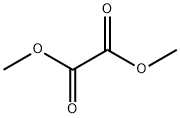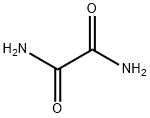
Oxamide synthesis
- Product Name:Oxamide
- CAS Number:471-46-5
- Molecular formula:C2H4N2O2
- Molecular Weight:88.07
Yield:471-46-5 98.6%
Reaction Conditions:
Stage #1:Dimethyl oxalate;methanol with ammonia at 45; under 760.051 Torr; for 3 h;
Stage #2: with ammonia at 20 - 170; under 760.051 Torr; for 0.75 - 3 h;
Steps:
1; 2; 1 Example 1; Example 2; Comparative Example 1
Example 1 A rotary evaporator having a capacity of 500 ml, equipped with an oil bath at a temperature of 450 C. and containing therein glass balls with a diameter of 1 cm, was charged with 50 g of dimethyl oxalate and 5.6 g of methyl alcohol to provide a starting material having a melting point of 430 C. The starting material was melted at a temperature of 450 C. While the rotary evaporator was rotated at speed of 100 rpm, an ammonia gas was fed in an average feed rate of 0.45 liter/min calculated under a standard temperature (00 C.) and pressure (1 atm.), to start the ammonia-addition and decomposition reaction of the dimethyl oxalate. The feed of the ammonia gas was continued for 180 minutes. The resultant solid reaction product was removed from the evaporator and dried in a vacuum dryer under a reduced pressure of 3 mmHg at a temperature of 400 C. for 12 hours, to evaporate and remove methyl alcohol from the solid reaction product. The resultant powdery product was 37.0 g of high purity oxamide. In the above-mentioned reaction procedure, the content of methyl alcohol in the reaction mixture was 24.9% by weight at 60 minutes after the start of the reaction, 21.7% of weight at 120 minutes after the start of the reaction and 18.8% by weight at 180 minutes after the start of the reaction. Also, in the reaction, the powdery product was obtained in an yield of 98.6% based on the molar amount of the dimethyl oxalate. Example 2 The same procedures as in Example 1 were carried out, with the following exceptions. The average feed rate of the ammonia gas was 0.34 liter/minute when determined under the standard temperature and pressure. The temperature of the oil bath was 600 C. After 60 minutes from the start of the reaction, the temperature of the oil bath was gradually elevated to 1700 C., to evaporate and remove the generated by-product consisting of methyl alcohol from the reaction product. A powdery solid product comprising oxamide with a high purity was obtained in an amount of 36.7 g, without the drying procedure. Comparative Example 1 A flat-bottomed separable flask was charged with a mixture of 300 g of methyl alcohol with 35.4 g of dimethyl oxalate. Then, while the mixture was stirred at a constant temperature of 200 C., an ammonia gas was fed at an average feed rate of 300 ml/minute under the standard temperature and pressure into the mixture for 45 minutes. The reaction procedure was further continued at a temperature of 200 C. for 60 minutes. When the reaction procedure was completed, it was found that the reaction mixture was in the state of a slurry in which oxamide particles were dispersed in methyl alcohol. The slurry was subjected to filtration through a filter paper sheet, to collect the oxamide particles. The filtered oxamide particles contained methyl alcohol in an amount of about 50% of weight. Thus, the filtered oxamide particles were heated at a temperature of 1100 C., to evaporate and remove methyl alcohol wherefrom. The resultant oxamide powder was in an amount of 25.9 g.
References:
Ube Industries, Ltd. US6348626, 2002, B1 Location in patent:Page column 5 - 6, 7 - 8
620-81-5
131 suppliers
$8.00/1g

471-46-5
208 suppliers
$6.00/1g
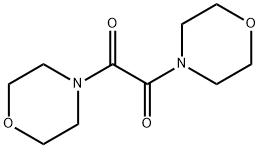
6342-79-6
3 suppliers
inquiry

471-46-5
208 suppliers
$6.00/1g
201230-82-2
1 suppliers
inquiry

471-46-5
208 suppliers
$6.00/1g
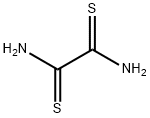
79-40-3
240 suppliers
$18.00/250mg

471-46-5
208 suppliers
$6.00/1g