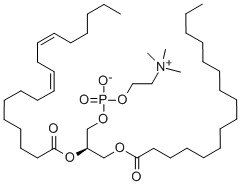
Lecithin
- CAS No.
- 8002-43-5
- Chemical Name:
- Lecithin
- Synonyms
- PC;PHOSPHATIDYLCHOLINE;L-α-Phosphatidylcholine;LECITHIN POWDER;LECITHIN LIQUID;l-α-phosphatidylcholine solution;L-α-Lecithin;LECITHIN SOYBEAN;Lecithin from egg;LECITHIN SOYA BEAN
- CBNumber:
- CB1242041
- Molecular Formula:
- C42H80NO8P
- Molecular Weight:
- 758.06
- MOL File:
- 8002-43-5.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2024/9/2 18:23:59
| Melting point | >145°C (dec.) |
|---|---|
| Density | d424 1.0305 |
| Flash point | 57 °C |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | chloroform: 0.1 g/mL, slightly hazy, slightly yellow to deep orange |
| form | solution |
| color | Pale Brown to Yellow |
| Odor | at 100.00?%. bland fatty |
| Water Solubility | NEGLIGIBLE |
| Merck | 14,5429 |
| BRN | 5209585 |
| Stability | Stable, but light, heat, moisture and air-sensitive. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| InChIKey | FWMYJLDHIVCJCT-VSZGHEPYSA-N |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 8002-43-5 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Lecithins (8002-43-5) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS06,GHS08 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H302-H315-H319-H331-H336-H351-H361d-H372 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P202-P301+P312-P302+P352-P304+P340+P311-P305+P351+P338-P308+P313 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | ||||||||||
| Risk Statements | ||||||||||
| Safety Statements | ||||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | OG7565000 | |||||||||
| F | 1-8-10 | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HS Code | 29239000 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 oral in rat: > 8mL/kg | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Lecithin price More Price(59)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | P7443 | L-α-Phosphatidylcholine from soybean, ≥99% (TLC), lyophilized powder | 8002-43-5 | 100MG | ₹12881.75 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | P7443 | L-α-Phosphatidylcholine from soybean, ≥99% (TLC), lyophilized powder | 8002-43-5 | 500MG | ₹41871.1 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | P7443 | L-α-Phosphatidylcholine from soybean, ≥99% (TLC), lyophilized powder | 8002-43-5 | 1G | ₹67472.23 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | P5394 | L-α-Phosphatidylcholine from dried egg yolk, Type X-E, ≥40% (enzymatic) | 8002-43-5 | 10G | ₹8064.63 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | P5638 | L-α-Phosphatidylcholine from soybean, Type II-S, 14-29% choline basis | 8002-43-5 | 500G | ₹8508.45 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
Lecithin Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Food-grade lecithin is obtained from soybeans and other plant sources. It is a complex mixture of acetone-insoluble phosphatides that consists chiefly of phosphatidyl choline, phosphatidyl etha nolamine, and phosphatidyl inositol, combined with various amounts of other substances such as triglycerides, fatty acids, and carbohydrates. Refined grades of lecithin may contain any of these components in varying proportions and combinations depending on the type of fractionation used. In its oil-free form, the prepon-derance of triglycerides and fatty acids is removed and the product contains 90% or more of phosphatides representing all or certain fractions of the total phosphatide complex. The consistency of both natural grades and refined grades of lecithin may vary from plastic to fluid, depending upon free fatty acid and oil content, and upon the presence or absence of other diluents. Its color varies from light yellow to brown, depending on the source, on crop variations, and on whether it is bleached or unbleached. It is odorless or has a characteristic, slight nutlike odor and a bland taste. Edible diluents, such as cocoa butter and vegetable oils, often replace soybean oil to improve functional and flavor characteris tics. Lecithin is only partially soluble in water, but it readily hydrates to form emulsions. The oil-free phosphatides are soluble in fatty acids, but are practically insoluble in fixed oils. When all phosphatide fractions are present, lecithin is partially soluble in alcohol and practically insoluble in acetone.
Chemical Properties
Lecithins vary greatly in their physical form, from viscous
semiliquids to powders, depending upon the free fatty acid content.
They may also vary in color from brown to light yellow, depending
upon whether they are bleached or unbleached or on the degree of
purity. When they are exposed to air, rapid oxidation occurs, also
resulting in a dark yellow or brown color.
Lecithins have practically no odor. Those derived from vegetable
sources have a bland or nutlike taste, similar to that of soybean oil.
Occurrence
Lecithin is found in foods such as eggs, beef liver, and peanuts. Commercial sources are available
Uses
lecithin (hydrogenated) is an emulsifier.
Definition
ChEBI: A glycerophosphocholine compound having O-acyl substituents at both the 1- and 2-positions of the glycerol. It is a major constituent of cell membranes.
Production Methods
Lecithins are essential components of cell membranes and, in
principle, may be obtained from a wide variety of living matter. In
practice, however, lecithins are usually obtained from vegetable
products such as soybean, peanut, cottonseed, sunflower, rapeseed,
corn, or groundnut oils. Soybean lecithin is the most commercially
important vegetable lecithin. Lecithin obtained from eggs is also
commercially important and was the first lecithin to be discovered.
Vegetable lecithins are obtained as a by-product in the vegetable
oil refining process. Polar lipids are extracted with hexane and, after
removal of the solvent, a crude vegetable oil is obtained. Lecithin is
then removed from the crude oil by water extraction. Following
drying, the lecithin may be further purified.
With egg lecithin, a different manufacturing process must be
used since the lecithin in egg yolks is more tightly bound to proteins
than in vegetable sources. Egg lecithin is thus obtained by solvent
extraction from liquid egg yolks using acetone or from freeze-dried
egg yolks using ethanol (95%).
Synthetic lecithins may also be produced.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Lecithins are used in a wide variety of pharmaceutical applications. They are also used in cosmetics and food products.
Lecithins are mainly used in pharmaceutical products as
dispersing, emulsifying, and stabilizing agents, and are included in
intramuscular and intravenous injections, parenteral nutrition
formulations, and topical products such as creams and ointments.
Lecithins are also used in suppository bases, to reduce the
brittleness of suppositories, and have been investigated for their
absorption-enhancing properties in an intranasal insulin formulation.
Lecithins are also commonly used as a component of enteral
and parenteral nutrition formulations.
There is evidence that phosphatidylcholine (a major component
of lecithin) is important as a nutritional supplement to fetal and
infant development. Furthermore, choline is a required component
of FDA-approved infant formulas. Other studies have indicated
that lecithin can protect against alcohol cirrhosis of the liver, lower
serum cholesterol levels, and improve mental and physical
performance.
Liposomes in which lecithin is included as a component of the
bilayer have been used to encapsulate drug substances; their
potential as novel delivery systems has been investigated. This
application generally requires purified lecithins combined in specific
proportions.
Therapeutically, lecithin and derivatives have been used as a
pulmonary surfactant in the treatment of neonatal respiratory
distress syndrome.
Side effects
Lecithin may be safe when used as a supplement at a maximum dose of 30 grams per day for up to 6 weeks. It may have side effects, including diarrhoea, nausea, stomach pain or a feeling of fullness. When applied to the skin: Lecithin is probably safe for most adults. When used medicinally or as a drug carrier, no related serious adverse reactions have been reported.
Safety
Lecithin is a component of cell membranes and is therefore consumed as a normal part of the diet. Although excessive consumption may be harmful, it is highly biocompatible and oral doses of up to 80 g daily have been used therapeutically in the treatment of tardive dyskinesia. When used in topical formulations, lecithin is generally regarded as a nonirritant and nonsensitizing material. The Cosmetic Ingredients Review Expert Panel (CIR) has reviewed lecithin and issued a tentative report revising the safe concentration of the material from 1.95% to 15.0% in rinse-off and leave-in products. They note, however, that there are insufficient data to rule on products that are likely to be inhaled.
storage
Lecithins decompose at extreme pH. They are also hygroscopic and
subject to microbial degradation. When heated, lecithins oxidize,
darken, and decompose. Temperatures of 160–180°C will cause
degradation within 24 hours.
Fluid or waxy lecithin grades should be stored at room
temperature or above; temperatures below 10°C may cause
separation.
All lecithin grades should be stored in well-closed containers
protected from light and oxidation. Purified solid lecithins should
be stored in tightly closed containers at subfreezing temperatures.
Purification Methods
Lecithin from hen egg white is purified by solvent extraction and chromatography on alumina. It is suspended in H2O and kept frozen until required [Lee & Hunt J Am Chem Soc 106 7411 1984, Singleton et al. J Am Oil Chem Soc 42 53 1965]. For purification of commercial egg lecithin, see Pangborn [J Biol Chem 188 471 1951].
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with esterases owing to hydrolysis.
Regulatory Status
GRAS listed. Accepted for use as a food additive in Europe. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (inhalations; IM and IV injections; otic preparations; oral capsules, suspensions and tablets; rectal, topical, and vaginal preparations). Included in nonparenteral and parenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Lecithin Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of2
chevron_rightPreparation Products
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shamrock Medicaments Ltd. | +91-9167620304 +91-9167620304 | Mumbai, India | 16 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Kothari Phytochemicals and Industries Ltd. | +91-9244448844 +91-9331023407 | West Bengal, India | 18 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Haneil Soyatech Pvt Ltd | +91-9730111745 +91-9730111745 | Maharashtra, India | 3 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Aditya Soya Tech | +91-9584928889 +91-9713063284 | Madhya Pradesh, India | 2 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Vippy Industries Limited | +91-7272258546 +91-7272258546 | Madhya Pradesh, India | 3 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Arihant Innochem Pvt Ltd | +91-2267674895 +91-2267674895 | Mumbai, India | 37 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Merck Ltd | +91-2262109800 +91-2262109000 | Maharashtra, India | 272 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Process Enterprises | 91-731-2877129 | Madhya Pradesh, India | 4 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Turakhia Brothers (Panchsheel Organics Limited) | 91-22-22084282 | Maharashtra, India | 55 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Pharma Affiliates | 172-5066494 | Haryana, India | 6761 | 58 | Inquiry |
Related articles
- What is the Difference between Sunflower Lecithin and Soy Lecithin?
- The most popular lecithins currently include sunflower lecithin and soy lecithin. This article will introduce their difference....
- Mar 26,2024
- Functions of lecithin
- Lecithin is known as the "third nutrient" alongside protein and vitamins; as a functional nutritional health product, it canno....
- Mar 9,2022
- Benefits of Lecithin
- Lecithin (also known as alpha-phosphatidylcholine) is a naturally occurring nutrient found in foods that is also sold as a die....
- Jan 12,2022
8002-43-5(Lecithin)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




