STRONTIUM
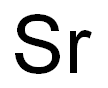
- CAS No.
- 7440-24-6
- Chemical Name:
- STRONTIUM
- Synonyms
- STRONTIUM;Aids072432;Aids-072432;strontium(2+);strontium atom;STRONTIUM METAL;Strontium pieces;Strontium, 99.9%;Strontium Powder;Strontium, Chunks
- CBNumber:
- CB2350213
- Molecular Formula:
- Sr
- Molecular Weight:
- 87.62
- MOL File:
- 7440-24-6.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2024/5/29 10:21:37
| Melting point | 757 °C (lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 1384 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 2.6 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: soluble |
| form | random pieces |
| color | White to pale yellow |
| Specific Gravity | 2.54 |
| Resistivity | 23 μΩ-cm, 20°C |
| Water Solubility | reacts quickly with H2O; soluble alcohol [HAW93] |
| Sensitive | Air & Moisture Sensitive |
| Merck | 13,8915 |
| Exposure limits |
ACGIH: TWA 2 ppm; STEL 4 ppm OSHA: TWA 2 ppm(5 mg/m3) NIOSH: IDLH 25 ppm; TWA 2 ppm(5 mg/m3); STEL 4 ppm(10 mg/m3) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7440-24-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Strontium (7440-24-6) |
| Bulk Modulus | 11.61 GPa |
|---|
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS02,GHS07 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H260-H315 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P231+P232-P302+P352 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | F,Xi,T | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 37/38-41-38-14-11-36/38-34-23/24/25-36-14/15 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 26-45-36/37/39-27-23 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 3264 8/PG 3 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | WK8400000 | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 4.3 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | II | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
STRONTIUM price More Price(22)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 460346 | Strontium dendritic pieces, purified by distillation, 99.9% trace metals basis | 7440-24-6 | 5G | ₹53330.25 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 460346 | Strontium dendritic pieces, purified by distillation, 99.9% trace metals basis | 7440-24-6 | 25G | ₹184783.25 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 441899 | Strontium dendritic pieces, purified by distillation, 99.99% trace metals basis | 7440-24-6 | 5G | ₹69366.25 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich | 441899 | Strontium dendritic pieces, purified by distillation, 99.99% trace metals basis | 7440-24-6 | 25G | ₹232068.35 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 441899 | Strontium dendritic pieces, purified by distillation, 99.99% trace metals basis | 7440-24-6 | 25G | ₹232068.35 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
STRONTIUM Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Strontium has the symbol Sr, the atomic number 38 and an atomic weight of 87.623 g/mol. As an alkaline earth metal, strontium is a soft silver-white or yellowish metallic element that is highly reactive chemically. Due to its extreme reactivity with oxygen and water, this element occurs naturally only in compounds with other elements. The metal turns yellow when exposed to air. It occurs naturally in the minerals Celestine(SrSO4) and strontianite(SrCO3). The isotope, 90Sr, is present in radioactive fallout and has a half-life of 28.90 years. The following table presents the abundance of strontium. Strontium commonly occurs in nature, the 15th most abundant element on earth, averaging 0.034% in all igneous rock. It is found chiefly as the form of the sulfate mineral Celestite(SrSO4) and the carbonate Strontianite (SrCO3). Of the two, Celestite occurs much more frequently in sedimentary deposits of sufficient size to make the development of mining facilities attractive. Strontianite is more useful of the two common minerals because strontium is used most often in the carbonate form, but few deposits have been discovered that are suitable for development.
Chemical Properties
Strontium is a silvery-white alkaline-earth metal that rapidly assumes an oxide film and yellow color on exposure to air. Strontium salts impart a brilliant red color to a flame. The finely divided metal ignites spontaneously in air; therefore, the metal should be stored under oxygen-free liquid. Naturally occurring isotopes include 88Sr (82.56%), 86Sr (9.86%), 87Sr, and 84Sr (0.56%). In addition, at least 11 strontium isotopes are produced by fission; of these, the 89Sr and 90Sr isotopes are considered to be environmentally significant. 89Sr emits b-particles with an average energy of 583 keV (1.46 MeV maximum) and has a halflife of 50.5 days. 90Sr is a long-range b-emitter (mean energy 195.8 keV; maximum 540 keV) with a half-life of 28 years. At least 20 strontium salts are known.
Physical properties
In its elemental state, strontium is a relatively soft, pale yellow metal somewhat similar toelemental calcium. When freshly cut, strontium has a silvery shine to its surface that soonturns grayish as it is oxidized by atmospheric oxygen (2Sr + O2 → 2SrO) and nitrogen (3Sr +N2 → Sr3N2), which prevents further oxidation. Strontium’s melting point is 769°C, its boiling point is 1348°C, and its density is 2.54 g/cm3.
Isotopes
There are 29 isotopes of strontium, ranging from Sr-75 to Sr-102. The fournatural forms of strontium are stable and not radioactive. These stable isotopes are Sr-84, which constitutes 0.56% of the element’s existence on Earth; Sr-86, which makesup 9.86%; Sr-87, which accounts for 7.00% of the total; and Sr-88, which makes up82.58% of strontium found on Earth. The remaining isotopes are radioactive with halflives ranging from a few microseconds to minutes, hours, days, or years. Most, but notall, are produced in nuclear reactors or nuclear explosions. Two important radioisotopesare Sr-89 and Sr-90.
Origin of Name
Strontium was named after the town Strontian, located in Scotland in the British Isles.
Occurrence
Strontium metal is not found in its elemental state in nature. Its salts and oxide compoundsconstitute only 0.025% of the Earth’s crust. Strontium is found in Mexico and Spain in the mineral ores of strontianite (SrCO3) and celestite (SrSO4). As these ores are treated with hydrochloricacid (HCl), they produce strontium chloride (SrCl2) that is then used, along with potassiumchloride (KCl), to form a eutectic mixture to reduce the melting point of the SrCl2, as a moltenelectrolyte in a graphite dish-shaped electrolysis apparatus. This process produces Sr cations collected at the cathode, where they acquire electrons to form strontium metal. At the same time,Cl- anions give up electrons at the anode and are released as chlorine gas Cl2↑.Two other methods of producing strontium are by thermal reduction of strontium oxideand by the distillation of strontium in a vacuum.
Characteristics
When strontium metal is exposed to water, it releases hydrogen, as do the other earth metals (Sr + 2H2O → Sr(OH)2 + H2↑). Strontium can ignite when heated above its melting point.When in a fine powder form, it will burn spontaneously in air. It must be stored in an inertatmosphere or in naphtha. Several of its salts burn with a bright red flame, making it usefulin signal flares and fireworks.
History
Both strontium and Strontianite are named after Strontian, a village in Scotland near which the mineral was first discovered in the ores taken from the lead mines. In 1787, an intriguing mineral came to Edinburgh from a Lead mine in a small village on the shores of Loch Sunart, Argyll, in the western highlands of Scotland. At that time, the substance was thought to be some sort of Barium compound. It was 3 years later that Scott s Irish chemist, Adair Crawford, published a paper claiming that the mineral held a new species including a new chemical element. Other chemists later prepared a number of compounds with the element, noting that it caused the candle s flame to burn red, while barium compounds gave a green color. The new mineral was named Strontite in 1793 by Thomas Hope, another professor of medicine at the University of Glasgow. This element was eventually isolated by Humphrey Davy in 1808 during his studies of the electrolysis of various alkaline earths containing molten chloride such as SrCl2 and mercuric oxide. He announced his work in a lecture to the Royal Society on 30 June 1808. In keeping with the naming of the other alkaline earths, he changed the name to Strontium.
Uses
This soft, yellowish, metallic element was isolated by Sir Humphry Davy in 1808. It was found in the minerals strontianite and celestine. The strontium halides were used in the making of collodion emulsions.
Definition
Metallic element of atomic number 38, group IIA of periodic table, aw 87.62, valence = 2, radioactive isotopes strontium-89 and strontium-90. There are four stable isotopes.
Hazard
As a powder, strontium metal may spontaneously burst into flames. Both its metal andsome of its compounds will explode when heated. Some of the compounds will explode ifstruck with a hammer.
Both the metal and some compounds will react with water to produce strontium hydroxide[Sr(OH)2] and release hydrogen gas. The heat from the exothermic reaction may cause thehydrogen to either burn or explode [Sr + 2H2O → Sr(OH)2 + H2↑].
Some compounds, such as strontium chromate and strontium fluoride, are carcinogensand toxic if ingested. Strontium-90 is particularly dangerous because it is a radioactivebone-seeker that replaces the calcium in bone tissue. Radiation poisoning and death mayoccur in people exposed to excessive doses of Sr-90. Strontium-90, as well as some otherradioisotopes that are produced by explosions of nuclear weapons and then transportedatmospherically, may be inhaled by plants and animals many miles from the source of thedetonation. This and other factors led to the ban on atmospheric testing of nuclear andthermonuclear weapons.
Carcinogenicity
The carcinogenicity of stable (nonradioactive) strontium chromate was attributed solely to intracellular soluble chromium. 90Sr has been examined in long-term studies in four species, involving beagles, mice, monkeys, and pigs. A summary of the findings of these studies can be found in Ref.. Following intravenous injection of 90Sr at doses ranging from 0.027 to 362×104 Bq/kg, the most prominent 90Sr -induced endpoint was bone sarcoma. Neoplasms involving the soft tissues near bone in the oronasopharynx and paranasal sinuses and bone marrow dysplasia were also significantly elevated over controls. Feeding studies in beagles extending from the in utero period to age 540 days resulted in the development of the same array of tumors, and, in addition, myeloproliferative disorders. Inhalation exposure to 90Sr Cl2 was associated with multiple carcinogenic and non-neoplastic lesions in dogs, with an excess of bone tumors reported as the major finding. Interestingly, inhalation exposure of dogs to insoluble forms of 90Sr was associated with lung tumors, but not bone tumors. In an additional study in which beagle dogs were injected with lowlevels of 90Sr (21.1 kBq/kg, or five times the maximum permissible (retained) body burden), 90Sr was not associated with a decrease in survival time in dogs. It has been estimated that 90Sr is approximately two orders of magnitude less toxic than radium. Two monkey studies were also summarized by the Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements. One of these studies involved administration of single intravenous injections of 90Sr (0.10–6.21 MBq) to rhesus monkeys. These monkeys had no symptoms or disease attributable to 90Sr 20 years after exposure. In another study, administration of 1.85 or 3.7 MBq of 90Sr as a single oral dose resulted in bone sarcomas.
Environmental Fate
Most stable strontium and some radioactive strontium compounds exist as dust in air, which eventually settles over land and water. Stable strontium dissolves in water and moves deeper in soil to underground water. The solid is found suspended in water. Strontium is also found naturally in soil due to the release of coal ash and industrial wastes. Soluble strontium compounds, through chemical reactions, can transform to insoluble and vice versa. The long half-life of strontium-90 (29 years) can allow airborne particles to move all around the world.
STRONTIUM Preparation Products And Raw materials
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLEARSYNTH LABS LTD. | +91-22-45045900 | Hyderabad, India | 6351 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Otto Chemie Pvt. Ltd. | +91 9820041841 | Mumbai, India | 5873 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Alfa Aesar | 1 800 209 7001 | Maharashtra, India | 6913 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Central Drug House(P) Ltd. | 91-11-49404040 | New Delhi, India | 6160 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Aritech Chemazone Private Limited | +91-9034345475 | Punjab, India | 684 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Archit Meta Chem | 08048371779Ext 300 | Ahmedabad, India | 64 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Kamat Exports Pvt. Ltd. | 91-22-24383438 | Maharashtra, India | 23 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Anchor Chemicals Industries | 08048372628Ext 188 | Mumbai, India | 12 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Jigs chemical | +91 (79) 26402695/26401498 | Gujarat, India | 319 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Panhas Chemicals Pvt. Ltd. | 91-9586648484 | Gujarat, India | 23 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| CLEARSYNTH LABS LTD. | 58 |
| Otto Chemie Pvt. Ltd. | 58 |
| Alfa Aesar | 58 |
| Central Drug House(P) Ltd. | 58 |
| Aritech Chemazone Private Limited | 58 |
| Archit Meta Chem | 58 |
| Kamat Exports Pvt. Ltd. | 58 |
| Anchor Chemicals Industries | 58 |
| Jigs chemical | 58 |
| Panhas Chemicals Pvt. Ltd. | 58 |
Related articles
- Strontium: Major Minerals, Chemistry properties and Reactions
- Strontium (Sr) is a soft silver-white yellowish metallic element. It is a member of alkaline earth elements (Group 2) and occu....
- May 29,2024
- How funny strontium flame test
- Positive result of a flame test for strontium (Sr), producing a red colour. This is due to the excitation of electrons in the ....
- Jan 24,2024
- Strontium Industrial Applications and Uses
- Strontium chemical symbol Sr, atomic number 38, and relative atomic mass (i.e., atomic weight) 87.62, is the fourth alkaline-e....
- Sep 25,2019
7440-24-6(STRONTIUM)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




