三塩化ホウ素 化学特性,用途語,生産方法
外観
うすい黄赤色~黄色~緑色透明液体
外観
無色~うすい黄色~うすい黄赤色透明液体
外観
無色~うすい黄色透明液体
性質
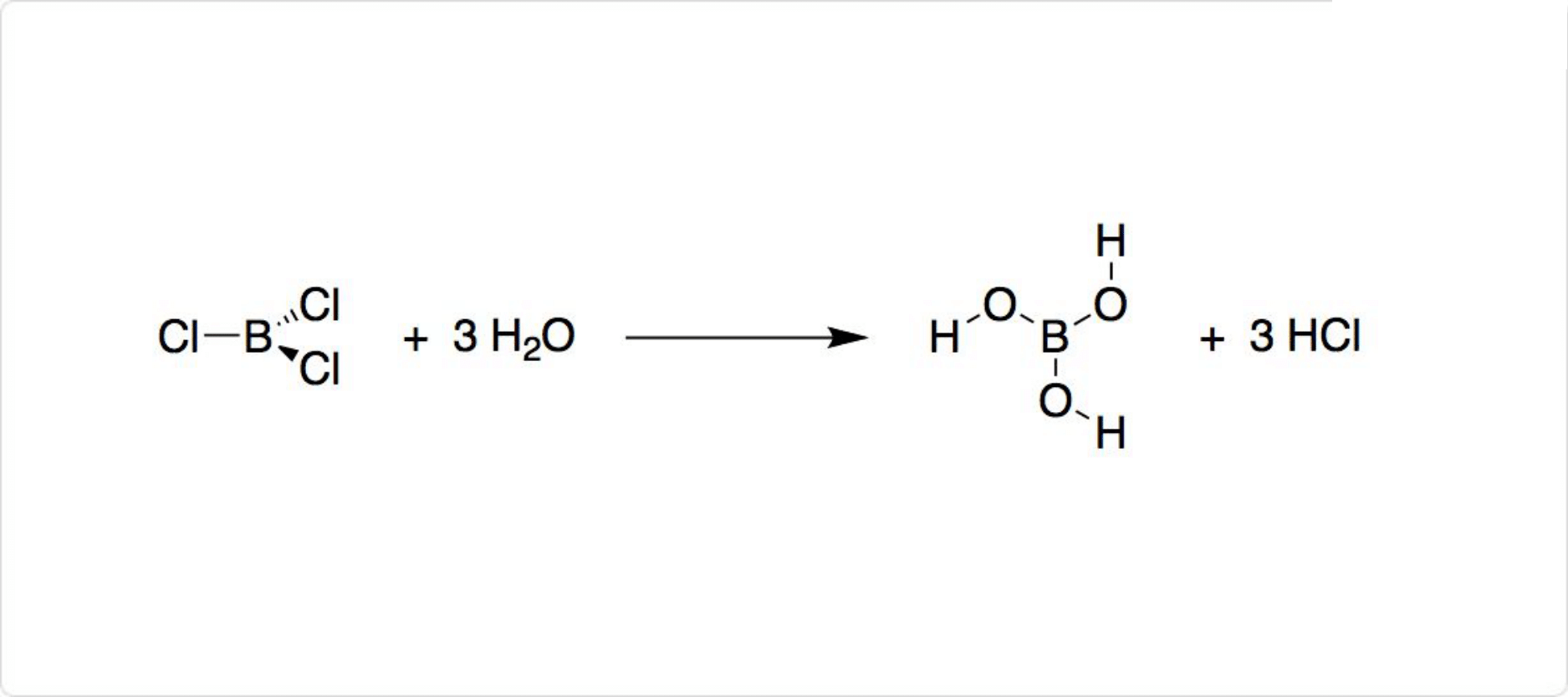
図. 三塩化ホウ素の加水分解
三塩化ホウ素の融点は−107.3°C、沸点は12.5°Cです。エーテルに溶けます。加水分解によって塩酸とホウ酸になり、アルコールと反応してホウ酸エステルを与えます。
三塩化ホウ素は湿気やアルコールで塩化水素が生じるため、取り扱いには注意が必要です。固体のBCl3・S(CH3)2はBCl3を放出するため、比較的安全で扱いやすい三塩化ホウ素の供給源として使用可能です。ただしH2OによってBCl3が分解し、溶液中にS(CH3)2が残ります。
反応
酸素を加えて放電させると、三塩化ホウ素から (B2O3) が生じます。同様に水素を加えて放電させると、単体のホウ素が得られます。
銅とともに加熱すると、三塩化ホウ素を還元でき、四塩化二ホウ素 (B2Cl4) を生成可能です。同様の方法で四塩化四ホウ素 (B4Cl4) も調製可能です。四塩化二ホウ素は室温で分解して、一般式が(BCl)n (n = 8、9、10、11) と表される化合物になります。(BCl)nはBのクラスター構造を有します。
解説
三塩化ホウ素とは、1つのホウ素 (B) 原子と3つの (Cl) 原子が結合した無機化合物です。
三塩化ホウ素の化学式は、BCl3と表されます。常温常圧では、無色のガスとして存在します。刺激臭を有する不燃性の毒性ガスで、引火点や発火点はありません。
ホウ素とハロゲンの反応によって、対応する三ハロゲン化ホウ素が得られます。工業的に三塩化ホウ素は、炭素の存在下で、500°Cで酸化ホウ素を塩素化して製造されます。実験室では、塩化アルミニウムと三フッ化ホウ素のハロゲン交換反応によって合成可能です。
構造
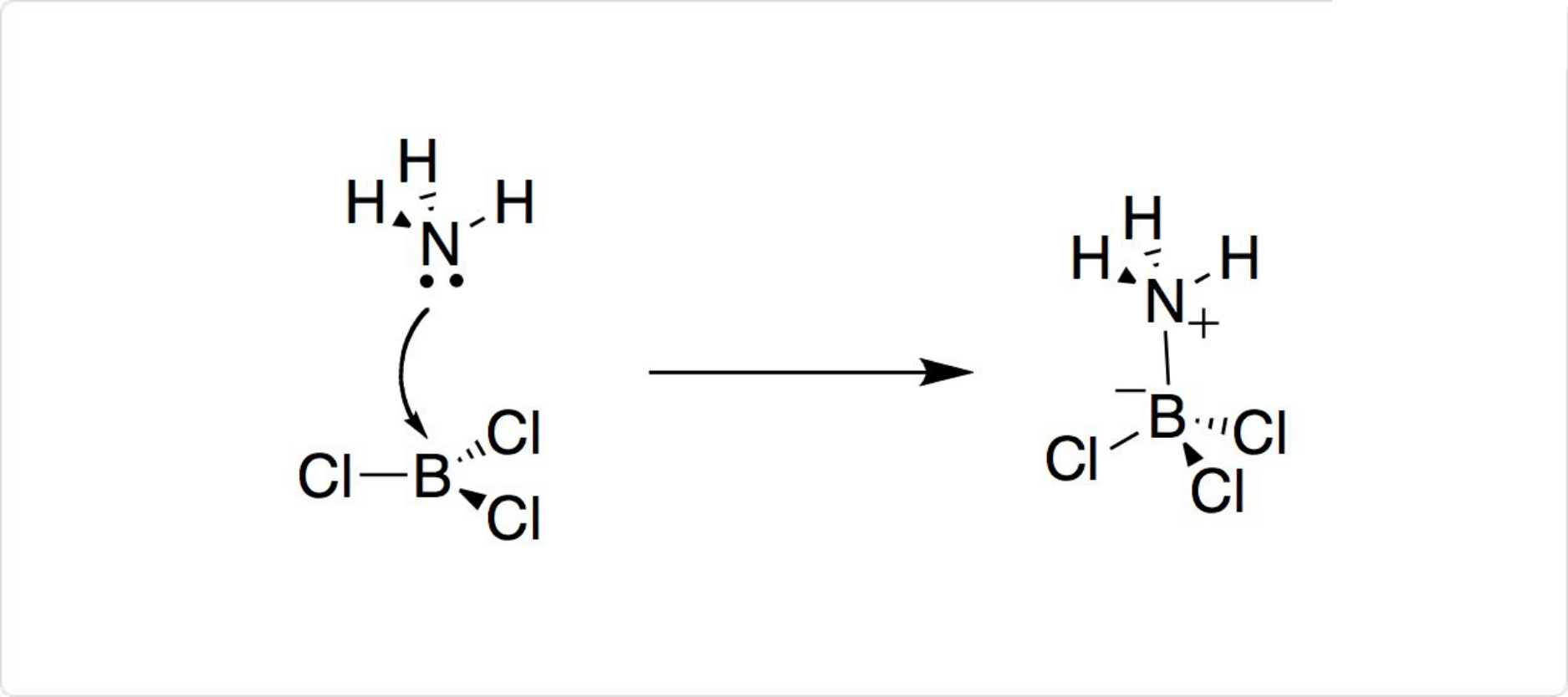
図3. 三塩化ホウ素の反応
三塩化ホウ素の分子量は117.17で、0°Cでの密度は1.43です。六方晶系結晶を形成し、気体分子の形は平面三角形です。
三塩化ホウ素は強いルイス酸であり、第三級アミン、ハロゲン化物イオン、エーテル、チオエーテル、ホスフィンと付加物を形成します。B-Clは1.74pmですが、多くの場合に付加体の形成によって、B-Cl結合長が増加します。例えばアンモニアが付加した場合には、B-Clは1.84pmです。
説明
Boron trichloride is a colorless, acid gas that
fumes in the presence of moist air. It is packaged
in steel cylinders as a liquid under its own
vapor pressure of 19.1 psia (132 kPa, abs) at
70°F
(21.1°C). It reacts with water or moist air to
produce hydrochloric and boric acid.
化学的特性
Boron trichloride is a colorless gas with a pungent odor. It reacts violently with water, and on decomposition and hydrolysis yields hydrochloric and boric acid. It has a pungent, highly irritating odor. Occupational exposure to boron and boron compounds can occur in industries that produce special glass, washing powder, soap and cosmetics, leather, cement, etc.
使用
Boron trichloride is used in the refining of aluminum,
copper, magnesium, and zinc to remove
oxides, nitrides, and carbides trom the molten
metal. Carbon monoxide, hydrogen, and nitrogen
can be removed from an aluminum melt by
treating with boron trichloride. It also improves
the tensile strength of aluminum and will allow
remelting without a major change in the grain
structure.
The electronic industry benefits trom boron
trichloride in many applications. It is used in the
production of optical fibers, as a p-type dopant
for thermal diffusion in silicon, and for ion implantation.
主な応用
One of the most important uses of Boron trichloride is in the preparation of boron
fibers ( Fibers, 13. Refractory Fibers). Typically an electrically heated tungsten filament is
passed through a chamber containing BCl3 and
hydrogen. The BCl3 is reduced, and boron is
deposited on the filament, producing a stiff,
strong boron fiber.Boron trichloride, like the trifluoride, has been
used as a Lewis acid catalyst in organic synthesis
in the polymerization of olefins and phosphazines, as well as in catalysis of other organic
reactions. Boron trichloride is also used in plasma etching of aluminum and silicon, in semiconductor manufacturing, and as a source of boron
for chemical vapor deposition. Steel is boronized
by contacting it with a reactive mixture of hydrogen, hydrocarbons, and BCl3 at high
temperatures.
一般的な説明
Boron trichloride appears as a colorless gas with a pungent odor. Fumes irritate the eyes and mucous membranes. Corrosive to metals and tissue and is toxic. Under prolonged exposure to fire or intense heat, the containers may rupture violently and rocket. Used as a catalyst in chemical manufacture, in soldering fluxes, and for many other uses.
空気と水の反応
Fumes in air, including moisture in air and soil, to form hydrochloric acid [Merck 11th ed. 1989]. Reacts vigorously with water and forms hydrochloric acid fumes and boric acid.
反応プロフィール
Boron trichloride vigorously attacks elastomers and packing materials. Contact with Viton, Tygon, Saran and natural and synthetic rubbers is not recommended. Highly corrosive to most metals in the presence of moisture. Reacts energetically with nitrogen dioxide/dinitrogen tetraoxide, aniline, phosphine, triethylsilane, or fat and grease [Mellor 5:132 1946-47]. Reacts exothermically with chemical bases (examples: amines, amides, inorganic hydroxides).
火災危険
When heated to decomposition, Boron trichloride emits toxic fumes of chlorides. Boron trichloride will react with water or steam to produce heat, and toxic and corrosive fumes. In hot water, decomposes to hydrochloric acid and boric acid. Fumes and hydrolyzes in moist air to form hydrochloric acid and oily, irritating corrosives. Avoid aniline, hexafluorisopropylidene amino lithium, nitrogen dioxide, phosphine, grease, organic matter, and oxygen. Nitrogen peroxide, phosphine, fat or grease react energetically with Boron trichloride . Oxygen and Boron trichloride react vigorously on sparking. Boron trichloride and aniline react violently in the absence of a coolant or diluent. Stable.
使用用途
主に三塩化ホウ素は、各種半導体内部や液晶パネル内部などの、微細アルミニウム配線のドライエッチングガスとして用いられます。
そのほか、農薬・医薬用化学品の原料、各種触媒の原料、 (BN) の原料として利用されています。化学気相成長法 (英: Chemical Vaper Deposition) を用いた各種CVD製品の原料にも使用可能です。
とくに半導体向けのドライエッチングガスでは、微細な配線を加工するため、非常に高純度な三塩化ホウ素エッチングガスが求められます。
職業ばく露
Used in refining of aluminum, magnesium,
copper alloys, and in polymerization of styrene.
Manufacture and purification of boron; catalyst in organic
reactions; semiconductors; bonding of iron or steel; purification
of metal alloys to remove oxides, nitrides, and
carbides; chemical intermediate for boron filaments; soldering
flux; electrical resistors; and extinguishing magnesium
fires in heat treating furnaces.
特徴
四塩化二ホウ素の分子量は163.43で、室温では無色の液体です。気体分子はCl2B-B-Cl2型で、それぞれのCl-B-Cl面が直交しています。B-Bは1.74Å、B-Clは1.73Åであり、∠Cl-B-Clは122°、∠Cl-B-Bは120°です。融点は-92.6°C、沸点は65.5°Cであり、0°Cでの密度は1.50g/cm3です。水との反応によってB2(OH)4に、Cl2との反応によってBCl3に、O2との反応によってBCl3やB2O3になります。
四塩化四ホウ素は淡黄色の結晶で、分子量は185.05です。正四面体型のB4クラスターを形成し、それぞれの頂点にB原子が位置し、Cl原子1つが結合しています。B-BとB-Clは1.70Åであり、融点は95°Cです。乾燥空気中で自然発火し、加水分解により水素を生じます。
貯蔵
Boron trichloride cylinders should be protected from physical damage. The cylinders
should be stored upright and fi rmly secured to prevent falling or being knocked over,
in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area of non-combustible construction away from heavily
traffi cked areas and emergency exits
純化方法
Purify it (from chlorine) by passage through two mercury-filled bubblers, then fractionally distil it under a slight vacuum. In a more extensive purification the nitrobenzene addition compound is formed by passage of the gas over nitrobenzene in a vacuum system at 10o. Volatile impurities are removed from the crystalline yellow solid by pumping at -20o, and the BCl3 is recovered by warming the addition compound at 50o. Passage through a trap at -78o removes entrained nitrobenzene, the BCl3 finally condensing in a trap at -112o [Brown & Holmes J Am Chem Soc 78 2173 1956]. Also purify it by condensing it into a trap cooled in acetone/Dry-ice, where it is pumped for 15minutes to remove volatile impurities. It is then warmed, recondensed and again pumped. [Gamble Inorg Synth III 27 1950.] TOXIC.
不和合性
Incompatible with lead, graphiteimpregnated
asbestos, potassium, sodium. Vigorously
attacks elastomers, packing materials, natural and synthetic
rubber; viton, tygon, saran, silastic elastomers.
Avoid aniline, hexafluorisopropylidene amino lithium,
nitrogen dioxide, phosphine, grease, organic matter; and
oxygen. Nitrogen peroxide, phosphine. Fat or grease
react vigorously with boron trichloride. It reacts with
water or steam to produce heat, boric acid, and corrosive
hydrochloric acid fumes. Oxygen and boron trichloride
react vigorously on sparking. Attacks most metals in the
presence of moisture.
廃棄物の処理
Return refillable compressed
gas cylinders to supplier. Nonrefillable cylinders should be
disposed of in accordance with local, state, and federal regulations.
Allow remaining gas to vent slowly into atmosphere
in an unconfined area or exhaust hood. Refillabletype
cylinders should be returned to original supplier with
any valve caps and outlet plugs secured and valve protection
caps in place.
予防処置
Boron trichloride vigorously attacks elastomers and packing materials, natural and synthetic rubbers. It also reacts energetically with nitrogen dioxide/dinitrogen tetraoxide, aniline, phosphine, triethylsilane, or fat and grease. It reacts exothermically with chemical
bases such as amines, amides, and inorganic hydroxides. Occupational workers should
use gloves of neoprene or butyl rubber, PVC or polyethylene, safety goggles, or glasses and
face shield, and safety shoes.
三塩化ホウ素 上流と下流の製品情報
原材料
準備製品