VACOR
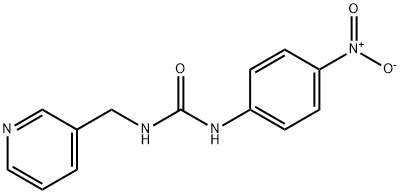
- CAS No.
- 53558-25-1
- Chemical Name:
- VACOR
- Synonyms
- VACOR;Vacot;dlp787;dlp-87;rh-787;lh 105;pnu[qr];Pyriminl;Phriminil;pyriminyl
- CBNumber:
- CB1496592
- Molecular Formula:
- C13H12N4O3
- Molecular Weight:
- 272.26
- MOL File:
- 53558-25-1.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2023/5/4 15:12:57
| Melting point | 223-225° (dec) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 415.32°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.2545 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6120 (estimate) |
| pka | 12.25±0.46(Predicted) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 53558-25-1 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Pyrinuron (53558-25-1) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS07,GHS05 |
|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H318-H335-H302-H315 |
| Precautionary statements | P264-P270-P301+P312-P330-P501-P264-P280-P302+P352-P321-P332+P313-P362-P280-P305+P351+P338-P310 |
| RIDADR | 2588 |
| HazardClass | 6.1(a) |
| PackingGroup | I |
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in male, female rats: 6.2, 7.2 mg/kg (Brooks, Htun) |
VACOR Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Pyriminil was used formerly as a rodenticide in products such as DLP 787 as a 10% house mouse tracking powder or Vacor. It is now banned in the United States and Europe for use as a rodenticide and is listed as an extremely hazardous substance by the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Toxic effects of pyriminil include neurotoxicity and pancreatic beta-cell death, which, if not immediately lethal, will lead to prolonged autonomic dysfunction and permanent insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in most species, including humans.
Chemical Properties
Pyriminil is a yellow crystalline solid, resem- bling corn meal.
Uses
Rodenticide.
General Description
Yellow, resembling corn meal. Used as a single-dose, acute rodenticide. Not registered as a pesticide in the U.S.
Reactivity Profile
A nitrated amine and amide. Amines are chemical bases. They neutralize acids to form salts plus water. These acid-base reactions are exothermic. The amount of heat that is evolved per mole of amine in a neutralization is largely independent of the strength of the amine as a base. Amines may be incompatible with isocyanates, halogenated organics, peroxides, phenols (acidic), epoxides, anhydrides, and acid halides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen is generated by amines in combination with strong reducing agents, such as hydrides. Organic amides/imides react with azo and diazo compounds to generate toxic gases. Flammable gases are formed by the reaction of organic amides/imides with strong reducing agents. Amides are very weak bases (weaker than water). Imides are less basic yet and in fact react with strong bases to form salts. That is, they can react as acids. Mixing amides with dehydrating agents such as P2O5 or SOCl2 generates the corresponding nitrile. The combustion of these compounds generates mixed oxides of nitrogen (NOx).
Health Hazard
VACOR may cause death by cardiovascular collapse and respiratory failure. It may cause diabetes. Also it affects the central nervous system. Human survivors regularly develop an insulin-deficient, ketosis-prone form of diabetes millitus.
Safety Profile
Human poison by ingestion. Human systemic effects: altered sleep time, blood pressure lowering, change in motor activity, dabetes mektus, dstorted perceptions, dyspnea, hallucinations, hyperglycemia, somnolence, structural change in nerve or sheath. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx.
Potential Exposure
A potential danger to those involved in the application of this single-dose, acute rodenticide. No longer registered, produced or used in the United States There are more than 20 global suppliers .
Environmental Fate
If released into air, soil, or water, pyriminil is unlikely to volatilize and is instead expected to be bound to particulates based on a low vapor pressure (3.39 × 10-9 mm Hg) and low Henry’s Law constant (1.84 × 10-16 atm-m3 mol-1). The pKa value for pyriminil is 3.5 for the conjugate acid of nitrogen in the pyridine ring, while the pKa is 7.6 for the benzyl amide. Based on these pKa values, pyriminil is predicted to be in the uncharged form under most environmental conditions. The Kow of pyriminil is 2.09 and the water solubility is high (4.81 × 102 mg l-1), which predicts that it will readily dissolve in water and disperse in aquatic media. However, pyriminil will also sorb to suspended particulates and has some potential to bioconcentrate (bioconcentration factor ? 8).
Incompatibilities
A nitrated amine. Amines are combustible. Azo, diazo, azido compounds can detonate. This applies in particular to organic azides that have been sensitized by the addition of metal salts or strong acids. Toxic gases are formed by mixing materials of this class with acids, aldehydes, amides, carbamates, cyanides, inorganic fluorides, halogenated organics, isocyanates, ketones, metals, nitrides, peroxides, phenols, epoxides, acyl halides, and strong oxidizing or reducing agents. Flammable gases are formed by mixing materials in this group with alkali metals. Explosive combination can occur with strong oxidizing agents, metal salts, peroxides, and sulfides.





