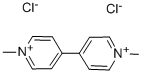
Paraquat dichloride
- CAS No.
- 1910-42-5
- Chemical Name:
- Paraquat dichloride
- Synonyms
- METHYL VIOLOGEN;TOTAL;esgram;METHYL VIOLOGEN DICHLORIDE;PARAQUA;Paraquat dichlorid;PARAQUAT DICHLORIDE TETRAHYDRATE;ok622;ah501;PP910
- CBNumber:
- CB0486572
- Molecular Formula:
- C12H14Cl2N2
- Molecular Weight:
- 257.16
- MDL Number:
- MFCD00011986
- MOL File:
- 1910-42-5.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
| Melting point | >300 °C(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 403.89°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.25 |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 25℃ |
| refractive index | 1.6400 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,Room Temperature |
| solubility | Methanol (Sligthly) |
| form | Crystals or Crystalline Powder |
| color | Beige or pink to brown |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
| Merck | 7031 |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| LogP | -4.5 at 20℃ |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1910-42-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EWG's Food Scores | 4 |
| FDA UNII | 2KZ83GSS73 |
| Pesticides Freedom of Information Act (FOIA) | Paraquat dichloride |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Paraquat dichloride (1910-42-5) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |    GHS08,GHS09,GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H301-H335-H311-H410-H372-H330-H315-H319 |
| Precautionary statements | P260-P271-P284-P304+P340-P310-P320-P403+P233-P405-P501-P260-P264-P270-P314-P501-P264-P270-P301+P310-P321-P330-P405-P501-P264-P280-P302+P352-P321-P332+P313-P362-P264-P280-P305+P351+P338-P337+P313P-P280-P302+P352-P312-P322-P361-P363-P405-P501-P273-P391-P501 |
| Hazard Codes | T+,N |
| Risk Statements | 24/25-26-36/37/38-48/25-50/53 |
| Safety Statements | 22-28-36/37/39-45-60-61-28A |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 1 |
| OEB | D |
| OEL | TWA: 0.1 mg/m3 (resp) [skin] |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | DW2275000 |
| HazardClass | 6.1(a) |
| PackingGroup | II |
| HS Code | 29333990 |
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in rats: 125 mg/kg (Conning) |
| IDLA | 1 mg/m3 |
Paraquat dichloride Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Paraquat dichloride is a dark blue liquid, non-combustible, stable herbicide chemical. It is incompatible with strong oxidising agents. On contact with fire paraquat decomposes gives off irritating or toxic fumes (or gases), nitrogen oxides, and hydrogen chloride. Paraquat dichloride contact and storage destroys metal. Paraquat dichloride hydrolyses in alkaline media and reacts with aluminium to produce hydrogen gas. Paraquat (N,N′-dimethyl-4,4′-bipyridinium dichloride) is one of the most widely used herbicides in the world. Paraquat dichloride is a herbicide currently registered to control weeds and grasses in many agricultural and non-agricultural areas. It is used preplant or preemergence on vegetables, grains, cotton, grasses, sugar cane, peanuts, potatoes, and tree plantation areas; post-emergence around fruit crops, vegetables, trees, vines, grains, soybeans, and sugar cane. It is also used on non-crop areas such as public airports, electric transformer stations, and around commercial buildings to control weeds. It has been reported that about seven pesticide products are registered which contain the active ingredient paraquat dichloride and classified as restricted use pesticides (RUPs). Paraquat dichloride and the products are primarily intended for ‘Occupational Use’. In the United States, Paraquat is classified as ‘restricted commercial use’, and people must obtain a license to use the product.
Chemical Properties
Paraquat is a yellow solid with a faint, ammonia-like odor.
Chemical Properties
off-white powder
Definition
ChEBI: Paraquat dichloride is an organic chloride salt. It has a role as a herbicide and a photosystem-I inhibitor. It contains a paraquat.
General Description
Colorless to yellow crystalline solid. Used as a contact herbicide and desiccant.
Air & Water Reactions
Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
Paraquat dichloride is stable in acidic media, but unstable in alkaline media. Paraquat dichloride is photochemically decomposed by UV irradiation in aqueous solutions and is rapidly inactivated by soil. The neat chemical may be sensitive to light. Paraquat dichloride is corrosive to metal and Paraquat dichloride can react with strong acids, bases, and oxidizing agents. Paraquat dichloride is hydrolyzed by alkali compounds and Paraquat dichloride is inactivated by inert clays and anionic surfactants.
Health Hazard
Can cause death due to severe injury to the lungs. The lowest lethal oral dose reported in humans is 43 mg/kg.
Fire Hazard
Avoid strong oxidizers.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Contact allergens
Paraquat is a quaternary ammonium compound with herbicide properties, as diquat. It is contained in Cekuquat? or Dipril?. It can cause contact and phototoxic contact dermatitis, acne, and leukoderma mainly in agricultural workers.
Safety Profile
A human poison by ingestion. Poison experimentally by ingestion, skin contact, intraperitoneal, intravenous, and subcutaneous routes. Human systemic effects by ingestion: acute renal failure, acute tubular necrosis, cough, diarrhea, dyspnea, headache, hyp
Potential Exposure
Those engaged in manufacture, formulation and application of this herbicide. Classified for restricted use: limited to use by a certified applicator, or those under applicator’s direct supervision.
Shipping
UN2781 Bipyridilium pesticide, solid, toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.
Purification Methods
Recrystallise the dichloride from MeOH/acetone mixture. It has also been recrystallised three times from absolute EtOH [Bancroft et al. Anal Chem 53 1390 1981]. Dry it at 80o in a vacuum. [Beilstein 23/8 V 30.]
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides (hydrolysis), alkylarylsulfonate wetting agents. Corrosive to metals. Decomposes in presence of ultraviolet (UV) light. Decomposes in heat (see physical properties, above) and in the presence of UV light, producing nitrogen oxides, hydrogen chloride.
Waste Disposal
Paraquat is rapidly inactivated in soil. It is also inactivated by anionic surfactants. Therefore an effective and environmentally safe disposal method would be to mix the product with ordinary household detergent and bury the mixture in clay soil. In accordance with 40CFR165, follow recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Must be disposed properly by following package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office. Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal.
Paraquat dichloride Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of3
Preparation Products
1910-42-5(Paraquat dichloride)Related Search:
1of4