- Chloral
-

- $100.00 / 25KG
-
2025-03-21
- CAS:75-87-6
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 5000kg/week
- Chloral
-

- $101.00 / 1KG
-
2023-12-29
- CAS:75-87-6
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: g-kg-tons, free sample is available
|
| | Chloral Basic information |
| Product Name: | Chloral | | Synonyms: | U.N. 2075;metachloral;2,2,2-Trichloroethanal;Acetaldehyde,trichloro-;anhydrouschloral;chloral,anhydrous,inhibited;chloralanhydrous;Cloralio | | CAS: | 75-87-6 | | MF: | C2HCl3O | | MW: | 147.39 | | EINECS: | 200-911-5 | | Product Categories: | API Intermediate | | Mol File: | 75-87-6.mol | 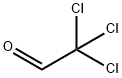 |
| | Chloral Chemical Properties |
| Melting point | -57.5°C | | Boiling point | 94-98 °C | | density | 1.51 g/mL at 20 °C(lit.) | | refractive index | n20/D 1.456 | | Fp | 75°C | | storage temp. | 2-8°C | | solubility | Chloroform (Sparingly), DMSO (Sparingly), Ethyl Acetate (Slightly) | | form | Solid | | pka | 10.04(at 25℃) | | color | Off-White | | Water Solubility | Soluble | | Merck | 13,9699 | | Dielectric constant | 6.7(Ambient) | | Stability: | Stable. Flammable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. | | CAS DataBase Reference | 75-87-6(CAS DataBase Reference) | | IARC | 2A (Vol. 63, 84, 106) 2014 | | NIST Chemistry Reference | Acetaldehyde, trichloro-(75-87-6) | | EPA Substance Registry System | Chloral (75-87-6) |
| | Chloral Usage And Synthesis |
| Description | Chloral is a combustible, oily liquid with a pungent irritating odor. Molecular weight=147.38; Boilingpoint=97-98℃; Flash point=75℃. Hazard Identification(based on NFPA 704 M Rating System): Health 3,Flammability 2, Reactivity 1. Soluble in water. Chloralhydrate is colorless crystals, with characteristic odor.Molecular weight=165.40; Boiling point=97℃ (decomposes); Freezing/Melting point=57-60℃. Hazard Identification (based on NFPA 704 M Rating System): Health 3,Flammability 2, Reactivity 1. Very soluble in water. | | Chemical Properties | colourless oily liquid with a pungent odour | | Chemical Properties | Chloral is a combustible, oily liquid with a
pungent irritating odor. | | Uses | Chloral is used in medicine as a hypnotic. | | Uses | manufacture of chloral hydrate, DDT. | | Production Methods | Chloral can be prepared by action of Cl2 on ethanol, chlorination of acetaldehyde, oxidation of 1,1,2-trichloroethylene in the presence of a catalyst (FeCl3, AlCl3, TiCl4 or SbCl3, and by reaction of CCl4 with formaldehyde. | | Definition | A colorless liquid aldehyde made by chlorinating
ethanal. It was used to make the insecticide
DDT. It can be hydrolyzed to give 2,2,2-
trichloroethanediol (chloral hydrate,
CCl3CH(OH)2). Most compounds with
two –OH groups on the same carbon atom
are unstable. However, in this case the effect of the three chlorine atoms stabilizes
the compound. It is used as a sedative. | | General Description | A colorless oily liquid with a penetrating odor. Reacts with water and denser than water. Contact may irritate skin, eyes and mucous membranes. Toxic by ingestion and inhalation. Used to make pesticides. | | Air & Water Reactions | Chloral is sensitive to exposure to moisture and light. Soluble in water. Chloral reacts with water to form chloral hydrate. | | Reactivity Profile | Chloral reacts with water to form chloral hydrate. Chloral polymerizes under the influence of light and in the presence of sulfuric acid forming a white solid trimer called metachloral. | | Hazard | Toxic by ingestion. Probable carcinogen. | | Health Hazard | INHALATION: Sore throat, shortness of breath, drowsiness, irritation of respiratory tract, unconsciousness. EYES: Redness, pain and blurred vision. SKIN: Redness and pain. INGESTION: Dizziness, drowsiness, nausea, and unconsciousness. Acute hazard: Poison may be fatal if inhaled, swallowed, or absorbed through skin. | | Safety Profile | A poison. Mutation
E data reported. | | Potential Exposure | Chloral is used as an intermediate
in the manufacture of such pesticides as DDT, methoxychlor, DDVP, naled, trichlorfon, and TCA. Chloral is
also used in the production of chloral hydrate; used as
a therapeutic agent with hypnotic, sedative, and narcotic
effects; used in a time prior to the introduction of
barbiturates | | First aid | If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove any contact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts the skin,remove contaminated clothing and wash immediately withsoap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. If thischemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure, begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR if heart actionhas stopped. Transfer promptly to a medical facility. Whenthis chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention.Give large quantities of water and induce vomiting. Do notmake an unconscious person vomit. | | storage | Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Storein a secure poison location. Prior to working with chloralyou should be trained on its proper handling and storage.Protect from light, moisture, air, and acids. DEA regulationsrequire storage in a locked storage area. Store in tightlyclosed containers in a cool, well-ventilated area. Metal containers involving the transfer of this chemical should begrounded and bonded. Drums must be equipped with selfclosing valves, pressure vacuum bungs, and flame arresters.Use only nonsparking tools and equipment, especially whenopening and closing containers of this chemical. Sources ofignition, such as smoking and open flames, are prohibitedwhere this chemical is used, handled, or stored in a mannerthat could create a potential fire or explosion hazard. | | Shipping | UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard
Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical
Name Required. | | Purification Methods | Distil chloral, then dry it by distilling through a heated column of CaSO4. [Beilstein 1 H 616, 1 I 328, 1 II 467, 1 III 2663, 1 IV 3142 for anhydr, 1 IV 3143 for hydrate.] | | Incompatibilities | Chloral hydrate reacts with strong bases
forming chloroform. Contact with acids, or exposure to
light may cause polymerization. Reacts with water, forming
chloral hydrate. Reacts with oxidizers, with a risk of fire or
explosions. | | Waste Disposal | Incineration after mixing with
another combustible fuel; care must be taken to assure complete combustion to prevent phosgene formation; an acid
scrubber is necessary to remove the halo acids produced. |
| | Chloral Preparation Products And Raw materials |
| Raw materials | Ethanol-->Sulfuric acid-->Chlorine-->CHLOROETHANE-->Chloral hydrate-->2,2,2-TRICHLORO-1-ETHOXYETHANOL | | Preparation Products | N,N-Dimethylformamide-->Chloroform-->1,2-Dichloroethane-->Vanillin-->CHLOROETHANE-->Chloromethane-->4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde-->Permethrin-->METHYL 3-(2,2-DICHLOROVINYL)-2,2-DIMETHYL-(1-CYCLOPROPANE)CARBOXYLATE-->Ethyl vanillin-->Cyfluthrin-->Trichloroacetic acid-->Dichlorvos-->ethyl 3-(2,2-dichlorovinyl)-2,2-dimethyl-1-cyclopropanecarboxylate-->Chloral hydrate-->Cypermethrin-->Allethrin-->3-Hydroxy-4-methoxybenzaldehyde-->N,N,N'-TRIMETHYL-1,3-PROPANEDIAMINE-->Dichloroacetic acid-->Trichlorfon-->DIPHENAMID-->4-Ethylbenzoic acid-->2-Fluoro-5-iodotoluene-->2-AMINO-4,6-DIFLUOROBENZOIC ACID-->TRIFORINE-->Trichloroethanol-->2,2,2-Trichloro-1-phenylethyl acetate-->4,4'-DDT-->SODIUM TRICHLOROACETATE-->Mecillinam-->Acetofenate-->Dichloroacetamide-->METHOXYCHLOR-->3-IMINO-2-INDOLINONE-->Tribromoacetaldehyde-->Disperse Yellow 54 |
|