Vitamin B12 is Better for Restoring a Low B12 Status Than a Daily High-Dose Vitamin Pill: An Experimental Study in Rats.[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2018. DOI:10.3390/nu10081096.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- What diseases may be caused by vitamin B12 deficiency? How is it treated? Jan 6, 2025
Vitamin B12 (also known as cobalamin) is a substance necessary for maintaining basic human functions, such as the growth and development of red blood cells and the nervous system.
- The side effects of Vitamin B12 Jul 26, 2024
Vitamin B12 is an essential water-soluble vitamin for proper red blood cell formation, neurological function, and DNA synthesis.
- The Benefits of Vitamin B12 Nov 18, 2022
The passage introduces the benefits of Vitamin B12.
Supplementation with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate monohydrate can synthesize neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin, maintaining a healthy nervous system.....
Nov 4,2025Biochemical EngineeringTAED is a vital component of laundry detergents as an alternative to “active oxygen” bleaching agents, from sodium perborate to urea peroxide.....
Aug 19,2024Organic reagentsVitamin B12
68-19-9You may like
- Vitamin B12
-

- $53.00 / 500mg
- 2025-12-19
- CAS:68-19-9
- Min. Order:
- Purity: 99.90%
- Supply Ability: 10g
- Vitamin B12
-

- $53.00 / 500mg
- 2025-12-19
- CAS:68-19-9
- Min. Order:
- Purity: 99.90%
- Supply Ability: 10g
- Vitamin B12
-

- $0.00 / 10g
- 2025-12-19
- CAS:68-19-9
- Min. Order: 10g
- Purity: 0.99
- Supply Ability: 10KG