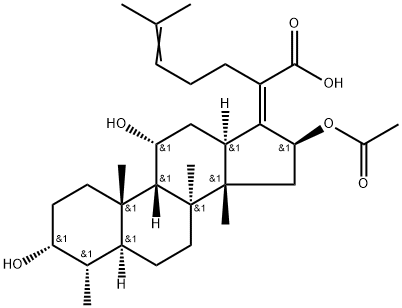
The steroid antibiotics---?Fusidic acid
Mar 18,2022
Fusidic acid was developed by Leo Laboratories in Copenhagen and obtained from the fungus Fusidium coccineum. It has a steroid structure but is chemically also related to cephalosporin P, which is one of the antibiotics formed by the mold Cephalosporium acremonium. Owing to its resemblance to prednisolone, fusidic acid is said to belong to its own class of antibiotics, the steroid antibiotics.
A number of derivatives of fusidic acid have been prepared, but their antibacterial activity is low compared with fusidic acid. The sodium salt of fusidic acid (sodium fusidate) is used clinically, and can be administered orally as film-coated tablets or intravenously as a 1- to 2-hour infusion. The drug is also available as topical preparations – as an ointment, cream, lotion, or gel – for treatment of skin infections, as well as various impregnated products such as gauze, tulle or wicks. Furthermore, sodium fusidate is sold as a gel for application in the conjunctival sac for treatment of conjunctivitis and other ocular infections.
Mechanism of Drug Action
Fusidic acid is related chemically to cephalosporin P, but the cephalosporin antibiotics are derived from cephalosporin C. In contrast to the cephalosporins, which inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis, fusidic acid inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by binding to and thereby preventing the translocation of the elongation factor ‘‘G’’ (EF-G) from the ribosome, and possibly by other mechanisms. The binding to EF-G blocks the effective translocation of peptidyl tRNA, which inhibits its linking to the grown peptide, thus inhibiting protein synthesis. The fusA gene encodes for the EF-G, and mutations in fusA cause resistance to fusidic acid by changing the configuration of the EF-G . The different mode of action between fusidic acid and the cephalosporin explains the lack of cross-resistance between fusidic acid and the penicillinase-resistant penicillins and cephalosporins. For this reason, methicillin-resistant staphylococci are usually susceptible to fusidic acid. Inhibition of protein synthesis results in less protein A on the surface of S. aureus, rendering the organism more susceptible to phagocytosis.
Gram-negative bacilli have always been thought to be fusidic acid resistant, probably because the drug could not penetrate their cell walls, although fusidic acid inhibits the protein synthesis of E. coli in cell free systems. Bennett and Shaw (1983) showed that one type of plasmid-associated fusidic acid resistance in E. coli involves binding of the drug to type 1 chloramphenicol acetyltransferase with consequent ‘‘sequestering’’ of the drug, and prevention of its attachment to the translational EF-G.
Drug interactions
Fusidic acid has been reported to cause symptoms of levomethadone withdrawal in 4 of 44 HIV-infected drug addicts . This may be a result of competition for metabolism in the liver or displacement because of the high serum protein binding of fusidic acid. Three case reports of rhabdomyolysis secondary to concomitant treatment with simvastatin and fusidic acid suggest that fusidic acid somehow competes for metabolism with the cytochrome P3A4 enzyme system, which is known to take part in the metabolism of simvastatin.
Toxicity
In general, fusidic acid can be regarded as relatively nontoxic. When administered orally, only mild upper gastrointestinal discomfort and diarrhea have been noted. Investigations have failed to show any evidence of renal or hemopoietic toxicity. There is a risk of thrombophlebitis after i.v. administration into a peripheral vein for more than 24 hours, but this appears to be less with the newer fusidic acid i.v. formulation. No severe allergic reactions have been observed, but occasional mild rashes have been reported. The drug appears to be safe in penicillin-allergic patients. Allergic contact dermatitis has been reported after topical fusidic acid use. In one case this was attributed to formaldehyde in the ointment. In chronic infections fusidic acid has been given for several months without obvious toxic effects .
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Fusidic acid:Chemical properties,Uses,Mechanism of action and Side effects Jun 19, 2025
Fusidic acid, a narrow-spectrum antibiotic, is used both systemically and topically to treat primary skin infections, including impetigo.
- Fusidine: Properties and Clinical Applications Sep 23, 2024
Fusidine, a topical antibiotic with a steroid-like structure, effectively treats skin infections like impetigo, with low side effects and high efficacy against resistant bacteria.
Fosfomycin is a phosphoenolpyruvate analogue produced by Streptomyces fradiae and by some Pseudomonas spp., but is now mostly obtained synthetically. It is a broad-spectrum antibiotic with bactericidal properties.....
Mar 18,2022APIGatifloxacin is an 8-methoxy fluoroquinolone and is marketed by Bristol Myers Squibb as Tequint. Three formulations are available: oral, ophthalmic, and intravenous. Like other members of this class, gatifloxacin has activity against many G....
Mar 18,2022APIFusidic Acid
6990-06-3You may like
- Fusidine
-

- 2025-07-13
- CAS:6990-06-3
- Min. Order:
- Purity: 0.99
- Supply Ability:
- Fusidine,Fusidic acid
-
- $0.00 / 10g
- 2025-07-11
- CAS:6990-06-3
- Min. Order: 10000g
- Purity: 99.0%min. HPLC
- Supply Ability: 1000kg
- Fusidic Acid
-

- $0.00 / 25Kg/Bag
- 2025-07-11
- CAS:6990-06-3
- Min. Order: 2Kg/Bag
- Purity: 97.5% up / EP
- Supply Ability: 20 tons