Potassium hydride

- CAS No.
- 7693-26-7
- Chemical Name:
- Potassium hydride
- Synonyms
- KH;HK-9;PotassiuM hydrid;POTASSIUM HYDRIDE;potassiumhydride(kh);Potassium monohydride;Potassium hydride (KH);Hydrogen potassium salt;Potassiumhydride,30-35%inoil;PotassiuM hydride in paraffin
- CBNumber:
- CB5854282
- Molecular Formula:
- HK
- Molecular Weight:
- 40.11
- MOL File:
- 7693-26-7.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2023/10/21 9:26:16
| Melting point | decomposes [CRC10] |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 316 °C |
| Density | 1.54 |
| Flash point | 113 °C |
| storage temp. | Flammables + water-Freezer (-20°C)e area |
| solubility | Insoluble in benzene, diethyl ether and carbon disulfide. |
| form | dispersion (in mineral oil (~35%)) |
| color | Grayish beige |
| Water Solubility | decomposed by H2O [CRC10] |
| Sensitive | Moisture Sensitive |
| InChIKey | NTTOTNSKUYCDAV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Potassium hydride (KH) (7693-26-7) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS02,GHS05 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H260-H314 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P223-P231+P232-P280-P302+P335+P334-P303+P361+P353-P305+P351+P338 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | F,C | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 11-14/15-34 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 16-26-27-36/37/39-45-43 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 1409 4.3/PG 1 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| Autoignition Temperature | Ignites spontaneously at room temperature in moist air | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 4.3 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | I | |||||||||
| HS Code | 28500090 | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Potassium hydride price More Price(6)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 708860 | Potassium hydride in paraffin | 7693-26-7 | 5G | ₹10792.53 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 708860 | Potassium hydride in paraffin | 7693-26-7 | 25G | ₹25124.83 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 215813 | Potassium hydride 30?wt % dispersion in mineral oil | 7693-26-7 | 75G | ₹12427.1 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 215813 | Potassium hydride 30?wt % dispersion in mineral oil | 7693-26-7 | 300G | ₹36014.78 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| ALFA India | ALF-L13266-22 | Potassium hydride, 30% w/w in mineral oil | 7693-26-7 | 100g | ₹11378 | 2022-05-26 | Buy |
Potassium hydride Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
Potassium hydride is available in laboratory quantities only as a 20 – 35 % dispersion in oil. Potassium hydride is a considerably stronger base than lithium hydride or sodium hydride. It is able to remove protons from tertiary alcohols and ketones, a reaction that either does not occur or is very slow when sodium hydride is used. Potassium hydride also reacts with weak Lewis acids, converting sterically hindered boron trialkyls to the corresponding sterically hindered complex borohydrides: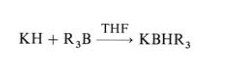
Uses
Potassium Hydride is used in preparation of Hydroxy-Xanthone derivatives via Isoprenylation followed by Claisen rearrangement starting from Fluoroxanthone derivatives.
Definition
potassium hydride: A white orgreyish white crystalline solid, KH;r.d. 1.43–1.47. It is prepared by passinghydrogen over heated potassiumand marketed as a light grey powderdispersed in oil. The solid decomposeson heating and in contact withmoisture and is an excellent reducingagent. Potassium hydride is a firehazard because it produces hydrogenon reaction with water.
Reactions
Potassium hydride acts as a base and as hydride donor. It is used for deprotonation, cyclization-condensation, elimination, and rearrangement reactions, and also as a reducing agent. Potassium hydride undergoes reaction quickly and quantitatively with acids, and of particular note is its capability to rapidly deprotonate tertiary alcohols where sodium hydride or potassium metal do so slowly or not at all. The reactions of metal hydrides take place at the crystal surface. The crystal lattice energies decrease from lithium to cesium hydride, and potassium hydride appears to have the optimal lattice energy and hydride radius for surface reactions. The presence of 18-crown-6 enhances the reactivity of potassium hydride, The crown ether can operate as a phase-transfer agent or as a simple “pickling” agent of the potassium hydride surface, dissolving the formed inorganic salts. Potassium hydride is usually superior to lithium and sodium hydride in the reactions. Unusually active potassium hydride can be prepared easily from hydrogen and superbasic reagents (t-BuOK-TMEDA) in hexane. “Superactive potassium hydride” is very active in deprotonation as well as in reduction. The reactivity of commercially available potassium hydride, which is prepared by the reaction of hydrogen gas with elemental potassium, depends upon the impurities in different lots (mainly potassium or its reaction products), thus leading to side reactions and variable yields. The superactive metal hydride contains no alkali metal.
General Description
This product has been enhanced for energy efficiency.
Hazard
Dangerous fire and explosion risk, evolves toxic and flammable gases on heating and on expo- sure to moisture.
Health Hazard
Potassium hydride react with the moisture on skin and other tissues to form highly corrosive sodium and potassium hydroxide. Contact of these hydrides with the skin, eyes, or mucous membranes causes severe burns; thermal burns may also occur due to ignition of the liberated hydrogen gas.
Fire Hazard
Potassium hydride is flammable solid that ignite on contact with moist air. Potassium hydride presents a more serious fire hazard than sodium hydride. The mineral oil dispersions do not ignite spontaneously on exposure to the atmosphere. Sodium hydride and potassium hydride fires must be extinguished with a class D dry chemical extinguisher or by the use of sand, ground limestone, dry clay or graphite, or "Met-L-X ? " type solids. Water or CO 2 extinguishers must never be used on sodium and potassium hydride fires.
Flammability and Explosibility
Potassium hydride and sodium hydride are flammable solids that ignite on contact with moist air. Potassium hydride presents a more serious fire hazard than sodium hydride. The mineral oil dispersions do not ignite spontaneously on exposure to the atmosphere. Sodium hydride and potassium hydride fires must be extinguished with a class D dry chemical extinguisher or by the use of sand, ground limestone, dry clay or graphite, or "Met-L-X?" type solids. Water or CO2 extinguishers must never be used on sodium and potassium hydride fires.
Safety Profile
Dangerous fire hazard by chemical reaction. Ignites spontaneously in air. Moderate explosion hazard when exposed to heat or by chemical reaction. Wdl react with water, steam, or acids to produce H2 which then igmtes. Can react vigorously with oxidizing materials. To fight fire, use CO2, dry chemical. Potentially explosive reactions with 0-2,4- dnitrophenylhydroxylamine, fluoroalkenes. Ignites on contact with air, oxygen + moisture, fluorine. Incompatible with Cl2, acetic acid, acrolein, acrylonitrile, (CaC + Cl2), ClO2, (H202 + Cl2), (CHFL + CH,OH), 1,2-dchloroethylene, maleic anhydride, (n-methyl-n-nitrosourea + CH2Cl2), nitroethane, NCb, nitromethane, nitroparaffins, o-nitrophenol, nitropropane, n-nitrosomethylurea, (nitrosomethylurea + CH2Cl2), H20, trichloroethylene, tetrahydrofuran, tetrachlorethane. When heated to decomposition it emits highly toxic fumes of K2O. See also POTASSIUM and HYDRIDES.
storage
Safety glasses, impermeable gloves, and a fire-retardant laboratory coat should be worn at all times when working with these substances. These hydrides should be used only in areas free of ignition sources and should be stored preferably as mineral oil dispersions under an inert gas such as argon.
Incompatibilities
Potassium hydride and sodium hydride react violently with water, liberating hydrogen, which can ignite. Oil dispersions of these hydrides are much safer to handle because the mineral oil serves as a barrier to moisture and air. Potassium hydride may react violently with oxygen, CO, dimethyl sulfoxide, alcohols, and acids. Explosions can result from contact of these compounds with strong oxidizers. Potassium hydride is generally more reactive than sodium hydride.
Waste Disposal
Excess potassium or sodium hydride and waste material containing these substances should be placed in an appropriate container under an inert atmosphere, clearly labeled, and handled according to your institution's waste disposal guidelines. Experienced personnel can destroy small quantities of sodium hydride and potassium hydride by the careful dropwise addition of t-butanol or iso-propanol to a suspension of the metal hydride in an inert solvent such as toluene under an inert atmosphere such as argon. Great care must be taken in the destruction of potassium hydride because of its greater reactivity. The resulting mixture of metal alkoxide should be placed in an appropriate container, clearly labeled, and handled according to your institution's waste disposal guidelines.
Potassium hydride Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
1of2
chevron_right| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biokemix | +91 (40) 6662-6366 | New Delhi, India | 487 | 50 | Inquiry |
| Alfa Aesar | 1 800 209 7001 | Maharashtra, India | 6913 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Triveni chemicals | 08048762458 | New Delhi, India | 6093 | 58 | Inquiry |
| CONIER CHEM AND PHARMA LIMITED | +8618523575427 | China | 49391 | 58 | Inquiry |
| career henan chemical co | +86-0371-86658258 +8613203830695 | China | 29826 | 58 | Inquiry |
| sgtlifesciences pvt ltd | +8617013299288 | China | 12382 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Shaanxi Didu New Materials Co. Ltd | +86-89586680 +86-13289823923 | China | 9003 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Henan Fengda Chemical Co., Ltd | +86-371-86557731 +86-13613820652 | China | 20313 | 58 | Inquiry |
| ABCR GmbH & CO. KG | 49 721 95061 0 | Germany | 6846 | 75 | Inquiry |
| Shaanxi Xihua Chemical Industry Co., Ltd | 029-81122149 13992773979 | China | 6246 | 58 | Inquiry |
Related articles
- Potassium hydride-Health Hazards and Toxicity
- Potassium hydride reacts violently with water, liberating highly flammable hydrogen gas; causes severe burns on eye or skin co....
- Sep 6,2019
7693-26-7(Potassium hydride)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




