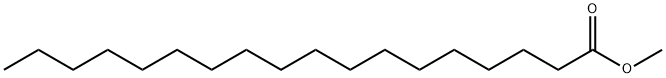
METHYL STEARATE synthesis
- Product Name:METHYL STEARATE
- CAS Number:112-61-8
- Molecular formula:C19H38O2
- Molecular Weight:298.5
67-56-1
738 suppliers
$7.30/5ml-f
57-11-4
1209 suppliers
$6.00/100g

112-61-8
397 suppliers
$8.00/25g
Yield:112-61-8 100%
Reaction Conditions:
Gel-0.5percent DVB at 65 - 67; under 760.051 Torr; for 2 h;Conversion of starting material;Molecular sieves 3A;Canola oil;
Steps:
2
Example 1; Esterification of Stearic Acid in Vegetable Oil; In a four-neck 1 L RB flask equipped with a Soxhlet condenser containing 50 g activated molecular sieves 3A, thermometer and mechanical stirrer, was added methanol rinsed ion exchange resin catalyst beads (13.75 g, 5% by weight of reaction mixture). Canola oil (202.5 g, 0.23 moles triglycerides) was charged to the flask and mechanical stirring started at 185 RPM. Then, stearic acid (22.5 g; 0.079 moles, 8.2% of oil) was added and the flask was heated by external infrared lamp to reach 60° C. over 20 minutes. At 60° C., methanol (50 g, 1.56 mole or 20 equivalents based on FFA) was charged to the flask. The mixture was allowed to reach reflux temperature (65-67° C.) with efficient stirring (235 rpm). The reflux was condensed through a water condenser and passed through the molecular sieves back into the flask.The reaction was carried out at 65° C.-67° C. (reflux temperature) and atmospheric pressure for 6 hours. Samples were taken at 30 minute intervals, using a long stem polyethylene pipette with small bore to avoid withdrawing catalyst beads. Samples were filtered through 0.45 um MILLIPORE PTFE filter into a tared one ounce glass vial. Sample weight was recorded. Samples separated into two phases, a methanolic phase on top containing a mixture of methyl esters of fatty acid and a bottom phase of mainly unreacted stearic acid and canola oil. After 6 hours, the mixture was cooled to ambient temperature. The catalyst was recovered by filtration from the organic phase. A final sample of the liquid phase was taken for analysis and the remaining oil, methanol, stearic acid mixture was discarded.Examples 2 through 36 are the same as Example 1 except for variations in catalyst type and amount, type of oils, type and amount of FFA, as mentioned in the tables.; GC Method:; GC/MS analysis of the reaction mixture was conducted to analyze for methyl stearate. The analysis showed 100% conversion in 120 minutes for a gel resin having 2% DVB content.The reaction mixture samples were diluted to 1% with THF. The dilute samples were injected into an HP 5890 Series II GC with an HP 5972 MS Detector. The GC column was SUPELCO EQUITY 1, 30 m×0.25 mm, with 0.25 um film thickness. The injector was 1 μl, split 22:1, with an injection temperature of 250° C. The carrier gas was helium, with linear velocity 32 cm/s (at) 210° C. in a constant flow mode. The oven temperature was held at 210° C. for 8 minutes, with a ramp of 15° C./min up to 320° C. for a 5 minute hold.GC/MS analysis of the starting canola oil and reaction mixture was conducted to analyze for esters. Analysis indicated the presence of a mixture of methyl esters of fatty acids {typical biodiesel mixture (methyl esters of palmitic, stearic, linoleic and linolenic acids, etc)} and the presence of stearic acid. The analysis also revealed the presence of glycerol.The Tables display percent yields of methyl stearate, except for Table 2, which displays percent of initial stearic acid remaining.
References:
Banavali, Rajiv Manohar;Pierce, Gregory C. US2008/114181, 2008, A1 Location in patent:Page/Page column 2
112-62-9
467 suppliers
$6.00/25g

112-61-8
397 suppliers
$8.00/25g

112-62-9
467 suppliers
$6.00/25g

112-61-8
397 suppliers
$8.00/25g

2778-96-3
201 suppliers
$128.00/100mg
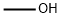
67-56-1
738 suppliers
$7.30/5ml-f
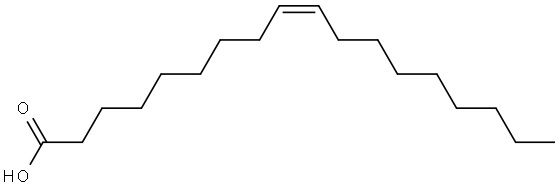
112-80-1
967 suppliers
$5.00/10g
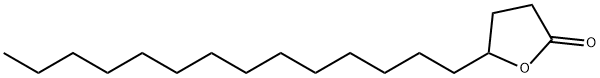
502-26-1
54 suppliers
inquiry

112-61-8
397 suppliers
$8.00/25g