- Bismuth trioxide
-

- $0.00 / 1KG
-
2025-04-16
- CAS:1304-76-3
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 98%min
- Supply Ability: 30tons/month
- Bismuth trioxide
-

- $9.90 / 1KG
-
2025-04-16
- CAS:1304-76-3
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 5tons
- Bismuth trioxide
-

- $0.00 / 1KG
-
2025-04-15
- CAS:1304-76-3
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 500000kg
|
| | Bismuth(III) Oxide Basic information |
| Product Name: | Bismuth(III) Oxide | | Synonyms: | BISMUTH OXIDE, (III) 99.9999%;Bismuth(III) oxideBismuth trioxide;Bismuth(III) oxide, NanoArc BI-7300, 99.5+%;Bismuth(III) oxide, NanoArc|r BI-7300, 99.5+%;Bismuth(III) oxide, Puratronic (metals basis);Bismuth (III) oxide NanoArc? BI-7300;Bi2-O3;Bismite | | CAS: | 1304-76-3 | | MF: | BiO3- | | MW: | 256.98 | | EINECS: | 215-134-7 | | Product Categories: | Bismuth;83: Bi;BismuthMaterials Science;BismuthMetal and Ceramic Science;Catalysis and Inorganic Chemistry;Chemical Synthesis;Nanomaterials;Nanoparticles: Oxides, Nitrides, and Other CeramicsNanomaterials;Nanopowders and Nanoparticle Dispersions;Oxides;BISMUTH, INORGANIC CHEMICAL;bismuth,metal salt, inorganic salt;metal oxide;Inorganics | | Mol File: | 1304-76-3.mol | 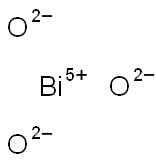 |
| | Bismuth(III) Oxide Chemical Properties |
| Melting point | 825 °C | | Boiling point | 1890°C | | density | 8.9 | | bulk density | 1000kg/m3 | | Fp | 1890°C | | storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. | | solubility | 0.006g/l practically insoluble | | form | powder | | color | Yellow | | Specific Gravity | 8.9 | | Odor | Odorless | | Water Solubility | INSOLUBLE | | Merck | 14,1273 | | crystal system | Monoclinic | | Space group | P21/c | | Lattice constant | | a/nm | b/nm | c/nm | α/o | β/o | γ/o | V/nm3 | | 0.5848 | 0.8166 | 0.751 | 90 | 113 | 90 | 0.3301 |
| | Stability: | Stable. | | InChIKey | KOCGCHBRHPOCBW-UHFFFAOYSA-N | | CAS DataBase Reference | 1304-76-3(CAS DataBase Reference) | | NIST Chemistry Reference | bismuth(III) oxide(1304-76-3) | | EPA Substance Registry System | Bismuth trioxide (1304-76-3) |
| Hazard Codes | Xi,Xn | | Risk Statements | 36/37/38-20/21/22 | | Safety Statements | 26-36/37-36 | | WGK Germany | 2 | | RTECS | EB2984460 | | TSCA | Yes | | HS Code | 2825 90 85 | | Toxicity | LD50 orally in Rabbit: 5000 mg/kg |
| | Bismuth(III) Oxide Usage And Synthesis |
| Chemical Properties | Bismuth(III) oxide is the compound produced by heating the metal, or its carbonate, in air. It is definitely a basic oxide, dissolving readily in acid solutions, and unlike the arsenic or antimony compounds, not amphiprotic in solution, although it forms stoichiometric addition compounds on heating with oxides of a number of other metals. It exists in three modifications, white rhombohedral, yellow rhombohedral, and gray-black cubical. Bismuth(II) oxide, BiO, has been produced by heating the basic oxalate. | | Chemical Properties | Heavy, Yellow Powder | | Physical properties | Yellow monoclinic crystal or powder; density 8.90 g/cm3; melts at 817°C; vaporizes at 1,890°C; insoluble in water; soluble in acids. | | Occurrence | Bismuth trioxide occurs in nature as mineral bismite. The oxide is used in fireproofing of papers and polymers; in enameling cast iron ceramic; and in disinfectants. | | Uses | In disinfectants, magnets, glass, rubber vulcanization; in fireproofing of papers and polymers; in catalysts. | | Uses | Bismuth(III) oxide is used in the preparation of BiFeO3perovskite nanoparticles. It finds use in disinfectants, magnets, glass, rubber, vulcanization, fireproofing papers and polymers and catalysts. Bismuth trioxide brings about the "dragon's eggs" effect in fireworks, as a replacement of red lead. Bismuth(III) compounds are attractive reagents and catalysts in organic synthesis because of their low cost and ease of handling. Bismuth trioxide nanoparticles also play an important role in high energy gas generators. The alpha crystalline form of bismuth(III) oxide has p-type electronic conductivity. | | Preparation | Bismuth trioxide is commercially made from bismuth subnitrate. The latter is produced by dissolving bismuth in hot nitric acid. Addition of excess sodium hydroxide followed by continuous heating of the mixture precipitates bismuth trioxide as a heavy yellow powder. Also, the trioxide can be prepared by ignition of bismuth hydroxide. | | General Description | Bismuth (III) oxide is a yellow, monoclinic crystalline powder. It is insoluble in water and hydroxide solutions but dissolves in acids to form bismuth (III) salts. It can be prepared by heating bismuth in air or by heating hydroxides, carbonates or nitrates of bismuth. | | reaction suitability | reagent type: catalyst
core: bismuth | | Structure and conformation |
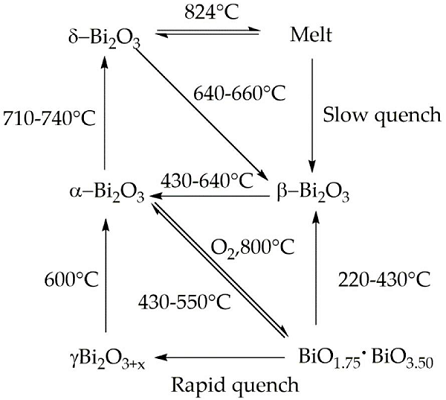
Bismuth(III) Oxides are the deeply studied class of bismuth compounds, and they present four different phases. At room temperature, monoclinic α-Bi2O3 is the common stable phase with a polymeric-distorted layered structure composed of pentacoordinate bismuth atoms enclosed into pseudo-octahedral units. At a temperature higher than 710 °C, the α phase is converted into the cubic δ phase, which has a defective structure with random oxygen vacancies. The β phase and several oxygen-rich forms are closely related to the δ phase. In particular, the vacancy structures of highly defected bismuth oxides are some sites filled with O?2 and Bi(III) and Bi (V) sites. Bismuth oxide γ-phase also shows a cubic structure, but it is highly unstable and hard to synthesize without supporting it onto other oxides or metallic species. The other two polymorphic metastable bismuth oxide phases are known as the ω phase, stable at temperatures higher than 800 °C and the ε phase, isolated in 2006 by Cornei and co-workers[1].
| | References |
[1] Mattia Bartoli, Alberto Tagliaferro, Pravin Jagdale. “A Short Review on Biomedical Applications of Nanostructured Bismuth Oxide and Related Nanomaterials.” Materials 13 22 (2020).
|
| | Bismuth(III) Oxide Preparation Products And Raw materials |
|