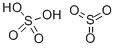발연황산 C화학적 특성, 용도, 생산
물성
수분을 흡수하면 황산은 검게 변하는 경우가 많다.
약간의 점성을 띤 산성 액체이다. 물에 녹으면 발열하지만, 의외로 얼음과 혼재하면 한제로 사용되기도 한다. 염산과 달리 비휘발성이기 때문에 농도가 낮은 황산이라도 황산에 함유된 수분이 증발하면 농축될 위험이 있다.
용도
황산은 주로 공업용품, 의약품, 비료, 폭약 등의 제조와 전지의 전해액으로 사용된다. 진한 황산과 진한 질산을 혼합한 혼산과 유기물이 반응하여 니트로화 반응을 일으킨다. 대표적인 예가 톨루엔과 반응하여 TNT를 제조할 수 있다.
독성
황산의 성질은 농도와 습도에 따라 크게 달라진다. 농도가 낮은 황산 (질량 퍼센트 농도가 약 90% 미만)을 희황산 또는 묽은 황산이라고 한다. 묽은 황산은 강산성이다. 농도가 높은 황산 (질량 퍼센트가 약 90% 이상)을 농황산 또는 진한 황산이라고 한다. 진한 황산은 산으로서의 성질이 약하다. 그 대신 흡습성이 강하기 때문에 강한 탈수작용을 한다. 만약 유기물에 접촉하면 수소와 산소를 물분자의 형태로 빨아 들인다. 황산이 피부에 닿으면 화상을 입는다. 화상을 입는 것은 이 같은 탈수작용과 발열때문이다.
개요
Fuming sulfuric acid is also called oleum, which is a trade name. It is a heavy, oily liquid, colorless to dark brown depending on purity, and fumes strongly in moist air and is extremely hygroscopic. Fuming sulfuric acid is a solution of sulfur trioxide in sulfuric acid. Sulfur trioxide is forced into solution with sulfuric acid to the point that the solution cannot hold any more. As soon as the solution is exposed to air, the fuming begins, forming dense vapor clouds. It is violently water reactive, as are most acids. Oleum is also a strong irritant to tissue. The four-digit UN identification number is 1831.
화학적 성질
viscous liquid, is a mixture of sulfur trioxide dissolved in sulfuric acid. The SO3 content may range between 15 and 30%.
물리적 성질
Dithionic acid, H2S2O6, is a chemical compound
known only in solution. This acid is dibasic and salts
called dithionates are known. All dithionates are readily
soluble in water. They are mild oxidizing and mild
reducing agents.
용도
In manufacture of fertilizers, explosives, dyestuffs, other acids, parchment paper, glue, purification of petroleum, pickling of metal.
일반 설명
Thick fuming yellow liquid. Density 16.5 lb / gal. Very toxic by inhalation. Corrosive to metals and tissue, quickly causing severe burns. Used to make chemicals, dyes, explosives and in petroleum refining.
공기와 물의 반응
Fumes in air. Soluble in water; dissolution generates dangerous amounts of heat that can cause localized boiling and spattering of the acidic mixture and generate heavy fumes. During sulfonation of mononitrobenzene with fuming sulfuric acid, a leak from an internal cooling coil permitted water to enter the reaction tank. A violent eruption occurred due to the heat of solution [MCA Case History 944(1963)].
반응 프로필
SULFURIC ACID reacts as a strong acid, as an oxidizing agent and as a dehydrating agent. Chars wood, sugar and many other organic materials on contact. The heat from these reactions may ignite the wood, sugar or organic matter. May react explosively with acetic acid, acetic anhydride, acetonitrile, acrolein, acrylic acid, acrylonitrile, allyl alcohol, allyl chloride, ammonium hydroxide, aniline, cresol, butyraldehyde, cumene, ethyl acetate, ethylene diamine, ethylene glycol, glyoxal, isoprene, isopropyl alcohol, methyl ethyl ketone, propylene oxide, pyridine, styrene, vinyl acetate; strong bases (sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide) or mineral acids (nitric acid, hydrochloric acid, hydrofluoric acid) [Lewis, 3rd ed., 1993, p. 1195]. Mixing in equal molar portions with any of the following substances in a closed container caused the temperature and pressure to increase: 2-aminoethanol, ammonium hydroxide (28%), chlorosulfonic acid, ethylenediamine, ethyleneimine, ethylene cyanohydrin, hydrochloric acid (36%), hydrofluoric acid (48.7%), isopropyl alcohol, nitric acid (70%), 2-nitropropane, propiolactone, propylene oxide, pyridine, styrene monomer, sodium hydroxide, sulfolane, vinyl acetate, vinylidene chloride [NFPA 1991]. Extremely hazardous in contact with carbides, bromates, chlorates, fulminates, picrates, and powdered metals. May induce violent polymerization in polymerizable organic compounds such as allyl chloride. Reacts exothermically with sodium hypochlorite to produce chlorine gas.
위험도
Reacts violently with water. Strong irritant
to tissue.
건강위험
Acid mist is irritating to eyes, nose and throat. Liquid causes severe burns of skin and eyes.
화재위험
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Toxic and irritating vapors are generated.
Safety Profile
Confirmed human carcinogen. A poison. Moderately toxic by inhalation. A corrosive irritant to skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. A very dangerous fire hazard by chemical reaction with reducing agents and carbohydrates. A severe explosion hazard by chemical reaction with acetic acid, acetic anhydride, acetonitrile, acrolein, acrylic acid, acrylonitrile, allylalcohol, allyl chloride, 2-amino ethanol, NH4OH, aniline, cresol, n-butyraldehyde, cumene, dichloroethyl ether, diethylene glycol monomethyl ether, diisobutylene, epichlorohydrin, ethyl acetate, ethylene cyanohydrin, ethylene diamine, ethylene glycol, ethylene glycol monoethyl ether acetate, ethylene imine, glyoxal, HCl, HF, isoprene, isopropyl alcohol, mesityl oxide, methyl ethyl ketone, HNO3, 2-nitropropane7 p-propiolacetone, propylene oxide, pyridine, NaOH, styrene monomer, vinylidene chloride, sulfolane, vinyl acetate. Will react with water or steam to produce heat and toxic and corrosive fumes. Can react vigorously with reducing materials. When heated to decomposition it emits highly toxic fumes of SOx. See also SULFUROUS ACID.
잠재적 노출
Used as a chemical feedstock in the manufacture of acetic acid, hydrochloric acid; citric acid; phosphoric acid; aluminum sulfate; ammonium sulfate;barium sulfate; copper sulfate; phenol, superphosphates, titanium dioxide; as well as synthetic fertilizers, nitrate explosives; artificial fibers; dyes, pharmaceuticals, detergents, glue, paint, and paper. It finds use as a dehydrating agent for esters and ethers due to its high affinity for water; as an electrolyte in storage batteries; for the hydrolysis of cellulose to obtain glucose; in the refining of mineral and vegetable oil; and in the leather industry. Other uses include fur and food processing; carbonization of wool fabrics; gas drying; uranium extraction from pitchblende; and laboratory analysis. Sulfuric acid is among the highestvolume produced chemical in the United States.
운송 방법
UN1830 Sulfuric acid with >51% acid or sulfuric acid with not >51% acid, Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material. UN1831 Sulfuric acid, fuming with 30% or more free sulfur trioxide and Sulfuric acid, fuming, with <30% free sulfur trioxide, Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material. UN1832 Sulfuric acid, spent, Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material.
비 호환성
A strong acid and oxidizer. Reacts violently with water with dangerous spattering and evolution of heat. Reacts violently with combustible and reducing materials; bases, organic materials; chlorates, carbides, picrates, fulminates, water, powdered metals. Corrosive to most common metals forming explosive hydrogen gas.
폐기물 처리
Add slowly to solution of soda ash and slaked lime with stirring; flush to drain with large volumes of water. Recovery and reuse of spent sulfuric acid may be a viable alternative to disposal, and processes are available.
발연황산 준비 용품 및 원자재
원자재
준비 용품
trysin-chymotrypsin
silica gel fine-pored lump
2,6-Dinitroaniline
8-Hydroxyquinoline-5-sulfonic acid
2',7'-dibromo-3',6'-dihydroxyspiro[isobenzofuran-1(3H),9'-[9H]xanthene]-3-one
에틸 황산
3-Bromo-2,6-dimethylpyridine
Cosmetic white oil
에텐일 옥타데칸산
FLAVIANIC ACID
4-Chlorobenzenesulfonic acid
라놀린
2-CHLORO-PYRIMIDINE-5-SULFONYL CHLORIDE
3-Pyridinesulfonic acid
3-Amino-4,6-dimethylpyridine
Chymotrypsin
Sodium 2-amino-1,4-benzenedisulfonate
4-Amino-1,3-benzenedisulfonic acid
2-Hydroxy-5-nitronicotinic acid
2-Anthraquinonesulfonic acid
다이클로로다이페닐트라이클로로에테인(디클로로디페닐트리클로로에탄)
메틸 블루
1,8-DINITROANTHRAQUINONE
N-(4-chlorophenyl)-2-hydroxy-9H-carbazole-3-carboxamide
starting type lead-acid storage battery
2-NAPHTHYLAMINE-4,6,8-TRISULFONIC ACID
Coumalic acid
2-Amino-3-bromo-5-nitropyridine
2-Naphthol-6,8-disulfonic acid
Atropine sulfate monohydrate
8-히드록시-7-요오드-퀴노린술폰산
2,5-DICHLORO-3,4-DINITROTHIOPHENE
3-Iodobenzoic acid
3,5-Dihydroxybenzoic acid
Pyridine-3-sulfonyl chloride hydrochloride
5-이소퀴놀린술폰산
4-Diazo-3,4-dihydro-7-nitro-3-oxo-1-naphthalenesulfonic acid
Mordant Black 9
5-Hydroxyisoquinoline
디하이드로티오-p-톨루이딘설폰산