|
|
| Product Name: | Cupric Chloride Dihydrate | | Synonyms: | COPPER (II) CHLORIDE, HYDROUS;COPPER(+2)CHLORIDE DIHYDRATE;Copper(II)chloridedihydrate(99.999%-Cu)PURATREM;Copper(II)chloridedihydrate,99+%(ACS);Copper chloride (CuCl2), dihydrate;copper(ii) chloride dihydrate, acs;copper(ii) chloride hydrate, puratronic;CUPRICCHLORIDE,DIHYDRATE,CRYSTAL,PURIFIED | | CAS: | 10125-13-0 | | MF: | Cl2CuH2O | | MW: | 152.46 | | EINECS: | 600-176-4 | | Product Categories: | metal halide | | Mol File: | 10125-13-0.mol | 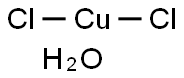 |
| | Cupric Chloride Dihydrate Chemical Properties |
| Melting point | 100 °C (dec.)(lit.) | | density | 2.54 | | vapor density | >1 (vs air) | | storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. | | solubility | 757g/l | | form | Solid | | Specific Gravity | 2.54 | | color | White | | PH | 3.0-3.8 (50g/l, H2O, 20℃) | | Water Solubility | 1150 g/L | | Sensitive | Air Sensitive & Hygroscopic | | Merck | 14,2633 | | Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 1 mg/m3
NIOSH: IDLH 100 mg/m3; TWA 1 mg/m3 | | Stability: | Reacts violently with potassium, sodium. Contact with acetylene can form shock-sensitive acetylides. Hygroscopic - incompatible with moisture. | | InChIKey | ORTQZVOHEJQUHG-UHFFFAOYSA-L | | LogP | -1.380 (est) | | CAS DataBase Reference | 10125-13-0(CAS DataBase Reference) | | EPA Substance Registry System | Cupric chloride dihydrate (10125-13-0) |
| | Cupric Chloride Dihydrate Usage And Synthesis |
| Physical properties | Copper Chloride Dihydrate appears as a green crystalline powder with no odor and occurs naturally as the mineral eriochalcite. It is soluble in Water, Alcohol, and Acetone at ambient conditions.
| | Uses | Cupric Chloride Dihydrate is industrially produced for use as a co-catalyst in the Wacker process.
| | Preparation | Cupric chloride dihydrate can be produced either by the reaction of copper with chlorine or by combining copper carbonate with Hydrochloric Acid.
| | Chemical Reactivity |
When heated to decomposition, cupric chloride dihydrate emits toxic fumes of hydrogen chloride gas and copper oxides.
| | Structure and conformation |
In Cupric Chloride Dihydrate, the copper again adopts a highly distorted octahedral geometry, the Cu(II) centers being surrounded by two water ligands and four chloride ligands, which bridge asymmetrically to other Cu centers.
| | Toxicity |
Cupric Chloride Dihydrate can be toxic. If copper chloride is absorbed, it results in headache, diarrhea, a drop in blood pressure, and fever. Ingestion of large amounts may induce copper poisoning, CNS disorders, and haemolysis.
|
| | Cupric Chloride Dihydrate Preparation Products And Raw materials |
|