Tantalum
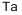
- CAS No.
- 7440-25-7
- Chemical Name:
- Tantalum
- Synonyms
- Tantal;TA000356;TA007920;TA000480;TA000586;TA007926;TA000450;TA000320;TA007095;TA007501
- CBNumber:
- CB3367656
- Molecular Formula:
- Ta
- Molecular Weight:
- 180.95
- MOL File:
- 7440-25-7.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/5/30 14:10:26
| Melting point | 2996 °C (lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 5425 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 16.69 g/cm3 (lit.) |
| vapor pressure | <0.01 mm Hg ( 537.2 °C) |
| storage temp. | no restrictions. |
| solubility | reacts with HF |
| form | wire |
| color | Gray to silver |
| Specific Gravity | 16.6 |
| Resistivity | 13.5 μΩ-cm, 20°C |
| Water Solubility | very resistant to attack by acids except HF, resistant to alkali solutions [KIR83] |
| Merck | 13,9143 |
| Exposure limits |
ACGIH: TWA 0.5 ppm(2.5 mg/m3); Ceiling 2 ppm (Skin) OSHA: TWA 3 ppm NIOSH: IDLH 30 ppm(250 mg/m3); TWA 3 ppm(2.5 mg/m3); Ceiling 6 ppm(5 mg/m3) |
| Stability | Stable. Powder is very flamable. |
| InChIKey | GUVRBAGPIYLISA-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | -1 at 20℃ |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7440-25-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Tantalum (7440-25-7) |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 179 GPa |
|---|---|
| Poissons Ratio | 0.35 |
| Shear Modulus | 69.0 GPa |
| Hardness, Vickers | 90 |
| Hardness, Brinell | 95, Converted from Vickers for 3000 kg load/10 mm ball Brinell test. |
| Hardness, Rockwell A | 35, Converted from Vickers. |
| Vickers Microhardness | 70 - 80, Electron beam melted, cold rolled, then annealed at 1200°C |
| Hardness, Rockwell B | 51, Converted from Vickers. |
| Hardness, Rockwell C | 12, Converted from Vickers. |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS02 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H228 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P210-P240-P241-P280-P370+P378 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | F,Xi,Xn,C | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 11-36/37/38-20/21/22-40-34-36/38 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 16-26-33-36/37/39-36-45-27-36/37 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 3089 4.1/PG 2 | |||||||||
| OEB | B | |||||||||
| OEL | TWA: 5 mg/m3, STEL: 10 mg/m3 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | - | |||||||||
| RTECS | WW5505000 | |||||||||
| Autoignition Temperature | 572 °F | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 4.1 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | II | |||||||||
| HS Code | 8103909000 | |||||||||
| IDLA | 2,500 mg Ta/m3 | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Tantalum price More Price(143)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 262919 | Tantalum foil, thickness 0.025?mm, ≥99.9% trace metals basis | 7440-25-7 | 9G | ₹19158.6 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 1.70356 | Tantalum ICP standard traceable to SRM from NIST (NH?)?TaF? in H?O 1000 mg/l Ta Certipur? | 7440-25-7 | 100ML | ₹20079.99 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| ALFA India | ALF-045133-G6 | Tantalum wire, 0.203mm (0.008 in.) dia, hard, 99.9% (metals basis) | 7440-25-7 | 10m | ₹9969 | 2022-05-26 | Buy |
| ALFA India | ALF-045133-G5 | Tantalum wire, 0.203mm (0.008 in.) dia, hard, 99.9% (metals basis) | 7440-25-7 | 5m | ₹18099 | 2022-05-26 | Buy |
| ALFA India | ALF-045133-G1 | Tantalum wire, 0.203mm (0.008 in.) dia, hard, 99.9% (metals basis) | 7440-25-7 | 1m | ₹8024 | 2022-05-26 | Buy |
Tantalum Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
Tantalum is a refractory metal in Group V-B of the periodic table. The pure metal is ductile, steel-blue to gray solid or black, odorless powder.
Physical properties
Tantalum has properties similar to niobium and vanadium above it in group 5. It is a veryhard and heavy metal with a bluish color when in its rough state, but if polished, it has a silveryshine. It is ductile, meaning it can be drawn into fine wires, and also malleable, meaningit can be hammered and worked into shapes. Thin strips and wires of tantalum will ignite inair if exposed to a flame.
Tantalum’s melting point is 2,996°C, which is almost as high as tungsten and rhenium. Itboiling point is 5,425°C, and its density is 19.3 g/cm3.
Isotopes
There are 49 isotopes of tantalum. Only the isotope Ta-181 is stable andaccounts for 99.988% of the total mass of the element on Earth. Just 0.012% of the element’s mass is contributed by Ta-180, which has a half-life of 1.2×10+15 years and isthus considered naturally stable. The remaining 47 isotopes are all artificially producedin nuclear reactions or particle accelerators and have half-lives ranging from a few microsecondsto few days to about two years.
Origin of Name
Tantalum was named after Tantalus, who was the father of Niobe, the queen of Thebes, a city in Greek mythology. (Note: The element tantalum was originally confused with the element nobelium.)
Occurrence
Tantalum is the 51st most abundant element found on Earth. Although it is found in afree state, it is usually mixed with other minerals and is obtained by heating tantalum potassiumfluoride or by the electrolysis of melted salts of tantalum. Tantalum is mainly obtainedfrom the following ores and minerals: columbite [(Fe, Mn, Mg)(Nb, Ta)2O6]; tantalite [(Fe,Mn)(Ta, Nb)2O6]; and euxenite [(Y, Ca, Er, La, Ce, U, Th)(Nb, Ta, Ti)2O6]. Tantalum’s oresare mined in South America, Thailand, Malaysia, Africa, Spain, and Canada. The UnitedStates has a few small native deposits but imports most of the tantalum it uses.
Since tantalum and niobium are so similar chemically, a solvent process must be employedto separate them from the common ores. They are dissolved in a solvent, resulting in 98% pure niobium oxide being extracted during this part of the process. This is followed by 99.5%pure tantalum oxide being extracted in a second solvent process.
Characteristics
Tantalum is almost as chemically inert at room temperatures (it has the ability to resistchemical attacks, including hydrofluoric acid) as are platinum and gold. It is often substitutedfor the more expensive metal platinum, and its inertness makes it suitable for constructingdental and surgical instruments and artificial joints in the human body.
Uses
In pen points; analytical weights; apparatus and instruments for chemical, surgical, and dental use instead of platinum, in tantalum capacitors (a type of electrolytic condenser, trademarked "Tantalytic").
Production Methods
It was identi?ed that tantalum minerals exists in over 70 differentchemicalcompositions.Thoseofgreatesteconomic importance are tantalite, microlite, and wodginite; however, it is common practice to name any tantalum-containing mineral concentrate as “tantalite”. Tantalum resources are widespread, with the most important known resources being found in Brazil and Australia. In mid-2008, the main mining operations were in Australia, Brazil,Canada,Mozambique,andEthiopiaandinmid-2009, in Brazil, Ethiopia, and China, with additional quantities originating in central Africa, Russia, and Southeast Asia. There is continued interest in exploration of this element in other countries, primarily in Egypt, Canada, Mozambique, and Saudi Arabia.
The major world mine producers of tantalum in 2010 were Brazil (180 tons), Mozambique (110 tons), Rwanda (100 tons), and Australia (80 tons). Other countries produced around 170 tons, so the total world production of tantalum was approximately 670 tons. The major producers of tantalum mineral concentrates are Australia, Brazil, and Canada.
Definition
A silvery transition element. It is strong, highly resistant to corrosion, and is easily worked. Tantalum is used in turbine blades and cutting tools and in surgical and dental work. Symbol: Ta; m.p. 2996°C; b.p. 5425 ± 100°C; r.d. 16.654 (20°C); p.n. 73; r.a.m. 180.9479.
General Description
Tantalum dust is a black odorless powder. Mp: 2996°C; bp: approx. 5250°C. Density: 16.65 g cm-3. Insoluble in water. Tantalum oxide dust is a white, microcrystalline powder Mp: 1800°C. Density: 7.6 g cm-3. Insoluble in water. The mixture is listed as a toxic inhalation hazard by OHSA.
Hazard
The dust and powder of tantalum are explosive. Several tantalum compounds are toxic ifinhaled or ingested, but the metal itself is nonpoisonous.
Health Hazard
Tantalum has a low order of toxicity but has produced transient inflammatory lesions in the lungs of animals. Surgical implantation of tantalum metal products such as plates and screws has not shown any adverse tissue reaction, thus demonstrating its physiological inertness.
Safety Profile
An inhalation hazard. Some industrial skin injuries from tantalum have been reported. Systemic industrial poisoning, however, is apparently unknown. Questionable carcinogen with experimental tumorigenic data. The dry powder iptes spontaneously in air. Incompatible with bromine trifluoride, fluorine, lead chromate. See also specific tantalum compounds.
Carcinogenicity
Although Oppenheimer et al., using embedded metal foil technique, have elicited two malignant ?brosarcomas in 50 embeddings of tantalum metal in 25Wistar rats aftera latent period of714days, these results remain a controversial issue. Miller et al. have studied tumorigenic transforming potential of tungsten, iron, nickel, and cobalt with tantalum as a comparison on an immortalized nontumorigenic human osteoblast-like cell line. No tumorigenic activity of Ta was reported, but data are not shown.
In the recent study, intramuscularly pellets (1mm 2mm cylinders) of weapons-grade WA were implantedtosimulateshrapnelwounds.Ratswereimplanted with 4 (low dose) or 20 pellets (high dose) of WA. Tantalum (20 pellets) and nickel (20 pellets) served as negative and positive controls, respectively. Rats implanted with tantalum (n=46) did not develop tumors.
Shipping
UN3089 Metal powders, flammable, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 4.1; Labels: 4.1-Flammable solid.
Incompatibilities
A flammable solid; the dry powder can ignite spontaneously in air. Incompatible with lead chromate. A strong reducing agent; incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, bromine trifluoride, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. Tantalum metal is attacked by hydrogen fluoride, fused alkalis, fuming sulfuric acid.
Waste Disposal
Sanitary landfill if necessary; recover if possible because of economic value. Technology exists for tantalum recovery from spent catalysts, for example.
Tantalum Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nano Research Elements | 08048372588Ext 365 | Delhi, India | 101 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Amigo Impex | 08046067838 | Mumbai, India | 9 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Amardeep Steel Centre | 08046050590 | Mumbai, India | 2 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Shubham Industries | 08046034096 | Mumbai, India | 7 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Bhagyashali Metal | 08048609059 | Mumbai, India | 8 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Parmanu Dhatu Nigam | 08048372587Ext 498 | Mumbai, India | 27 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Ramdev Steel Overseas | 08048617233 | Mumbai, India | 1 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Special Metals | 08048966927 | Mumbai, India | 8 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Manhar Metal Supply Corporation | 08048974875 | Mumbai, India | 8 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Intelligent Materials Private Limited | 08048953178 | Punjab, India | 197 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| Nano Research Elements | 58 |
| Amigo Impex | 58 |
| Amardeep Steel Centre | 58 |
| Shubham Industries | 58 |
| Bhagyashali Metal | 58 |
| Parmanu Dhatu Nigam | 58 |
| Ramdev Steel Overseas | 58 |
| Special Metals | 58 |
| Manhar Metal Supply Corporation | 58 |
| Intelligent Materials Private Limited | 58 |
Related articles
- The Ta-containing minerals
- Tantalum is estimated to make up between 1 and 2 ppm of the Earth’s crust by weight.
- May 30,2024
- Tantalum industrial applications and uses
- Tantalum’s good thermal conductivity (57.5 W.m–1.K–1 at 20°C) gives a suitable construction material when corrosion resistance....
- Sep 26,2019
- Industrial Preparation of Tantalum Metal
- Tantalum can be prepared in several ways from different tantalum-containing materials. The primary source is columbotantalite ....
- Sep 26,2019
7440-25-7(Tantalum)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




