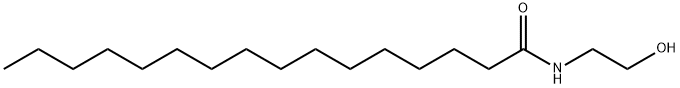
Applications and safety of Palmitoylethanolamide in the food industry
Dec 16,2024
What is Palmitoylethanolamide?
Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA) is a natural plant active substance present in the diet and is also an endogenous cytoprotective lipid. It can be isolated from soy lecithin, egg yolk and peanut flour, or prepared by chemical synthesis. PEA has a wide range of pharmacological activities, including anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antimicrobial, immunomodulatory and neuroprotective effects.
It can be used in the treatment of neurological disorders (Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, spinal cord injury, stroke), retinopathy (glaucoma and diabetic retinopathy), pain (chronic inflammatory diseases, neuroinflammatory disorders, migraine and menstrual pain).
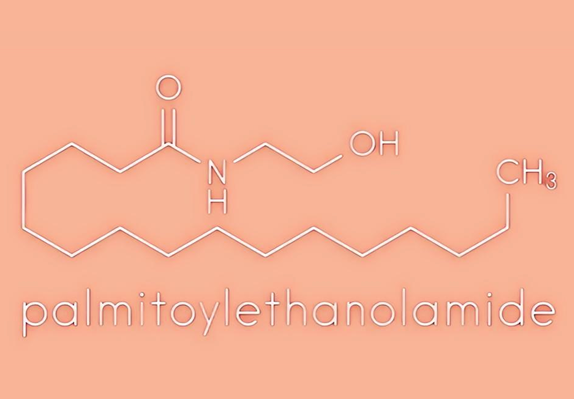
Uses and Benefits of Palmitoylethanolamide in Foods
Palmitoylethanolamide is a natural bioactive ingredient and therefore is also used as a food supplement, nutraceutical or dietary food for the treatment of diseases. In Italy, PEA is available as a food supplement (PeaPure) and as a medical dietary food (Normast, PeaVera and Visimast). These products have been approved in Italy for the nutritional support of glaucoma and neuroinflammatory diseases.
PEA is sold mainly in the form of powders (micronised and ultra-micronised powders) or capsules, with powder particle size specifications including: 10 microns and less than 10 microns (7 microns, 6 microns, ≤ 4 microns). The size of the powder particle size is closely related to bioavailability. Preclinical studies have shown that micronised or ultramicronised forms of PEA (i.e. formulations that maximise the bioavailability and efficacy of PEA) can be a potential therapeutic agent for the effective treatment of different conditions characterised by neurodegeneration, (neuro)inflammation and pain.
Safety of Palmitoylethanolamide
Palmitoylethanolamide is well tolerated and has no serious side effects. Studies have demonstrated the safety and efficacy of PEA when used as a nutritional therapy for glaucoma up to 1.8 grams per day, with excellent tolerability. The oral administration of one gram of PEA per day has also been reported to have no adverse effects. The LD50 of PEA was also found to be greater than the limiting dose of 2000 mg/kg body weight (bw) in animal studies. The doses used in the 90-day rat oral toxicity study were based on the results of the 14-day preliminary study, i.e., 250, 500, and 1000 mg/kg bw/day. The no-effect level (NOEL) for both subchronic studies was the highest dose tested. Does not induce gene mutations and genotoxic effects.
References:
[1] S. BEGGIATO L F M C Tomasini. Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA) as a Potential Therapeutic Agent in Alzheimer’s Disease[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2019. DOI:10.3389/fphar.2019.00821.
[2] DUNCAN SCHWALLER. Palmitoylethanolamide gels edible oils[J]. Food Chemistry, 2022, 386. DOI:10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.132671.
[3] NESTMANN E R. Safety of micronized palmitoylethanolamide (microPEA): lack of toxicity and genotoxic potential[J]. Food Science & Nutrition, 2016, 5 2: 171-365. DOI:10.1002/fsn3.392.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Palmitoylethanolamide: Benefits and Uses, Side Effects Mar 13, 2024
Palmitoylethanolamide has anti-inflammatory, analgesic, anticonvulsant, antibacterial, antipyretic, antiepileptic, immunomodulatory, and neuroprotective activities.
- Uses and Safety of Palmitoylethanolamide Jul 7, 2022
Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA) is a chemical made from fat. It is found naturally in foods such as egg yolks and peanuts, and in the human body.
- Bioactivity of Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA) Jan 5, 2022
Palmitoylethanolamide is an endogenous lipid that acts as a selective GPR55 agonist (EC50 values are 4, 19 800 and > 30 000 nM at GPR55, CB2 and CB1 receptors respectively).
1,7-Dimethylxanthine is a naturally occurring alkaloid compound that can enhance alertness and reduce drowsiness.....
Feb 27,2025APIUracil (U) and thymine (T) are both nitrogenous bases in the genetic information of genes and play an important role in the structure and function of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA).....
Dec 16,2024APIPalmitoylethanolamide
544-31-0You may like
Palmitoylethanolamide manufacturers
- Palmitoylethanolamide
-

- $60.00 / 1kg
- 2025-04-02
- CAS:544-31-0
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99
- Supply Ability: 5000
- Palmitoylethanolamide
-

- $0.00 / 1kg
- 2025-04-02
- CAS:544-31-0
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 1000 kg
- Palmitoylethanolamide
-

- $0.00 / 1KG
- 2025-04-02
- CAS:544-31-0
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 98%min
- Supply Ability: 30tons/month