ハフニウムジオキシド 化学特性,用途語,生産方法
外観
白色~ほとんど白色, 粉末
溶解性
水, 酸に不溶。王水にわずかに溶ける。
用途
材料研究用。金属原料。誘電体材料、トランジスタ材料。
使用上の注意
含量は金属ベースで差数法によって算出したもので、重量又は容量分析等の化学的方法によるものではありません。使用目的により、正確な含量が必要な場合は、それらの方法によって測定する必要があります。
説明
Hafnium is a shiny, silvery, ductile metal and resistant to corrosion. The physical properties of hafnium metal samples are markedly affected by zirconium impurities, especially the nuclear properties, as these two elements are among the most difficult to separate because of their chemical similarity. Hafnia is used in optical coatings and as a high-k dielectric in dynamic randomaccess memory (DRAM) capacitors. Hafnium (IV) oxide is a colourless, inert solid and has been reported as one of the most common and stable compounds of hafnium. It is an electrical insulator. Hafnium dioxide is an intermediate in some processes that give hafnium metal. It reacts with strong acids and strong bases. It dissolves slowly in hydrofluoric acid. At high temperatures, it reacts with chlorine in the presence of graphite or carbon tetrachloride and forms the hafnium tetrachloride. Hafnium-based oxides are currently important materials to replace silicon oxide as a gate insulator because of its high dielectric constant. Hafnium (Hf) is found in association with zirconium ores, production based on zircon (ZrSiO4) concentrates which contain 0.5%–2% hafnium. Hafnium has extensive applications in industries especially because of its resistance to corrosion. Different compounds of hafnium used in ceramics industry are hafnium boride, hafnium carbide, hafnium nitride, hafnium oxide, hafnium silicate, and hafnium titanate. Hafnium-based oxides are currently leading candidates to replace silicon oxide as a gate insulator in fieldeffect transistors.
化学的特性
Hafnium oxide is a white cubic crystal, insoluble in water, hydrochloric acid, nitric acid and other common inorganic acids, and slowly dissolves in hydrofluoric acid to form fluorohafnate. It reacts with hot concentrated sulfuric acid or bisulfate to produce hafnium sulfate. Mix and heat with carbon in the presence of chlorine to obtain hafnium tetrachloride. It reacts with potassium fluorosilicate to produce potassium fluorohafnate.
物理的性質
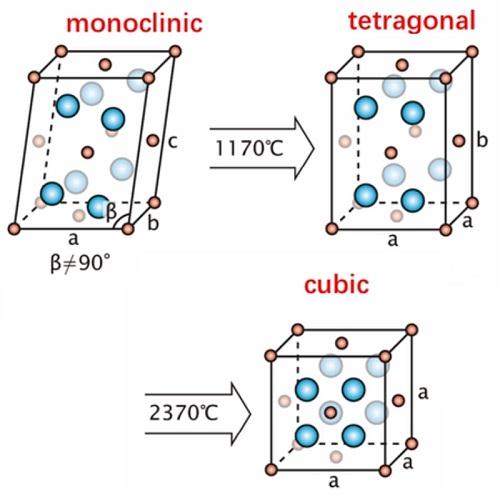
Hafnium oxide (HfO2) is a white crystalline powder. Pure hafnium oxide exists in three forms, one in the amorphous state and the other two in the crystalline state. When unstable compounds such as hafnium hydroxide and hafnium oxychloride are calcined at <400°C, amorphous hafnium oxide can be obtained. Continue to heat the hafnium oxide to 450-480°C, and start to transform into monoclinic crystals, and continue to heat to 1000-1650°C to gradually increase the lattice constant, and transform into a monomer of 4 hafnium oxide molecules. At 1700~1865℃, it starts to transform into tetragonal crystal system. Hafnium is a refractory metal which occurs in nature in zirconium minerals.
使用
Hafnium(IV) oxide is used as Intermediates, Paint additives and coating additives, metal Products. And it is also used in optical coatings, as a refractory material in the insulation of such devices as thermocouples.
職業ばく露
Hafnium metal has been used as a
control rod material in nuclear reactors. Thus, those
engaged in fabrication and machining of such rods may be
exposed.
輸送方法
UN1326 Hafnium powder, wetted with not
<,25% water (a visible excess of water must be present)
(1) mechanically produced, particle size<53 μm; (2)
chemically produced, particle size<840 μm, Hazard Class:
4.1; Labels: 4.1-Flammable solid. UN2545 Hafnium pow der, dry, Hazard Class: 4.1; Labels: 4.1-Flammable solid.
UN1346 Hafnium powder, wetted with not less than 25%
water (a visible excess of water must be present)
(1) mechanically produced, particle size less than 53 μm;
(2) chemically produced, particle size less than 840 μm,
Hazard Class: 4.1; Labels: 4.1-Flammable solid.
不和合性
Fine powder or dust may form explosive
mixture in air. The powder is highly flammable and a strong
reducing agent. The powder or dust reacts with moisture
forming flammable hydrogen gas; may spontaneously ignite
on contact with moist air; and at higher temperatures, with
nitrogen, phosphorous, oxygen, halogens, and sulfur; contact
with hot nitric acid; heat, shock, friction, strong oxidizers;
or ignition sources may cause explosions.
廃棄物の処理
Recovery. Consider recycling,
otherwise, this chemical must be disposed of in compliance
with existing federal and local regulations.
参考文献
R. Ruh, P.W.R. Corfield, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 53, 126 (1970), DOI: 10.1111/j.1151-2916.1970.tb12052.x.
ハフニウムジオキシド 上流と下流の製品情報
原材料
準備製品