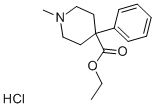
메페리딘 수화염화물
|
|
메페리딘 수화염화물 속성
- 녹는점
- 186-189°
- 끓는 점
- 282°C (rough estimate)
- 밀도
- 1.0858 (rough estimate)
- 굴절률
- 1.5200 (estimate)
- 인화점
- 11 °C
- 저장 조건
- 2-8°C
- 용해도
- 물에 매우 잘 녹고 알코올에 잘 녹습니다.
- 물리적 상태
- 결정성 고체
- CAS 데이터베이스
- 50-13-5
안전
- 위험 및 안전 성명
- 위험 및 사전주의 사항 (GHS)
| 위험품 표기 | T,F | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 위험 카페고리 넘버 | 25-39/23/24/25-23/24/25-11 | ||
| 안전지침서 | 26-36/37/39-45-36/37-16-7 | ||
| 유엔번호(UN No.) | 1544 | ||
| WGK 독일 | 3 | ||
| RTECS 번호 | NS5950000 | ||
| 위험 등급 | 6.1(b) | ||
| 포장분류 | III | ||
| HS 번호 | 2933330000 | ||
| 독성 | LD50 orally in rats: 170 mg/kg (Barlow, Lewis) | ||
| 기존화학 물질 | KE-24833 |
메페리딘 수화염화물 C화학적 특성, 용도, 생산
화학적 성질
White or almost white, crystalline powder.용도
Analgesic; sedative; anesthetic. Controlled substance (opiate).정의
An addictive drug, use by prescription only.Clinical Use
Meperidine is a μ agonist with approximately one-tenth the potency of morphine after intramuscular dose. Meperidine produces the analgesia, respiratory depression, and euphoria caused by other μ opioid agonists, but it causes less constipation and does not inhibit cough. When given orally, meperidine has 40 to 60% bioavailability because of significant first-pass metabolism. Because of the limited bioavailability, it is one-third as potent after an oral dose compared to a parenteral dose.Meperidine has received extensive use in obstetrics because of its rapid onset and short duration of action. When it is given intravenously in small (25-mg) doses during delivery, the respiratory depression in the newborn child is minimized. Meperidine is used as an analgesic in a variety of nonobstetric anesthetic procedures. Meperidine is extensively metabolized in the liver, with only 5% of the drug being excreted unchanged. Prolonged dosage of meperidine may cause an accumulation of the metabolite normeperidine. Normeperidine has only weak analgesic activity, but it causes CNS excitation and can initiate grand mal seizures. It is recommended that meperidine be discontinued in any patient who exhibits signs of CNS excitation.
Meperidine has a strong adverse reaction when given to patients receiving a monoamine oxidase inhibitor. This drug interaction has been seen recently in patients with Parkinson's disease taking the monoamine oxidase–selective inhibitor selegiline (Eldepryl).
The elimination half-life of meperidine is 3 to 4 hours, and it can double in patients with liver disease. Acidification of the urine will cause enhanced clearance of meperidine, but there is a lesser effect on the clearance of the toxic metabolite normeperidine.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, subcutaneous, intravenous, and intraperitoneal routes. Moderately toxic by parenteral route. Experimental teratogenic effects. Mutation data reported. An analgesic. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of HCl and NOx.메페리딘 수화염화물 준비 용품 및 원자재
원자재
준비 용품
메페리딘 수화염화물 관련 검색:
염화 칼륨 피콜리네이트 크롬(III) 메페리딘 수화염화물
Bisacodyl
Sodium chloride
Phloroglucinol
Trimethoprim
ALODAN
MEPERIDINE
DIPHENOXYLATE HYDROCHLORIDE
Lomotil
ETHYL 1-(3-CHLOROPROPYL)-4-PHENYLPIPERIDINE-4-CARBOXYLATE HYDROCHLORIDE
ETHYL 1-(3-HYDROXYPROPYL)-4-PHENYLPIPERIDINE-4-CARBOXYLATE HYDROCHLORIDE
MEPERIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE, [3H]- 3-10 CI(111-370 GBQ)/MMOL, DELIVERED >= 96% PURE WITH HPLC RADIOCHROMATOGRAM
4-Fluorophenyl-1-methylene-2-(4-carbethoxy-4-phenylpiperidino)-ethyl k etone hydrochloride
MEPERIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE, [3H]-
4-Piperidinecarboxylic acid, 1-(4-oxo-4-(6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-5H-benzocy clohepten-2-yl)butyl)-4-phenyl-, ethyl ester, hydrochloride
MEPERIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE, [N-METHYL-3H]