Melphalan synthesis
- Product Name:Melphalan
- CAS Number:148-82-3
- Molecular formula:C13H18Cl2N2O2
- Molecular Weight:305.2

![L-Phenylalanine, 4-aMino-N-[(1,1-diMethylethoxy)carbonyl]-, ethyl ester](/CAS/20150408/GIF/67630-01-7.gif)
67630-01-7
46 suppliers
$18.00/100mg

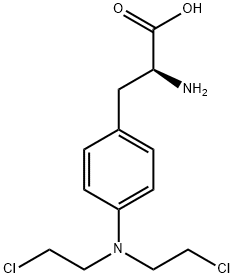
148-82-3
7 suppliers
$30.00/5mg
Yield:-
Steps:
Multi-step reaction with 3 steps
1.1: sodium carbonate / acetonitrile / 2 h / 23 - 85 °C / Large scale
2.1: trichlorophosphate / Isopropyl acetate / 2.5 h / 40 - 50 °C / Inert atmosphere
3.1: hydrogenchloride; water / Isopropyl acetate / 12 h / Reflux
3.2: pH 2
References:
FARMABIOS S.P.A.;POZZOLI, Claudio Gianluca;CANEVARI, Valentina;CURTI, Matteo WO2014/191426, 2014, A1
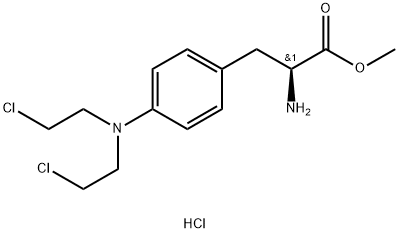
62978-52-3
34 suppliers
inquiry

148-82-3
7 suppliers
$30.00/5mg
![L-Phenylalanine, 4-[bis(2-chloroethyl)amino]-N-[(1,1-dimethylethoxy)carbonyl]-, ethyl ester](/CAS/20210305/GIF/189744-28-3.gif)
189744-28-3
0 suppliers
inquiry

148-82-3
7 suppliers
$30.00/5mg
![N-Boc-4-[bis(2-hydroxyethyl)amino]-L-phenylalanine Methyl Ester](/CAS/GIF/1217651-06-3.gif)
1217651-06-3
24 suppliers
inquiry

148-82-3
7 suppliers
$30.00/5mg
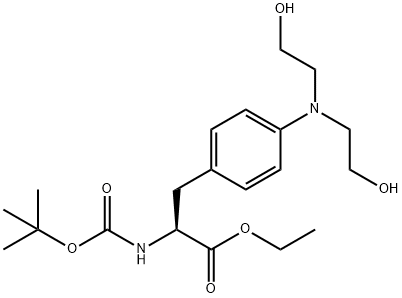
189744-27-2
2 suppliers
inquiry

148-82-3
7 suppliers
$30.00/5mg