Methylamine Hydrochloride: A Comprehensive Overview for Chemical Professionals
Dec 31,2024
Introduction
Methylamine Hydrochloride is a derivate of methylated amine which could be used as nitrogen source to induced the FLD expression.Vukic´evic et al have established a convenient onepot solvent-free synthesis of N-methyl imines from aromatic aldehydes, using methylamine hydrochloride as the methylamine source.

Structure
Methylamine hydrochloride CH5N·HCl crystallizes in the tetragonal system, space group P4/nmm (129) with lattice parameters a=b= 0.6068(1) nm and c= 0.50689(8) nm[1].
Synthesis
Each may be prepared as its hydrochloride by methylating ammonium chloride with formaldehyde under suitable conditions. Methylamine hydrochloride is easy and safe to handle. It could be either commercially obtained or prepared by a very simple procedure from an inexpensive formaldehyde solution and ammonium chloride[2].
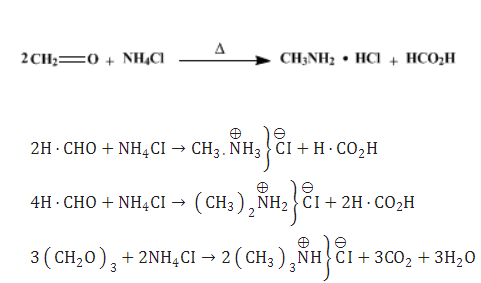
Methylamine hydrochloride is obtained by heating two equivalents of formaldehyde (as formalin) with ammonium chloride at about 100°. Any dimethylamine hydrochloride formed may be removed by extraction with chloroform.
Dimethylamine hydrochloride is the main product when four equivalents of formaldehyde and a somewhat higher temperature are used.
With a large excess of formaldehyde (as paraformaldehyde) at 160°, trimethylamine hydrochloride is obtained in good yield.
![]() References
References
[1] B. Lasocha, W. Lasocha, B. Gaweł. “Powder diffraction investigations of some organic hydrochlorides.” Powder Diffraction 21 1 (2006): 310–313.
[2] Niko S. Radulović , Rastko D. Vukićević, Ana B. Miltojević . “Simple and efficient one-pot solvent-free synthesis of N-methyl imines of aromatic aldehydes.” 2013. Pages 257-270.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- What are the uses of Methylamine hydrochloride in different fields? May 14, 2024
Methylamine hydrochloride is used as a synthetic raw material or pharmaceutical intermediate component in the manufacture of pharmaceuticals.
- Methylamine hydrochloride: Application, Pharmacokinetics, Toxicity, storage, Preparation Apr 27, 2023
Methylamine hydrochloride is a salt of the organic compound methylamine and hydrochloric acid. It has the chemical formula CH3NH2·HCl and is a white to slightly yellow crystalline powder.
- Method for Recycling Methylamine Hydrochloride Oct 21, 2019
Methylamine is an organic compound with a formula of CH3NH2. This colorless gas is a derivative of ammonia, but with one hydrogen atom being replaced by a methyl group. It is the simplest primary amine.
Supplementation with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate monohydrate can synthesize neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin, maintaining a healthy nervous system.....
Nov 4,2025Biochemical EngineeringMagnesium glycinate and magnesium citrate are best absorbed by the body. In contrast, magnesium oxide, which is cheaper but poorly absorbed, may result in more of a tendency toward loose stools or diarrhea.....
Jun 11,2024Food AdditivesMethylamine hydrochloride
593-51-1You may like
Methylamine hydrochloride manufacturers
- Methylamine hydrochloride
-

- $10.00 / 1ASSAYS
- 2025-12-21
- CAS:593-51-1
- Min. Order: 1ASSAYS
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 10 tons
- Methylamine HCL powder
-

- $10.00 / 1ASSAYS
- 2025-12-21
- CAS:593-51-1
- Min. Order: 1ASSAYS
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 10 tons
- Methylamine HCL
-

- $10.00 / 1ASSAYS
- 2025-12-21
- CAS:593-51-1
- Min. Order: 1ASSAYS
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 10 tons






