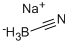One of the reductants for reductive amination: sodium cyanoborohydride
May 8,2024
Description
After the imine is formed, it must be reduced to the amine. Using the familiar reducing agent sodium borohydride (NaBH4) for this process is possible. Sodium cyanoborohydride (NaBH3CN) and sodium triacetoxyborohydride (NaBH(OAc)3 ) are the other two commonly used reductants for reductive amination. Since the reaction rate for reducing iminium ions is much faster than for ketones or even aldehydes, the reductive amination can be carried out as a one-pot procedure by introducing the reducing agent into a mixture of the amine and carbonyl compounds.
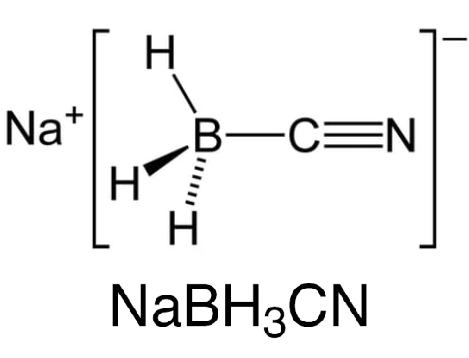
In practice, NaBH3CN is a little bit better than NaBH4. The advantage of using NaBH3CN is that it isn’t a strong enough reducing agent to reduce aldehydes or ketones but a strong enough nucleophile to reduce iminium ions. Therefore, more of the starting aldehyde/ketone will be converted into the amine. This is particularly important when working with very precious samples of aldehyde.
Sodium cyanoborohydride is soluble in water (100 mg/ml, with heating), methanol, ethanol, and THF. It is insoluble in nonpolar solvents such as benzene or hexane. It is a selective reducing agent used for various chemical reductions, including aldehydes, ketones, oximes, enamines, reductive aminations of aldehydes and ketones, and reductive alkylations of amines and hydrazines. The utility of sodium cyanoborohydride as a reducing agent is greatly enhanced by its stability under acid conditions and solubility in aprotic solvents. Sodium cyanoborohydride is a milder and more selective reducing agent than sodium borohydride.
Uses
Reduction of aldehydes and ketones. At pH 3-4, benzaldehyde can be reduced to benzyl alcohol with 87% yield. Under the same conditions, cyclohexanone can be reduced to cyclohexanol with 88% yield.
Reduction of oximes. At pH 4, cyclopentanone oxime can be reduced to the corresponding hydroxylamine with 77% yield with no reduction to the amine.
Reductive amination of aldehydes and ketones. At pH 6, benzaldehyde and ethylamine, in the presence of sodium cyanoborohydride, form the secondary amine N-ethylbenzylamine with 91% yield. The steroid 5- α -androstane-3,17-dione can be selectively aminated at the 3-position using ammonium acetate with 100% yield.
Tertiary methylated amines can be synthesized by the reaction of an aromatic or aliphatic amine with aqueous formaldehyde and sodium cyanoborohydride in acetonitrile. M-Nitroaniline is alkylated with formaldehyde to m-Nitro-N, N-dimethylaniline with 68% yield.
Safety
The reaction rate for the reduction by sodium cyanoborohydride of iminium ions is much faster than that of ketones or aldehydes. However, when done as a one-pot procedure, it liberates the highly toxic gas HCN with strong acids. A safer reducing agent with comparable reactivity is Sodium TriAcetOxyBorohydride.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Sodium Cyanoborohydride: A Versatile Agent in Chemical Synthesis May 23, 2024
Sodium cyanoborohydride (NaCNBH?) is a chemical compound extensively utilized in the realm of organic synthesis.
- What is Sodium cyanoborohydride? Sep 19, 2023
Sodium cyanoborohydride is a mild reducing agent that is commonly used for a variety of chemical reductions
Supplementation with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate monohydrate can synthesize neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin, maintaining a healthy nervous system.....
Nov 4,2025Biochemical EngineeringSilicon (Si) is a nonmetallic chemical element in the carbon family. Silicon makes up 27.7 percent of Earth's crust, the second most abundant element, surpassed only by oxygen.....
May 8,2024Inorganic chemistrySodium cyanoborohydride
25895-60-7You may like
Sodium cyanoborohydride manufacturers
- Sodium cyanoborohydride
-

- 2025-12-17
- CAS:25895-60-7
- Min. Order:
- Purity: 0.99
- Supply Ability:
- Sodium cyanoborohydride
-
- $41.00 / 25g
- 2025-12-17
- CAS:25895-60-7
- Min. Order: 25g
- Purity: 0.95
- Supply Ability: 100kg
- Sodium cyanoborohydride
-

- $10.00 / 1KG
- 2025-12-11
- CAS:25895-60-7
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 10 mt