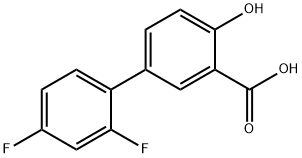
디플루니살 C화학적 특성, 용도, 생산
개요
Diflunisal is more
potent than aspirin but produces fewer side effects and has a biological half-life three to four times greater than that
of aspirin. It is rapidly and completely absorbed on oral administration, with peak plasma levels being achieved within
2 to 3 hours of administration. It is highly bound (99%) to plasma proteins after absorption. Its elimination half-life is
8 to 12 hours, and it is excreted into urine primarily as glucuronide conjugates. The most frequently reported side
effects include disturbances of the GI system (e.g., nausea, dyspepsia, and diarrhea), dermatological reactions, and
CNS effects (e.g., dizziness and headache).
화학적 성질
White Solid
용도
As a prostaglandin synthetase inhibitor, diflunisal exhibits analgesic, fever-reducing, and
anti-inflammatory action. It is used for long- and short-lasting symptomatic relief of low
to moderate pain in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
일반 설명
Diflunisal (Dolobid), is a longer acting and more potent drugthan aspirin because of its hydrophobic, 2,4-difluorophenylgroup attached to the 5-position of the salicyclic acid. In alarge-scale comparative study with aspirin, it was also bettertolerated with less GI complications than aspirin. It ismarketed in tablet form for treating mild to moderate postoperativepain as well as RA and OA.
Diflunisal is highly protein bound. Its metabolism is subjectto a dose-dependent, saturable, and capacity-limitedglucuronide formation. This unusual pharmacokineticprofile is a result of an enterohepatic circulation and the reabsorptionof 65% of the drug and its glucuronides, followedby cleavage of its unstable, acyl glucuronide back tothe active drug. Thus, diflunisal usage in patients with renalimpairment should be closely monitored.
Pharmacokinetics
Diflunisal is more
potent than aspirin but produces fewer side effects and has a biological half-life three to four times greater than that
of aspirin. It is rapidly and completely absorbed on oral administration, with peak plasma levels being achieved within
2 to 3 hours of administration. It is highly bound (99%) to plasma proteins after absorption. Its elimination half-life is
8 to 12 hours, and it is excreted into urine primarily as glucuronide conjugates. The most frequently reported side
effects include disturbances of the GI system (e.g., nausea, dyspepsia, and diarrhea), dermatological reactions, and
CNS effects (e.g., dizziness and headache).
Clinical Use
Diflunisal (pKa 3.3) was introduced in the United States in 1982 and has gained considerable acceptance as an
analgetic and as a treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Diflunisal is metabolized primarily to ether and
ester glucuronide conjugates.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion,
subcutaneous, and intraperitoneal routes.
Human systemic effects by ingestion: tolerance, and cholestatic jaundce (due to
the stoppage of the flow of bile),
agranulocytosis, increased body temperature.
An experimental teratogen. Other
experimental reproductive effects. An
analgesic and anti-inflammatory agent.
When heated to decomposition it emits
toxic fumes of F-. See also FLUORIDES.
디플루니살 준비 용품 및 원자재
원자재
준비 용품