Indometacin Chemische Eigenschaften,Einsatz,Produktion Methoden
R-Sätze Betriebsanweisung:
R28:Sehr giftig beim Verschlucken.
R36/37/38:Reizt die Augen, die Atmungsorgane und die Haut.
S-Sätze Betriebsanweisung:
S28:Bei Berührung mit der Haut sofort abwaschen mit viel . . . (vom Hersteller anzugeben).
S36/37:Bei der Arbeit geeignete Schutzhandschuhe und Schutzkleidung tragen.
S45:Bei Unfall oder Unwohlsein sofort Arzt zuziehen (wenn möglich, dieses Etikett vorzeigen).
S36:DE: Bei der Arbeit geeignete Schutzkleidung tragen.
S26:Bei Berührung mit den Augen sofort gründlich mit Wasser abspülen und Arzt konsultieren.
Beschreibung
Aqueous solutions of indomethacin are not stable because of the ease of hydrolysis of the p-chlorobenzoyl group.
The original synthesis of indomethacin by Shen et al. involved the formation of 2-methyl-5-methoxyindole acetic
acid and subsequent
acylation after protection of the carboxyl group as the t-butyl ester. It was introduced in the United States in 1965. It
is still one of the most potent NSAIDs in use. It also is a more potent antipyretic than either aspirin or
acetaminophen, and it possesses approximately 10 times the analgetic potency of aspirin.
Chemische Eigenschaften
Crystalline Solid
Verwenden
Inhibits cyclooxygenase (IC50=0.1uM) selectively over liposygenases (IC50=100uM for 5-,12- and 15-LO). A clinically useful NAISD
synthetische
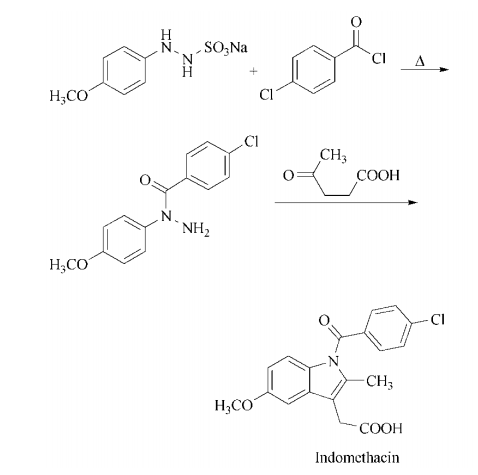
acylation of sodium 2-(4-
methoxyphenyl)hydrazine-1-sulfonate with
4-chlorobenzoyl chloride followed by
heating yields 1-(4- chlorobenzoyl)-1-(4-
methoxyphenyl)hydrazine. Condensation with
levulinic acid in a Fischer indole synthesis affords indomethacin.
Definition
The antiinflammatory drug indomethacin.
Indications
Indomethacin (Indocin) is used in the treatment of
acute gouty arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing
spondylitis, and osteoarthritis. It is not recommended
for use as a simple analgesic or antipyretic because of its
potential for toxicity.While indomethacin inhibits both
COX-1 and COX-2, it is moderately selective for COX-
1. It produces more CNS side effects than most of the
other NSAIDs. Severe headache occurs in 25 to 50% of
patients; vertigo, confusion, and psychological disturbances
occur with some regularity. GI symptoms also
are more frequent and severe than with most other NSAIDs. Hematopoietic side effects (e.g., leukopenia,
hemolytic anemia, aplastic anemia, purpura, thrombocytopenia,
and agranulocytosis) also may occur. Ocular
effects (blurred vision, corneal deposits) have been observed
in patients receiving indomethacin, and regular
ophthalmological examinations are necessary when the
drug is used for long periods. Hepatitis, jaundice, pancreatitis,
and hypersensitivity reactions also have been
noted.
Weltgesundheitsorganisation (WHO)
Indometacin was introduced in 1963 and it is one of the first
NSAIDs. Convulsions are rarely reported in relation with the use of this group of
agents. Indometacin farnesil is a pro-drug of indometacin, and the occurrence of
gastro-intestinal adverse effects could be expected. See also under nonsteroidal
antiinflammatory agents.
Biologische Funktion
Indomethacin (Indocin) is an acetic acid derivative related
functionally to sulindac (Clinoril), a prodrug with
a long half-life, and etodolac (Lodine).They are metabolized
in the liver and excreted as metabolites in the bile and via the kidney. They are potent inhibitors of
COX and thus extremely effective antiinflammatory
agents.
Allgemeine Beschreibung
Crystals.
Air & Water Reaktionen
Practically insoluble in water. Decomposes in alkali.
Reaktivität anzeigen
A weak organic acid.
Brandgefahr
Non-combustible, substance itself does not burn but may decompose upon heating to produce corrosive and/or toxic fumes. Some are oxidizers and may ignite combustibles (wood, paper, oil, clothing, etc.). Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated.
Pharmazeutische Anwendungen
Indomethacin is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agent used in pain and moderate to severe
inflammation in rheumatic diseases and other musculoskeletal disorders. It is a COX (cyclooxygenase)
inhibitor and therefore interrupts the production of prostaglandins.
A series of new silicon compounds, based on the structure of indomethacin, have been synthesised and
are under investigation as novel anticancer agents. The carboxyl group of indomethacin was reacted with
a series of amino-functionalised silanes. The resulting products have been shown to be significantly more
lipophilic and more selective to COX-2. Furthermore, in vitro testing has shown an increased uptake of the
new compounds at the tumour site. The silane-functionalised indomethacin derivatives exhibited a 15-fold
increased antiproliferative effect when tested against pancreatic cancer .
Biologische Aktivität
Cyclooxgenase (COX) inhibitor; displays selectivity for COX-1 (IC 50 values are 230 and 630 nM for human COX-1 and COX-2 respectively). Widely used anti-inflammatory agent.
Clinical Use
Indomethacin is available for the short-term treatment of acute gouty arthritis, acute pain of ankylosing spondylitis,
and osteoarthritis. An injectable form to be reconstituted also is available as the sodium trihydrate salt for IV use in
premature infants with patent ductus arteriosus. Because of its ability to suppress uterine activity by inhibiting
prostaglandin biosynthesis, indomethacin also has an unlabeled use to prevent premature labor.
Nebenwirkungen
All of these drugs produce analgesic effects, antipyresis,
and antiinflammatory effects.Due to the high incidence
of gastric irritation, headache, nausea, and other side effects,
including hematological effects and coronary
vasoconstriction, they are not useful as an initial treatment
for pain. GI irritation and ulceration occur to a
lesser extent with etodolac. Indomethacin is useful in
the treatment of acute gout, osteoarthritis, ankylosing
spondylitis, and acceleration of the closure of the ductus
arteriosus in premature infants. The tocolytic effects of
indomethacin to prevent preterm labor are the result of
its effects on prostaglandin synthesis. However, the toxicity
of the drug limits such application, since it increases
fetal morbidity. Indomethacin is contraindicated
in pregnancy, in asthmatics, and in those with gastric ulcers
or other ulceration of the GI tract. Indomethacin
may increase the symptoms associated with depression
or other psychiatric disturbances and those associated
with epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease. The drug should
be used with caution in such patients.
Indometacin Upstream-Materialien And Downstream Produkte
Upstream-Materialien
Downstream Produkte

