Disodium Phosphate Dodecahydrate: An In-Depth Analysis
Jul 10,2024
Introduction
Disodium Phosphate Dodecahydrate (DSPD) is a widely used chemical compound with significant applications across various industries. It is a vital ingredient in many industrial processes and everyday products, underscoring its importance in both commercial and scientific contexts. As a versatile and essential substance, DSPD holds a prominent place in the field of chemistry, serving functions that range from food preservation to water treatment. Its unique chemical structure and properties enable it to perform a variety of roles effectively. This article delves into the properties, composition, uses, and storage methods of Disodium Phosphate Dodecahydrate, providing an in-depth understanding for professionals in the chemical domain.

Figure 1 Characteristics of Disodium Phosphate Dodecahydrate
Properties
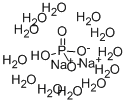
Disodium Phosphate Dodecahydrate, with the chemical formula Na₂HPO₄·12H₂O, is a hydrate form of disodium phosphate. It is characterized by its crystalline structure and high solubility in water. The compound appears as a white, odorless, and efflorescent solid, which means it tends to lose water of crystallization when exposed to air.
Molecular Weight: 358.14 g/mol
Melting Point: 35-40°C (dissolves in its water of crystallization)
Solubility: Highly soluble in water, insoluble in alcohol
pH: Solutions typically have a pH of around 9
Density: Approximately 1.52 g/cm³
The dodecahydrate form is particularly notable for its twelve water molecules of hydration, which play a crucial role in its physical properties and behavior in various applications.
Composition
The primary components of Disodium Phosphate Dodecahydrate are:
Sodium Ions (Na⁺): Essential for various biochemical processes and industrial applications.
Phosphate Ions (HPO₄²⁻): A key component in many biological systems, playing a crucial role in energy transfer and storage.
Water of Crystallization (H₂O): The twelve molecules of water are integral to the structure, influencing its solubility and thermal properties.
The balance of these components is critical for maintaining the integrity and functionality of the compound in different contexts.
Uses
Disodium Phosphate Dodecahydrate finds applications in a multitude of fields due to its chemical properties:
Food Industry: Used as an emulsifier, thickening agent, and preservative. It helps in maintaining the texture and quality of processed foods.
Water Treatment: Acts as a sequestrant, helping in the removal of calcium and magnesium ions, thus softening the water.
Detergents and Cleaning Agents: Incorporated in formulations to enhance cleaning efficiency by preventing the re-deposition of dirt.
Pharmaceuticals: Utilized as a buffering agent to maintain pH levels in various medicinal formulations.
Textile Industry: Employed in dyeing processes to ensure even color distribution and fixation.
Laboratory Reagent: Commonly used in analytical chemistry for the preparation of buffer solutions and other analytical procedures.
The versatility of DSPD makes it a valuable component in both industrial and laboratory settings, facilitating a range of processes through its unique properties.
Storage Methods
Proper storage of Disodium Phosphate Dodecahydrate is crucial to preserve its efficacy and prevent degradation. The following guidelines should be observed:
Temperature: Store in a cool, dry place, ideally below 30°C to prevent the loss of water of crystallization.
Humidity: Keep the compound in a low-humidity environment. Use airtight containers to avoid efflorescence and maintain stability.
Light: Protect from direct sunlight and intense artificial light to prevent any potential chemical changes.
Compatibility: Store away from incompatible substances such as strong acids and oxidizing agents, which could cause hazardous reactions.
Adhering to these storage conditions ensures the compound remains in optimal condition for its intended use.
Conclusion
Disodium Phosphate Dodecahydrate is an essential chemical with a broad spectrum of applications across various industries. Its unique properties, stemming from its composition and hydration state, make it a vital component in food processing, water treatment, pharmaceuticals, and beyond. Understanding the characteristics, applications, and proper storage methods of DSPD is crucial for professionals in the chemical field to leverage its full potential. This comprehensive overview highlights the importance of Disodium Phosphate Dodecahydrate and underscores the need for meticulous handling to maintain its functionality and effectiveness.
![]() References
References
[1] Hammick D L, Goadby H K, Booth H. CLXXV.—Disodium hydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate[J]. Journal of the Chemical Society, Transactions, 1920, 117: 1589-1592.
[2] Wang T Y, Huang J. Synthesis and characterization of microencapsulated sodium phosphate dodecahydrate[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2013, 130(3): 1516-1523.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
Methylparaben belongs to a group of chemicals known as parabens. These are preservative ingredients that people have used for almost 100 years to prevent the growth of fungi, bacteria, and yeast, which could cause products to spoil.....
Jul 9,2024Organic reagentsPhenacetin, known chemically as N-(4-ethoxyphenyl)acetamide, is a well-known pharmaceutical compound that has a storied history in medicinal chemistry.....
Jul 10,2024APISodium phosphate dibasic dodecahydrate
10039-32-4You may like
- What is albendazole used for?
Jul 10, 2024
- X-PHOS: Properties and Applications as Catalyst
Jul 10, 2024
- Phenacetin: A Comprehensive Overview for Chemistry Professionals
Jul 10, 2024
Sodium phosphate dibasic dodecahydrate manufacturers
- Sodium phosphate dibasic dodecahydrate
-

- $6.00 / 1KG
- 2024-07-10
- CAS:10039-32-4
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 20TONS
- Sodium phosphate dibasic dodecahydrate
-

- $100.00 / 10kilograms
- 2024-07-10
- CAS:10039-32-4
- Min. Order: 1kilograms
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 100tons
- Sodium phosphate dibasic dodecahydrate
-

- $67.00 / 1kg
- 2024-07-01
- CAS:10039-32-4
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 5000 tons