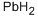납
|
|
납 속성
- 녹는점
- 327.4 °C (lit.)
- 끓는 점
- 1740 °C (lit.)
- 밀도
- 1.00 g/mL at 20 °C
- 굴절률
- 2.881 (632.8 nm)
- 저장 조건
- Store at +5°C to +30°C.
- 용해도
- H2O: 용해성
- 물리적 상태
- 철사
- 색상
- 올리브 녹색 또는 빨간색에서 갈색까지
- Specific Gravity
- 11.288
- 냄새
- 무취가스
- 수소이온지수(pH)
- 3.8 (20°C in H2O)
- Flame Color
- Blue-white
- 비저항
- 20.65 μΩ-cm
- 수용성
- 뜨거운 농축 HNO3, 끓는 농축 HCl, H2SO4 [MER06]와 반응합니다.
- Merck
- 13,5414
- 노출 한도
- TLV-TWA 0.15 mg/m3 as Pb (ACGIH and MSHA), 0.05 mg (Pb)/m3 (OSHA); 10-h TWA 0.1 mg(inorganic lead)/m3 (NIOSH).
- 안정성
- 안정적인. 강한 산화제, 칼륨, 나트륨과 호환되지 않습니다.
- CAS 데이터베이스
- 7439-92-1(CAS DataBase Reference)
- IARC
- 2B (Vol. 23, Sup 7) 1987
- EPA
- Lead (7439-92-1)
안전
- 위험 및 안전 성명
- 위험 및 사전주의 사항 (GHS)
| 위험품 표기 | T,Xi,Xn,N | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 위험 카페고리 넘버 | 61-33-40-48/20-62-36/38-20/22-51/53-50/53-48/20/22-52/53-34-23/24/25 | ||
| 안전지침서 | 53-45-61-36/37-36-26-60-36/37/39 | ||
| 유엔번호(UN No.) | UN 3082 9/PG 3 | ||
| OEB | D | ||
| OEL | TWA: (8-hour) 0.050 mg/m3 [*Note: The REL also applies to other lead compounds (as Pb) -- see Appendix C.] | ||
| WGK 독일 | 3 | ||
| RTECS 번호 | OF7525000 | ||
| TSCA | Yes | ||
| 위험 등급 | 8 | ||
| 포장분류 | III | ||
| HS 번호 | 78011000 | ||
| 유해 물질 데이터 | 7439-92-1(Hazardous Substances Data) | ||
| 독성 | LDLO oral (pigeon) 160 mg/kg PEL (OSHA) 0.05 mg/m3 PEL (action level) 0.03 mg/m3 TLV-TWA (ACGIH) 0.05 mg/m3 (PEL and TLV apply to lead and inorganic lead compounds) |
||
| IDLA | 100 mg Pb/m3 | ||
| 기존화학 물질 | KE-21887 | ||
| 유해화학물질 필터링 | 06-5-8 | ||
| 함량 및 규제정보 | 물질구분: 제한물질; 혼합물(제품)함량정보: 납 및 이를 0.06% 이상 함유한 혼합물 |
납 C화학적 특성, 용도, 생산
개요
Lead was one of the earliest metals used by humans, with possible use extending as far back as the seventh millennium BC, and reaching its preindustrial peak usage during the reign of the Roman Empire, around the beginning of the Common Era.화학적 성질
Lead is a lustrous silvery metal that tarnishes in the presence of air and becomes a dull bluish gray. The chemical symbol, Pb, is derived from plumbum, the Latin word for waterworks, because of lead’s extensive use in ancient water pipes. Lead has four electrons in its valence shell, but only two ionize readily. The usual oxidation state of lead in inorganic compounds is therefore +2 rather than +4. Lead generally forms stable compounds; the most important ones are lead oxide (PbO) and lead carbonate (PbCO3)2. Four stable lead isotopes exist in nature (208Pb , 206Pb , 207Pb, and 204Pb , in order of abundance). Lead mined from deposits of different geologic eras has entered the environment, so that today there are wide variations and extensive mixture of isotopic ratios of lead in commerce and in the environment. These differences in isotopic ratios may sometimes be used as nonradioactive tracers in environmental and metabolism studies.물리적 성질
Lead is a bluish-white, heavy metallic element with properties that are more metal-like thanthe properties of metalloids or nonmetals. Lead can be found in its native state, meaning thatelemental metallic lead can be found in deposits in the Earth’s crust. However, most lead isfirst mined as galena ore (lead sulfide, PbS). The galena is mixed with lead sulfate, lead sulfide,and lead oxide and is then roasted at a high temperature. The air supply is reduced, followedby an increase in heat and the vaporization of the sulfates and oxides of lead, which are drawnoff as gases. The molten lead is then recovered.Lead is only slightly soluble in water. However, it is also toxic. This is the reason lead isno longer used to pipe fresh water into homes. It does not react well with acids, with theexception of nitric acid. Lead’s melting point is 327.46°C, its boiling point is 1,740°C, andits density is 11.342 g/cm3.
Isotopes
There are 47 isotopes of lead, four of which are stable. One of these four is Pb-204, which makes up 1.4% of the natural abundance of lead found on Earth. In reality thisisotope is not stable but has a half-life that is so long (1.4×10+17 years), with some of theancient deposits still existing, that it is considered stable. The other three stable isotopes oflead and their proportion to the total natural abundance are as follows: Pb-206 = 24.1%,Pb-207 = 22.1%, and Pb-208 = 52.4%. All the other isotopes are radioactive.Origin of Name
From the Latin word alumen, or aluminis, meaning “alum,” which is a bitter tasting form of aluminum sulfate or aluminum potassium sulfate.출처
Lead is the 35th most abundant element on Earth. Although it has been found in its freeelemental metal state, it is usually obtained from a combination of the following ores: galena(PbS), anglesite (PbSO4), cerussite (PbCO3), and minum (Pb3O4). Lead ores are locatedin Europe (Germany, Rumania, and France), Africa, Australia, Mexico, Peru, Bolivia, andCanada. The largest deposits of lead in the United States are in the states of Missouri, Kansas,Oklahoma, Colorado, and Montana.One of the most famous mining towns is the high-altitude western city of Leadville,Colorado. The boom started with the gold rush of the 1860s, followed by silver mining in the1870s and 1880s. Today, this city is the site of mining operations not only for lead, but alsofor zinc and molybdenum. At the height of its fame, Leadville had a population of almost50,000 people. Today the population is about 2,500.
Lead is commonly obtained by roasting galena (PbS) with carbon in an oxygen-rich environmentto convert sulfide ores to oxides and by then reducing the oxide to metallic lead.Sulfur dioxide gas is produced as a waste product. Large amounts of lead are also recoveredby recycling lead products, such as automobile lead-acid electric storage batteries. About onethirdof all lead used in the United States has been recycled.
Characteristics
Although lead can be found as a metal in the Earth’s crust, it is usually mined and refinedfrom minerals and ores. Lead is one of the most common and familiar metallic elementsknown. Although it is somewhat scarce, found at proportions of 13 ppm, it is still more prevalentthan many other metals. Lead is noncombustible. and it resists corrosion.When lead, which is very soft, is freshly cut, it has shiny blue-white sheen, which soonoxidizes into its familiar gray color. Lead is extremely malleable and ductile and can be workedinto a variety of shapes. It can be formed into sheets, pipes, buckshot, wires, and powder.Although lead is a poor conductor of electricity, its high density makes it an excellent shieldfor protection from radiation, including X-rays and gamma rays.
용도
Construction material for tank linings, piping, and other equipment handling corrosive gases and liqs used in the manufacture of sulfuric acid, petroleum refining, halogenation, sulfonation, extraction, condensation; for x-ray and atomic radiation protection; manufacture of tetraethyllead, pigments for paints, and other organic and inorganic lead Compounds; bearing metal and alloys; storage batteries; in ceramics, plastics, and electronic devices; in building construction; in solder and other lead alloys; in the metallurgy of steel and other metals.생산 방법
The geometric mean soil lead level is 38 mg/kg. Lead rarely occurs in the elemental state, but exists widely throughout the world in a number of ores, the most common of which is the sulfide, galena. The other minerals of commercial importance are the oxides, carbonate (cerussite), and the sulfate (anglesite), which are much less common.Lead also occurs in various uranium and thorium minerals, arising directly from radioactive decay. Because certain isotopes are concentrated in lead derivatives from such sources, both the atomic weight and the density of the samples vary significantly from normal lead. Lead ores generally occur in nature in association with silver and zinc. Other metals commonly occurring with lead ores are copper, arsenic, antimony, and bismuth. Most of the world production of arsenic, antimony, and bismuth is a result of their separation from lead ores. Commercial lead ores may contain as little as 3% lead, but a lead content of 10% is most common. The ores are concentrated to ≥ 40% lead content before smelting. A variety of mechanical separation processes may be employed for the concentration of lead ores, but the sulfide ores are generally concentrated by flotation processes.
정의
lead: Symbol Pb. A heavy dull greysoft ductile metallic element belongingto group 14 (formerly IVB) ofthe periodic table; a.n. 82; r.a.m.207.19; r.d. 11.35; m.p. 327.5°C; b.p.1740°C. The main ore is the sulphidegalena (PbS); other minor sources includeanglesite (PbSO4), cerussite (PbCO3), and litharge (PbO). Themetal is extracted by roasting the oreto give the oxide, followed by reductionwith carbon. Silver is also recoveredfrom the ores. Lead has a varietyof uses including building construction,lead-plate accumulators, bullets,and shot, and is a constituent of suchalloys as solder, pewter, bearing metals,type metals, and fusible alloys.Chemically, it forms compoundswith the +2 and +4 oxidation states,the lead(II) state being the more stable.일반 설명
Soft silver-bluish white to gray metal.공기와 물의 반응
Insoluble in water.반응 프로필
In the presence of carbon, the combination of chlorine trifluoride with aluminum, copper, Lead, magnesium, silver, tin, or zinc results in a violent reaction [Mellor 2, Supp. 1: 1956]. A solution of sodium azide in copper pipe with Lead joints formed copper and Lead azide, both are detonating compounds [Klotz 1973]. Sodium acetylide becomes pyrophoric when mixed with metals like Lead. Mixtures of trioxane with 60% hydrogen peroxide in contact with metallic Lead when heated detonated. Lead containing rubber ignited in a nitric acid atmosphere. Lead is incompatible with strong oxidants such as: ammonium nitrate, chlorine trifluoride, hydrogen peroxide, etc.건강위험
The acute toxicity of lead and inorganic lead compounds is moderate to low. Symptoms of exposure include decreased appetite, insomnia, headache, muscle and joint pain, colic, and constipation. Inorganic lead compounds are not significantly absorbed through the skin.Chronic exposure to inorganic lead via inhalation or ingestion can result in damage to the peripheral and central nervous system, anemia, and chronic kidney disease. Lead can accumulate in the soft tissues and bones, with the highest accumulation in the liver and kidneys, and elimination is slow. Lead has shown developmental and reproductive toxicity in both male and female animals and humans. Lead is listed by IARC in Group 2B ("possible human carcinogen") and by NTP as "reasonably anticipated to be a carcinogen," but is not considered to be a "select carcinogen" under the criteria of the OSHA Laboratory Standard.
화재위험
Flash point data for Lead are not available, however, Lead is probably non-combustible.인화성 및 폭발성
Lead powder is combustible when exposed to heat or flame.공업 용도
Not only is lead the most impervious of all common metals to x-rays and gamma radiation, it also resists attack by many corrosive chemicals, most types of soil, and marine and industrial environments. Although lead is one of the heaviest metals, only a few applications are based primarily on its high density. The main reasons for using lead often include low melting temperature, ease of casting and forming, good sound and vibration absorption, and ease of salvaging from scrap.With its high internal damping characteristics, lead is one of the most efficient sound attenuators for industrial, commercial, and residential applications. Sheet lead, lead-loaded vinyls, lead composites, and lead-containing laminates are used to reduce machinery noise. Lead sheet with asbestos or rubber sandwich pads are commonly used in vibration control.
Carcinogenicity
Lead and lead compounds are reasonably anticipated to be human carcinogens based on limited evidence of carcinogenicity from studies in humans and sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity from studiesin experimental animals.저장
work with lead dust, molten lead, and lead salts capable of forming dusts should be conducted in a fume hood to prevent exposure by inhalation.비 호환성
Violent reactions of lead with sodium azide, zirconium, sodium acetylide, and chlorine trifluoride have been reported. Reactivity of lead compounds varies depending on structure.폐기물 처리
Excess lead and waste material containing this substance should be placed in an appropriate container, clearly labeled, and handled according to your institution's waste disposal guidelines. For more information on disposal procedures, see Chapter 7 of this volume.납 준비 용품 및 원자재
원자재
준비 용품
납 공급 업체
글로벌( 311)공급 업체
| 공급자 | 전화 | 이메일 | 국가 | 제품 수 | 이점 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yujiang Chemical (Shandong) Co.,Ltd. | +8617736087130 |
catherine@yjchem.com.cn | China | 994 | 58 |
| Henan Tianfu Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-0371-55170693 +86-19937530512 |
info@tianfuchem.com | China | 21622 | 55 |
| career henan chemical co | +86-0371-86658258 +8613203830695 |
sales@coreychem.com | China | 29855 | 58 |
| Hubei xin bonus chemical co. LTD | 86-13657291602 |
linda@hubeijusheng.com | CHINA | 22963 | 58 |
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co.,Ltd. | +86-0551-65418671 +8618949823763 |
sales@tnjchem.com | China | 34563 | 58 |
| Hebei Zhanyao Biotechnology Co. Ltd | 15369953316 +8615369953316 |
admin@zhanyaobio.com | China | 2123 | 58 |
| Shaanxi Dideu Medichem Co. Ltd | +86-029-89586680 +86-18192503167 |
1026@dideu.com | China | 7922 | 58 |
| Henan Alfa Chemical Co., Ltd | +8615838112936 |
alfa10@alfachem.cn | China | 13017 | 58 |
| changzhou huayang technology co., ltd | +8615250961469 |
2571773637@qq.com | China | 9647 | 58 |
| Alfa Chemistry | |
Info@alfa-chemistry.com | United States | 24072 | 58 |