What is levofloxacin used for?
Aug 16,2024
Introduction
Levofloxacin is a third-generation fluoroquinolone drug. Compared to previous generations of fluoroquinolones, it possesses expanded activity against Gram-positive bacteria and atypical intracellular pathogens. Levofloxacin is the L-isomer of ofloxacin. Oral and intravenous formulations are considered interchangeable because plasma levofloxacin concentrations are similar with either route of administration. Levofloxacin is indicated for a wide variety of infections, including those in the upper respiratory tract (community-acquired and nosocomial), urinary tract, and sinusitis.
Chemical property
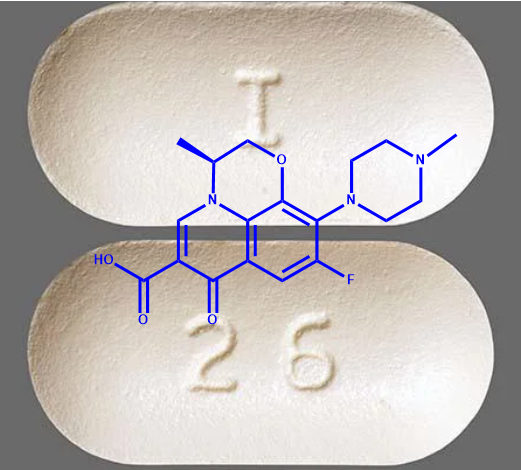
Levofloxacin is a light-sensitive, pale yellow-white to yellow-white crystal or crystalline powder and is odourless with a bitter taste. It expresses slightly acidic (carboxylic acid moiety dissociation constant of 6.24) and strongly lipophilic properties (log Kow = -0.39, logP = 2.1). It is soluble in dimethyl sulfoxide, dimethyl formamide, glacial acetic acid and chloroform, slightly soluble in ethanol, sparingly soluble in water, and practically insoluble in ether. At a pH of 0.6-5.8, levofloxacin water solubility is constant at approximately 100 pg/mL (sparingly soluble). Above pH 5.8, the solubility increases rapidly to a maximum at pH 6.7 (272 pg/mL).
Uses
Levofloxacin is effective in the treatment of a variety of infectious diseases. Its spectrum of activity includes Gram-positive aerobic bacteria, Gram-negative aerobic bacteria, some anaerobic bacteria, and other microorganisms, including Chlamydia spp., Mycoplasma spp., and Mycobacterium spp. Similar to human levofloxacin, veterinary levofloxacin is available in both oral and parenteral forms in non-EU countries.
Levofloxacin is FDA-approved for the treatment of nosocomial pneumonia, community-acquired pneumonia, acute bacterial rhinosinusitis, acute bacterial exacerbation of chronic bronchitis, acute bacterial prostatitis, acute pyelonephritis, urinary tract infection, skin or skin structure infections, prophylaxis, and treatment of plaque due to Yersinia pestis, and to reduce the incidence of disease progression of inhalational anthrax.
Side effects
The drug is in the fluoroquinolone class of medications, and adverse effects include pseudomembranous colitis, hepatotoxicity, and QT prolongation, necessitating patient education on discontinuation if such symptoms arise. Some of the more common side effects of levofloxacin include:
nausea
headache
diarrhea
insomnia (trouble sleeping)
constipation
dizziness
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Toxicity of Levofloxacin Mar 15, 2022
Levofloxacin (Levaquins, Iquixs, Quixins) is a fluoroquinolone that is the optical S-(-) isomer of ofloxacin. It was originally developed by Daiichi Seiyaku Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd, in Japan. Its chemical formula is (-)-(S)-9-fluoro-2,3-dihy
1,7-Dimethylxanthine is a naturally occurring alkaloid compound that can enhance alertness and reduce drowsiness.....
Feb 27,2025APIL-proline is one of the 20 amino acids used by the human body to synthesize proteins. This amino acid is encoded in the human genetic code with the codons CCA, CCC, CCG and CCU.....
Aug 16,2024Amino Acids and ProteinsLevofloxacin
100986-85-4You may like
- Levofloxacin Hemihydrate
-

- $0.00 / 1kg
- 2025-10-28
- CAS:100986-85-4
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 20tons
- Levofloxacin hydrochloride
-
- 2025-10-28
- CAS:100986-85-4
- Min. Order:
- Purity: 0.99
- Supply Ability:
- Levofloxacin hydrochloride
-

- $0.00 / 1Kg/Bag
- 2025-10-28
- CAS:100986-85-4
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 98%-102%
- Supply Ability: 5 tons






