Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (API), popularly speaking, are the raw materials of medicines, only pharmaceutical raw materials are processed into pharmaceutical preparations , can they become medicines available for clinical use, so drugs we usually eat are the finished drugs through processing. Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients based on its sources can be divided into two major categories ,including chemical synthetic drugs and natural chemical drugs. Chemical synthetic drugs can be divided into organic synthetic drugs and inorganic synthetic drugs. Inorganic synthetic drugs are inorganic compounds ( very few is element), such as aluminum hydroxide, magnesium trisilicate which are used for the treatment of gastric and duodenal ulcers ; organic synthetic drugs are mainly composed of drugs made by basic organic chemical raw materials, through a series of organic chemical reactions (such as aspirin, chloramphenicol, caffeine, etc.). Natural chemical drugs ,based on its sources,can be divided into two categories including biochemical drugs and plant chemical drugs. Antibiotics are generally made by the microbial fermentation, which belongs to the biochemistry category. A variety of semi-synthetic antibiotics occurs in recent years,which are biosynthesis and chemical synthesis combining products.Among active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, the organic synthetic drugs varieties, yields and values have the largest proportion,which are the main pillars of the chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The quality of active Pharmaceutical Ingredients decides whether the formulation is good or bad , so its quality standards are very strict ,countries in the world have developed national pharmacopoeia standards and strict quality control methods for its widely used active Pharmaceutical ingredients.
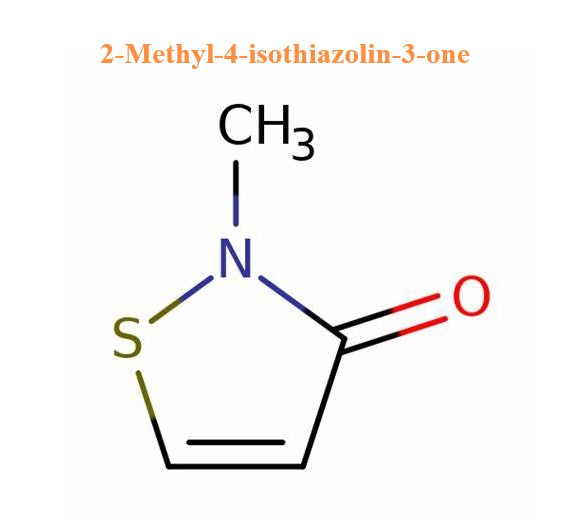
2-Methyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one: Uses and Toxicity
2-Methyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one, also known as Methylisothiazolinone, abbreviated as MIT, is a highly effective biocide and preservative widely used in cosmetics, personal care and industry.
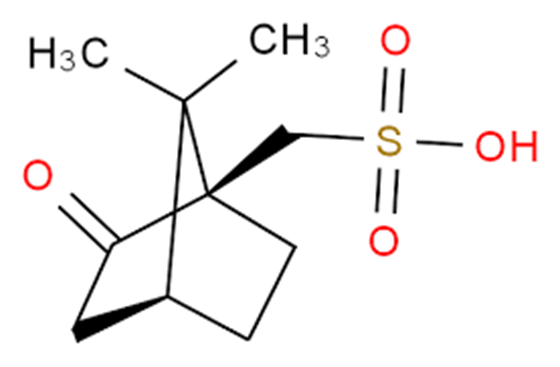
Dec 16,2024 API(1R)-(-)-10-Camphorsulfonic acid: Uses and Mechanism
(1R)-(-)-10-Camphorsulfonic acid is a non-alkyl acid containing an oxidising group that may be involved in hydrogen bonding and is mainly used to separate optically active isomers.
Dec 16,2024 APIUnderstanding Climbazole: Properties, Uses, and Storage Guidelines
Climbazole has garnered attention in both the pharmaceutical and personal care industries due to its efficacy in treating fungal infections, especialy dandruff.
Dec 16,2024 APIUses of Sulfanilic acid
Sulfanilic acid (SA) is a typical representative compound of sulfonated aromatic amines and an intermediate in some sulfonated azo dyes.
Dec 16,2024 APIHow to separate P-XYLENE from xylene?
P-XYLENE is a xylene isomer that is widely used as a feedstock for the manufacture of other industrial chemicals.
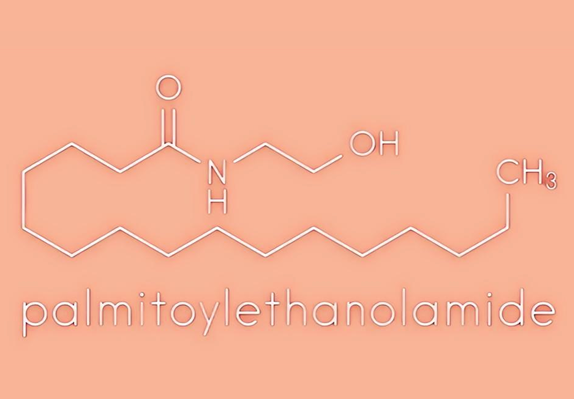
Dec 16,2024 APIApplications and safety of Palmitoylethanolamide in the food industry
Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA) is a natural plant active substance present in the diet and is also an endogenous cytoprotective lipid.
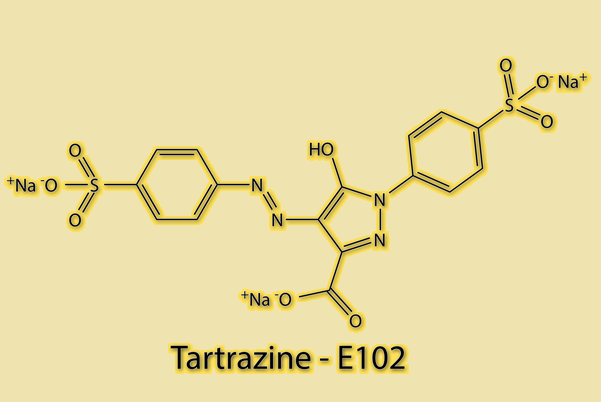
Dec 16,2024 APITartrazine: Effects, Synthesis and Side Effects
Tartrazine (Yellow 5) is a yellow, water-soluble azo dye that is widely used as a food colourant in food, pharmaceuticals and cosmetics.
Dec 16,2024 APIPharmacological Activity and Potential Health Benefits of Capsaicin
Capsaicin is the main active ingredient of chilli peppers and the most stimulating natural alkaloid.
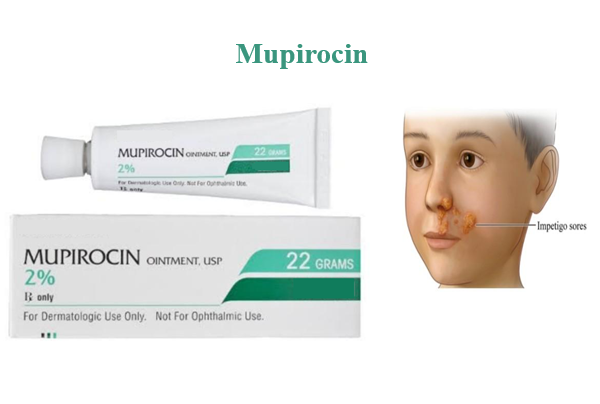
Dec 16,2024 APIMupirocin: Indications, Mechanism of action and Side Effects
Mupirocin is a topical antibiotic analogue for the control and treatment of a wide range of skin and soft tissue infections.
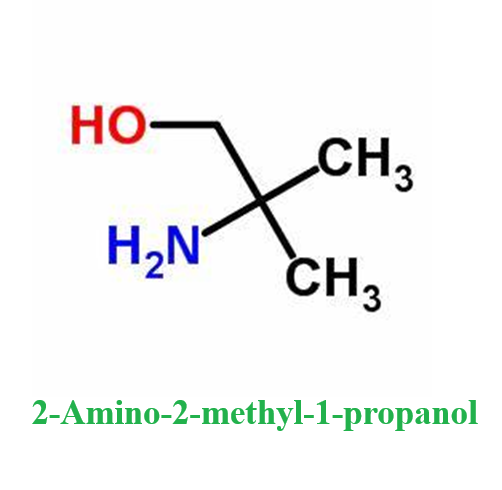
Dec 16,2024 APIAbsorption properties relating to carbon dioxide removal by 2-Amino-2-methyl-1-propanol (AMP) mixtures
A study of the mass transfer performance of 2-Amino-2-methyl-1-propanol (AMP) and piperazine (PZ) +AMP mixtures for CO2 uptake from natural gas (NG) with a high CO2 concentration suggests that PZ +AMP
Dec 16,2024 API