- Ammonium carbamate
-

- $0.00 / 1KG
-
2020-02-26
- CAS: 1111-78-0
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99.0%+
- Supply Ability: 100 tons
- AMMONIUM CARBAMATE
-

- $1.00 / 1KG
-
2019-07-10
- CAS:1111-78-0
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 100kg
|
| | AMMONIUM CARBAMATE Basic information |
| Product Name: | AMMONIUM CARBAMATE | | Synonyms: | "anhydride"ofammoniumcarbonate;Ammonium carbaminate;ammoniumaminoformate;AMMONIUM CARBAMATE;AMMONIUM CARBAMATE R. G.;Carbamicacid,monoammoniumsalt;Ammoniumcarbamat;Ammonium carbamate: (Carbamic acid, ammonium salt) | | CAS: | 1111-78-0 | | MF: | CH6N2O2 | | MW: | 78.07 | | EINECS: | 214-185-2 | | Product Categories: | Industrial/Fine Chemicals | | Mol File: | 1111-78-0.mol | 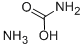 |
| | AMMONIUM CARBAMATE Chemical Properties |
| Melting point | 59-61°C (subl.) | | Boiling point | 58.76°C (estimate) | | density | 1,6 g/cm3 | | bulk density | 750kg/m3 | | vapor pressure | 100 mm Hg ( 26.7 °C) | | refractive index | 1.4616 (estimate) | | storage temp. | 2-8°C | | solubility | 790g/l | | form | Powder | | color | White | | PH | 10 (100g/l, H2O, 20℃) | | explosive limit | 2% | | Water Solubility | Soluble in cold water and ammonium hydroxide. Slightly soluble in alcohol. Insoluble in acetone. | | Merck | 14,507 | | BRN | 3914091 | | Stability: | Stable, but may be moisture sensitive. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong acids, strong bases. | | InChIKey | BVCZEBOGSOYJJT-UHFFFAOYSA-N | | CAS DataBase Reference | 1111-78-0(CAS DataBase Reference) | | EPA Substance Registry System | Ammonium carbamate (1111-78-0) |
| | AMMONIUM CARBAMATE Usage And Synthesis |
| Chemical Properties | Ammonium carbamate is a colorless crystalline
powder or white powder. Ammonia-like odor. The
odor threshold is 5 ppm as NH3 (detection) and 46.8 ppm
as NH3 (recognition). | | Uses | Ammonium carbamate is used in the preparation of fertilizers. It acts as an ammoniating agent. It plays an important role in the formation of carbamoyl phosphate, which is essential for urea cycle and pyrimidines production. In addition to this, it is used in the preparation of trimethylsilyl carbamate. | | Air & Water Reactions | Water soluble. | | Reactivity Profile | AMMONIUM CARBAMATE is a carbamate salt. Carbamates are chemically similar to, but more reactive than amides. Like amides they form polymers such as polyurethane resins. Carbamates are incompatible with strong acids and bases, and especially incompatible with strong reducing agents such as hydrides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen is produced by the combination of active metals or nitrides with carbamates. Strongly oxidizing acids, peroxides, and hydroperoxides are incompatible with carbamates. AMMONIUM CARBAMATE is unstable in an alkaline media . AMMONIUM CARBAMATE is incompatible with the following: Strong oxidizers, strongly alkaline pesticides . Moderate fire and explosion hazards when exposed to heat or flame [USCG, 1999]. | | Hazard | Evolves irritating fumes when heated. | | Health Hazard | INHALATION: Irritating to mucous membranes of respiratory tract. EYES: Irritating. | | Fire Hazard | Behavior in Fire: Moderate fire and explosion hazards when exposed to heat or flame | | Safety Profile | Ammonium carbamate is Poison by intravenous route. See also CARBAMATES | | Shipping | UN2757 Carbamate pesticides, solid, toxic, | | Incompatibilities | Strong bases, strong oxidizers. Keep
away from heat (forms urea), moisture, and direct sunlight. |
| | AMMONIUM CARBAMATE Preparation Products And Raw materials |
|