Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (API), popularly speaking, are the raw materials of medicines, only pharmaceutical raw materials are processed into pharmaceutical preparations , can they become medicines available for clinical use, so drugs we usually eat are the finished drugs through processing. Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients based on its sources can be divided into two major categories ,including chemical synthetic drugs and natural chemical drugs. Chemical synthetic drugs can be divided into organic synthetic drugs and inorganic synthetic drugs. Inorganic synthetic drugs are inorganic compounds ( very few is element), such as aluminum hydroxide, magnesium trisilicate which are used for the treatment of gastric and duodenal ulcers ; organic synthetic drugs are mainly composed of drugs made by basic organic chemical raw materials, through a series of organic chemical reactions (such as aspirin, chloramphenicol, caffeine, etc.). Natural chemical drugs ,based on its sources,can be divided into two categories including biochemical drugs and plant chemical drugs. Antibiotics are generally made by the microbial fermentation, which belongs to the biochemistry category. A variety of semi-synthetic antibiotics occurs in recent years,which are biosynthesis and chemical synthesis combining products.Among active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, the organic synthetic drugs varieties, yields and values have the largest proportion,which are the main pillars of the chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The quality of active Pharmaceutical Ingredients decides whether the formulation is good or bad , so its quality standards are very strict ,countries in the world have developed national pharmacopoeia standards and strict quality control methods for its widely used active Pharmaceutical ingredients.
Function and pharmacokinetic parameters of tulathromycin A
Tulathromycin A is a new macrolide antibiotic specially used for mammals.
Oct 11,2022 APIThe adverse effects of Tianeptine
Tianeptine is an antidepressant agent with a novel neurochemical profile.
Oct 11,2022 APIThe synthesis and research of UV-326
UV-326 is a representative product of this kind of products, characterized by low toxicity and strong ability to absorb ultraviolet light.
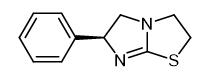
Oct 11,2022 APISynthesis and Toxicology of Levamisole
Levamisole is commonly used for deworming of various animals and is effective against both adults and larvae.
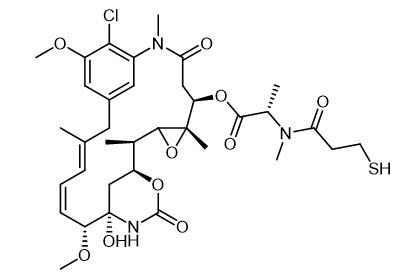
Oct 11,2022 APISynthesis and Bioactivity of Maytansine
Maytansine DM1 is a cytotoxin that is used as the cytotoxic component of antibody-drug conjugates.
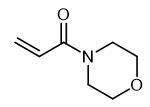
Oct 11,2022 APISynthesis, Hazard and Application of N-Acryloylmorpholine
N-Acryloylmorpholine is used in UV-curable inks, coatings and adhesives.
Oct 10,2022 APISynthesis and Application of GW-501516
GW 501516 causes impaired bone formation, leading to decreased BMD and deterioration of bone properties in OVX rats.
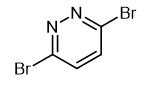
Oct 10,2022 APISynthesis and Precautions of 3,6-Dibromopyridazide
3,6-Dibromopyridazide is an important intermediate in organic synthesis.
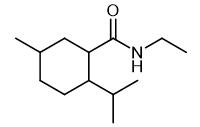
Oct 10,2022 APISynthesis and Application of N-Ethyl-p-menthane-3-carboxamide
N-Ethyl-p-menthane-3-carboxamide is a refrigerant.
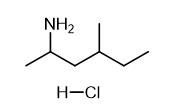
Oct 9,2022 APISynthesis and Detection of 1,3-Dimethylpentanamine Hydrochloride
1,3-Dimethylpentanamine hydrochloride is a pharmaceutical intermediate with anti-malaria and anti-cancer properties.
Oct 9,2022 API