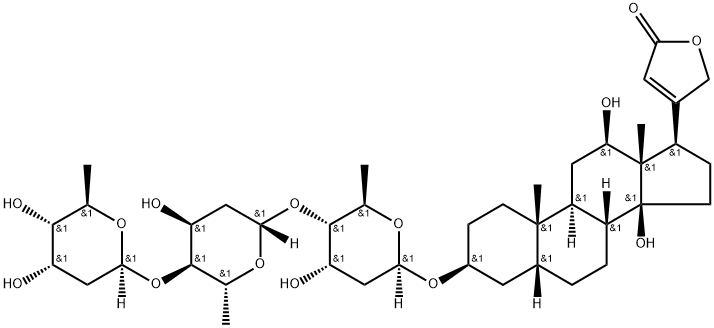
DIGOXIN
- CAS No.
- 20830-75-5
- Chemical Name:
- DIGOXIN
- Synonyms
- digitalis;DIGACIN;digoxine;LANOXIN;lanoxicaps;DIGOXIN, AP;Digoxin for peak identification CRS;dokim;Digon;dixina
- CBNumber:
- CB2407221
- Molecular Formula:
- C41H64O14
- Molecular Weight:
- 780.95
- MOL File:
- 20830-75-5.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2024/3/14 15:18:26
| Melting point | 248 °C |
|---|---|
| alpha | 25Hg +13.4 to 13.8° (c = 10 in pyridine) |
| Boiling point | 661.93°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.1110 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 12 ° (C=10, Pyridine) |
| Flash point | 9℃ |
| storage temp. | Refrigerator |
| solubility | Soluble in dimethyl sulfoxide and methanol. |
| form | powder |
| pka | 13.50±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | White to Almost white |
| Water Solubility | 46.08mg/L(room temperature) |
| Merck | 14,3167 |
| BRN | 77011 |
| BCS Class | 1 (LogP), 3 (CLogP) |
| LogP | 1.260 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 20830-75-5 |
| IARC | 2B (Vol. 108) 2016 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Digoxin (20830-75-5) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS06,GHS08 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H300-H331-H373 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P260-P264-P270-P301+P310-P304+P340+P311-P314 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | T,T+,F | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 25-26/27/28-23/25-39/23/24/25-23/24/25-11-28-26 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 22-36/37/39-45-36/37-16-28A | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 3462 6.1/PG 2 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | IH6125000 | |||||||||
| F | 3-10 | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 6.1 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | II | |||||||||
| HS Code | 29389090 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | cat,LD50,oral,200ug/kg (0.2mg/kg),Archives Internationales de Pharmacodynamie et de Therapie. Vol. 159, Pg. 1, 1966. | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
DIGOXIN price More Price(12)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | D6003 | Digoxin analytical standard | 20830-75-5 | 100MG | ₹2392.33 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | PHR1771 | Digoxin Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material | 20830-75-5 | 300MG | ₹24312.95 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | D6770 | Digoxin analytical standard | 20830-75-5 | 1VIAL | ₹37671 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | D6003 | Digoxin analytical standard | 20830-75-5 | 1G | ₹11539.45 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | D6003 | Digoxin analytical standard | 20830-75-5 | 5G | ₹45096.95 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
DIGOXIN Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Digoxin, 3β,14β-dihydroxy-5β-card-20(22)-enolide-3-rigitoxide, is also a glycoside isolated from various types of foxgloves. It differs from digitoxin in that it has an additional hydroxyl group at C16 of the steroid skeleton. It is extracted form the leaves of Digitalis lanta, Digitalis orientalis, or Scrophulariaceae.
Chemical Properties
White Crystalline Powder
Physical properties
Appearance: white crystals or crystalline powder, odorless. Solubility: easily dissolved in pyridine, slightly soluble in dilute alcohol, slightly soluble in chloroform, insoluble in water and ethyl ether. Specific optical rotation: +9.5 to +12.0°. Melting point: 248–250?°C.
Uses
Digoxin exhibits strong systolic action and slows heart rate. It is removed from the organism faster than digitoxin. It is used from chronic cardiac insufficiency in decompensated valvular disease of the heart, myocardium overload in arterial hypertension, tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, and other analogous situations.
Indications
Digoxin is used for congestive heart failure (CHF), paroxysmal supraventricular tachycarelia, atrial fibrillation, and atrial flutter.
Definition
ChEBI: A cardenolide glycoside that is digitoxin beta-hydroxylated at C-12. A cardiac glycoside extracted from the foxglove plant, Digitalis lanata, it is used to control ventricular rate in atrial fibrillation and in the management of congestive heart failure with atrial fibrillation, but the margin between toxic and therapeutic doses is small.
General Description
Digitalis (Crystodigin) is isolated fromD. lanata and D. purpurea among other Digitalis spp., and isthe chief active glycoside in digitalis leaf, with 1 mg digitoxinequal to 1 g of digitalis leaf therapy. In patients who missdoses, digitalis is very useful for maintenance therapy becauseof the longer half-life it provides. The longer durationand increased half-life are a result of the lack of the C-12hydroxy that is present in digoxin. In digoxin, this hydroxyplays two roles: (a) it serves as a site for metabolism, whichreduces the compound’s half-life; and (b) it gives more hydrophiliccharacter, which results in greater water solubilityand ease in renal elimination.
Health Hazard
Material is a digitalis glycoside. Ingestion can cause death. Material is considered super toxic; probable human oral lethal dose is less than 5 mg/kg, a taste (less than 7 drops) for a 70 kg (150 lb.) person. Persons at risk include those taking drugs for thyroid and renal diseases. Quinidine and diuretics taken concurrently with DIGOXIN can be hazardous. It should be used with extreme care during pregnancy and in nursing mothers.
Fire Hazard
Avoid light.
Safety Profile
A deadly poison by most routes. Human systemic effects by ingestion: anorexia, cardlac arrhythmias, nausea and vomiting, visual field changes, pulse rate decrease, fall in blood pressure. An experimental teratogen. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid and irritating fumes. See also DIGITALIS.
Environmental Fate
Molecular weight: Digitoxin, 764.96; Digoxin, 780.96. Cardiac glycosides have a characteristic chemical structure called an aglycone ring. This is coupled with one or more sugars. The aglycone portion of the glycoside includes a steroid nucleus and a lactone ring at the C17 position. Hydroxyl groups, oriented to the beta position, are present at the C3 and C14 positions. Increases in numbers of hydroxyl groups cause an increase in polarity and decrease in lipid solubility. Increases in numbers of sugars also increase polarity and reduce lipid solubility. Sugars are attached to the steroid nucleus through a hydroxyl group at the C3 position and influences solubility, absorption, toxicity, and other pharmacological parameters.
Purification Methods
Crystallise digoxin from aqueous EtOH, aqueous pyridine, EtOH/CHCl3, and dry it in a vacuum at 100o. The melting point depends on heating rate, but when placed in a bath at 260o and heated slowly it decomposes at 265o. In EtOH it has max at 220nm ( 12,800). [Smith J Chem Soc 508 1930, X-ray: Go et al. Cryst Struct Commun 8 149, 1031 1979, Beilstein 18/4 V 381.] HIGHLY TOXIC.
DIGOXIN Preparation Products And Raw materials
Related articles
- Mechanism of Digoxin
- Digoxin is a cardiac glycoside derived from the plant species digitalis (foxglove). A lthough previously used in the managemen....
- Feb 18,2022
20830-75-5(DIGOXIN)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




