ニッケルカルボニル 化学特性,用途語,生産方法
解説
テトラカルボニルニッケル[Ni(CO)4]は,1890年,L. Mond(モンド)らにより最初の金属カルボニルとして発見された.活性なニッケル金属上に常温でCOを通して得られる.流動性のよい有毒な無色の液体.融点-25 ℃,沸点43 ℃.蒸気圧34.8 kPa(15 ℃).密度1.31 g cm-3(20 ℃).臨界温度195 ℃.臨界圧力3.0 MPa.空気中で不安定で,COを発生しながら酸化される.また,熱により分解してニッケル金属を生じる.Mondはこの性質を利用してニッケルの精錬を行った.大部分の有機溶媒に可溶,水,希酸,アルカリ水溶液に不溶.COはニッケルのまわりに正四面体に配位し,Ni-C-Oは直線形,Ni-C0.184 nm,C-O0.115 nm.高圧アセチレン重合,オキソ反応などの触媒として用いられる.ニッケルカルボニル化合物としては,このほかに [Ni2(CO)6]2-,[Ni4(CO)9]2- や,ほかの配位子が共存している[Ni(CO)3(SbCl3)],[Ni(CO)2{P(C6H5)3}]など多種類のものが知られている.[CAS 12612-55-4:Ni(CO)4]
森北出版「化学辞典(第2版)
用途
純ニッケル製造、ニッケルメッキ、アクリル酸エステル樹脂の製造
製造法
ニッケルカルボニルは,ニッケルの一酸化炭素錯体。テトラカルボニルニッケル(O)が知られている。最初の金属カルボニルとして1890年、ドイツ生まれのイギリスのモンドLuding Mond(1839―1909)によって発見された。酸化ニッケルを新しく還元してつくった金属ニッケルに60℃で一酸化炭素を作用させると得られる。揮発性、可燃性の無色の液体で、固体状態では針状結晶。水にはほとんど溶けないが、ベンゼン、エーテル、クロロホルムなどには溶ける。60℃以下では安定であるが、約200℃で黒色粉末状の金属ニッケルと一酸化炭素とに分解する。 2Ni(CO)4―→Ni+2C+CO2(200℃)この反応は純粋なニッケルの工業的製造に利用される。急に熱すると分解して爆発する。きわめて毒性が強いので吸入しないようにするなど十分に注意を要する。[鳥居泰男]
特徴
正四面体形,Ni-C 181.5 pm (198 K)
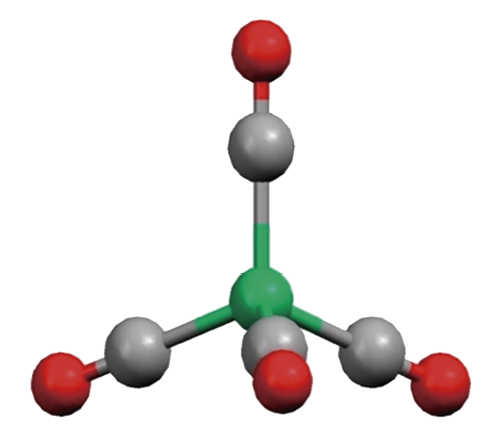
説明
Nickel carbonyl is a clear colourless to yellow volatile liquid, is flammable, and burns with
a yellow flame. It is denser than water and insoluble in water but soluble in alcohol, benzene,
chloroform, acetone, ethanol, carbon tetrachloride, and nitric acid. The vapours are
heavier than air. In industries, nickel carbonyl is used in nickel coat steel and other metals
and to make very pure nickel. Nickel carbonyl gets peroxidised by air as a solid deposit
and decomposes to ignite.
化学的特性
Nickel carbonyl is a colorless, highly volatile,
flammable liquid with a musty odor. The Odor Threshold
is 1.3 ppm. It decomposes above room temperature producing
carbon monoxide and finely divided nickel.
物理的性質
Colorless volatile liquid; diamagnetic; flammable; burns with a bright luminous flame; density 1.319 g/mL; freezes at -25°C; boils at 43°C; vapor pressure 320.6 torr at 20°C; vapor density 5.89 (air=1); critical temperature about 200°C; critical pressure 30 atm; practically insoluble in water, 180 mg/L at 10°C; miscible with most organic solvents including ethanol, acetone, and benzene; soluble in nitric acid and aqua regia.
来歴
Nickel tetracarbonyl was prepared first in 1888 by Mond and Langer by passing carbon monoxide over finely divided nickel. It is the most important zero valent compound of nickel and is used industrially to make high-purity nickel powder and pellets and to produce nickel coatings on steel.
使用
Nickel carbonyl is used in nickel vapoplating processes in
the metallurgical and electronics industry, and in the catalytic
methyl- and ethylacrylate monomer synthesis. For many
years it had been used to produce pure nickel by the
Mond process, which has been considered to be outdated
since around 1970.
定義
nickel carbonyl: A colourlessvolatile liquid, Ni(CO)
4; m.p.-25°C;b.p. 43°C. It is formed by direct combinationof nickel metal with carbonmonoxide at 50–60°C. The reaction isreversed at higher temperatures, andthe reactions are the basis of theMond process for purifying nickel.The nickel in the compound has anoxidation state of zero, and the compoundis a typical example of a complexwith pi-bonding ligands, inwhich filled d-orbitals on the nickeloverlap with empty p-orbitals on thecarbon.
製造方法
Nickel tetracarbonyl is made by passing carbon monoxide over finely divided nickel at 50 to 100°C. (The finely divided nickel is obtained from reduction of nickel oxide by hydrogen below 400°C.) Ni + 4CO → Ni(CO)
4In several commercial processes the reaction is carried out at a temperature of 200°C under 400 atm carbon monoxide pressure for obtaining high yield of nickel tetracarbonyl and also to prevent thermal dissociation.
Nickel tetracarbonyl may be prepared in the laboratory by the Hieber process, a disproportion reaction of several nickel compounds of organic thio acids, such as nickel(II) phenyldithiocarbamate, (C
6H
5—NH—C(=S)—S)
2Ni, with carbon monoxide under controlled conditions. In such disproportionation reactions, the divalent nickel ion converts to a tetravalent nickel complex (Hieber. H. 1952. Z.anorg.Chem., 269, pp. 28). The overall reaction is: 2NiII + 4CO → NiIV(complex) + Nio(CO)
4.
調製方法
Nickel carbonyl is produced in a reaction of carbon monoxide
and nickel metal. It may also be formed as a by-product in
the industrial processes using nickel catalysts, such as coal
gasification, crude oil refining, and hydrogenation reactions
(293). Conditions for its formation occur in those
processes where carbon monoxide is in contact with an
active form of nickel under conditions of elevated pressure
at 50–150°C.
一般的な説明
A clear colorless to yellow liquid. Boiling point 43°C. Flash point below 0°F. Very toxic by ingestion and inhalation. Carcinogenic. Denser than water and insoluble in water. Vapors heavier than air. Used to nickel coat steel and other metals and to make very pure nickel.
空気と水の反応
Highly flammable over a wide range of vapor-air concentrations. Is peroxidized by air to give a solid deposit that tends to decompose and ignite. Insoluble in water.
反応プロフィール
NICKEL CARBONYL is easily oxidized. Presents a very serious fire hazard if exposed to heat, flame, sparks, oxidizing agents. Explodes when heated to about 60°C. Reacts explosively with bromine (liquid), oxygen in the presence of mercury, or hydrocarbons (butane) mixed with oxygen. Undergoes violent reactions with air, oxygen, dinitrogen tetraoxide. Caused an explosion when added to an n-butane-oxygen at 20-40°C [J. Am. Chem. Soc. 70:2055-6. 1948]. Reacts with tetrachloropropadiene to form an extremely explosive dinickel chloride dimer. Emits highly toxic fumes of carbon monoxide when heated to decomposition or in contact with mineral acids or acid fumes [Bretherick, 5th ed., 1995, p. 1734]. Vapor explodes in air or oxygen at 20°C and a partial pressure of 15 mm.
危険性
Flammable, dangerous fire risk, explodes
at 60C (140F). A lung irritant and confirmed carcinogen.
健康ハザード
Probable oral lethal dose for a human is between 50 and 500 mg/kg, between one teaspoon and one ounce per 150 lb. person. NICKEL CARBONYL has also been estimated to be lethal in man at atmospheric exposures of 30 ppm for 20 minutes. Autopsies show congestion, collapse, and tissue destruction, as well as hemorrhage in the brain. Dermatitis, recurrent asthmatic attacks, and increased number of white blood cells (eosinophils) in respiratory tract are acute health hazards. NICKEL CARBONYL is poisonous. It can be fatal if inhaled, swallowed, or absorbed through skin. Vapors may cause irritation, congestion, and edema of lungs.
火災危険
Nickel carbonyl is a highly flammable liquid (NFPA rating = 3) that may ignite
spontaneously and explodes when heated above 60℃. Its lower flammable limit in
air is 2% by volume; the upper limit has not been reported. Carbon dioxide, water, or
dry chemical extinguishers should be used for nickel carbonyl fires.
燃焼性と爆発性
Nickel carbonyl is a highly flammable liquid (NFPA rating = 3) that may ignite
spontaneously and explodes when heated above 60 °C. Its lower flammable limit in
air is 2% by volume; the upper limit has not been reported. Carbon dioxide, water, or
dry chemical extinguishers should be used for nickel carbonyl fires.
化学性质
常温で液体であり,凝固点?25℃,揮発性が高く,蒸気圧は43℃で100 kP(a 1 atm),きわめて毒性が強い,アルコール,ベンゼンなどによく溶ける,水には不溶であるが,濃硫酸と爆発的に反応する
職業ばく露
Nickel carbonyl is used as an intermediate
product in the refining of nickel. The primary use for
nickel carbonyl is in the production of nickel by the Mond
process. Impure nickel powder is reacted with carbon monoxide
to form gaseous nickel carbonyl which is then treated
to deposit high purity metallic nickel and release carbon
monoxide. Other uses include gas plating; the production
of nickel products; in chemical synthesis as a catalyst, particularly
for oxo reactions (addition reaction of hydrogen
and carbon monoxide with unsaturated hydrocarbons to
form oxygen-function compounds); e.g., synthesis of
acrylic esters; and as a reactant.
貯蔵
Work with nickel
carbonyl should be conducted in a fume hood to prevent exposure by inhalation and
splash goggles and impermeable gloves should be worn at all times to prevent eye
and skin contact. Nickel carbonyl should only be used in areas free of ignition
sources. Containers of nickel carbonyl should be stored in secondary containers in
the dark in areas separate from oxidizers.
輸送方法
UN1259 Nickel carbonyl, Hazard Class: 6.1;
Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, 3-Flammable liquid,
Inhalation Hazard Zone A. A United States DOT Severe
Marine Pollutant.
合成方法
金属ニッケルに50?100℃の温度で高圧の一酸化炭素を作用させる
不和合性
May spontaneously ignite on contact
with air. In the presence of air, oxidizes and forms a
deposit which becomes peroxidized; this tends to decompose
and ignite. May explode when heated above 60 C.
Decomposes on contact with acids producing carbon monoxide.
Violent reaction with oxidizers; may cause fire and
explosions. Vapor may promote the ignition of mixtures of
combustible vapors (such as gasoline) and air. Attacks
some plastics, rubber and coatings. Store under inert gas
blanket.
廃棄物の処理
Incineration in admixture
with a flammable solvent. Also, nickel carbonyl used in
metallizing operations may be recovered and recycled.
Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance
on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste
containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform
with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation,
treatment, and waste disposal.
参考文献
D. Braga, F. Grepioni, A.G. Orpen, Organometallics, 12, 1481 (1993), DOI: 10.1021/om00028a082.
ニッケルカルボニル 上流と下流の製品情報
原材料
準備製品