1-BOC-Piperazine: Applications in Chemical Synthesis and its Preparation Method
Sep 12,2024
General Description
1-BOC-Piperazine is a crucial intermediate in the synthesis of biologically active compounds, including piperazinyl amides and derivatives with dual receptor affinities, such as 5-piperazinyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2(3H)-ones. Traditional preparation methods for 1-BOC-Piperazine involve reactions of anhydrous piperazine with di-tert-butyl carbonate, but these processes can yield low efficiency and high costs. Recent advancements using diethylamine as a starting material provide a more efficient synthetic route involving chlorination, Boc protection, and cyclization, resulting in higher yields exceeding 93.5%, enhanced purity, and reduced environmental impact, making this approach suitable for industrial applications.

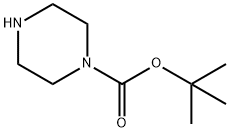
Figure 1. 1-BOC-Piperazine
Applications in Chemical Synthesis
Synthesis of Piperazinyl Amides
1-BOC-Piperazine plays a crucial role in the synthesis of piperazinyl amides, particularly in the preparation of compounds that exhibit significant biological activity. In recent research focused on synthesizing piperazinyl amides of 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid, 1-BOC-Piperazine was utilized as a key intermediate. The process began with the amidation reaction, where 1-BOC-Piperazine was reacted with 3-acetyl-18β-glycyrrhetinic acid under specific conditions. This method eliminated the need for solvents and provided an efficient route to producing compound 8, a vital intermediate in the synthesis. The strategic use of 1-BOC-Piperazine thus enhances the efficiency and efficacy of the entire synthetic process. 1
Dual D2 and 5-HT1A Receptor Affinities with 1-BOC-Piperazine Derivatives
The application of 1-BOC-Piperazine extends beyond piperazinyl amides to the synthesis of novel compounds that possess dual receptor binding affinities, specifically for D2 and 5-HT1A receptors. In one study, 1-BOC-Piperazine was integral for synthesizing 5-piperazinyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2(3H)-ones. The synthesis involved coupling reactions between 1-BOC-Piperazine and various aryl halides. This strategic coupling allowed for the generation of arylpiperazine derivatives, which were then subjected to further reductive amination with biaryl aldehydes. The resulting compounds exhibited promising pharmacological properties, making 1-BOC-Piperazine a critical component in designing therapeutic agents aimed at treating psychiatric disorders. 2
Advancements and Structural Insights
The versatility of 1-BOC-Piperazine is further highlighted by its involvement in structural activity relationship studies that seek to optimize receptor binding affinities. By systematically altering substituents on the piperazine ring, researchers were able to ascertain how different structural modifications impact the interactions with D2 and 5-HT1A receptors. The incorporation of 1-BOC-Piperazine in these studies allows for an expanded understanding of how these compounds function at a molecular level and informs the development of more effective drugs. Additionally, the elucidation of byproducts during the synthesis of compounds containing 1-BOC-Piperazine helps refine the synthetic pathways, ensuring a more streamlined approach in future research efforts. Thus, 1-BOC-Piperazine stands out as a pivotal compound in medicinal chemistry, paving the way for innovative therapeutic solutions.
Preparation Method
Conventional Approaches
The preparation of 1-BOC-Piperazine, an essential intermediate in various pharmaceutical syntheses, can be carried out through two primary methods. The first method involves the selective reaction of anhydrous piperazine with di-tert-butyl carbonate, wherein one nitrogen atom in piperazine is protected, allowing the other amine group to react with the desired functional group. Although this method can produce 1-BOC-Piperazine, the simultaneous protection of both nitrogen atoms results in low yields due to the need for extensive washing to purify the product, significantly increasing operational costs and waste treatment requirements. The second method improves selectivity by reacting piperazine with acetic acid to form a salt, followed by acylation with di-tert-butyl carbonate. While this method enhances the specificity of the N-protection step, it still relies on costly anhydrous piperazine and utilizes toluene, posing health risks to laboratory personnel. 3
Innovative Approach
Recent advancements propose a more efficient synthesis of 1-BOC-Piperazine using diethylamine as a starting material, involving three key steps: chlorination, Boc protection, and cyclization. Initially, diethylamine reacts with a chlorinating agent to produce di(2-chloroethyl)amine. Subsequently, this compound is reacted with Boc anhydride under neutral conditions, generating di(2-chloroethyl) carbamate. In the final step, the carbamate is cyclized using ammonia to yield 1-BOC-Piperazine. This method not only employs readily available raw materials but also operates under mild conditions, resulting in higher yields of over 93.5% and superior purity. Additionally, the process avoids hazardous solvents and reduces costs, making it suitable for industrial production. Overall, this innovative approach demonstrates significant advancements in the preparation method of 1-BOC-Piperazine, enhancing both economic viability and environmental friendliness. 3
References:
[1] DONG CAI. Efficient synthesis of piperazinyl amides of 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid.[J]. Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2020, 16. DOI:10.3762/bjoc.16.73.
[2] ULLAH N. Synthesis and dual D2 and 5-HT1A receptor binding affinities of 5-piperidinyl and 5-piperazinyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2(3H)-ones.[J]. Journal of Enzyme Inhibition and Medicinal Chemistry, 2014, 29 2. DOI:10.3109/14756366.2013.776556.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- The synthesis method of 1-BOC-Piperazine Sep 2, 2024
N-Boc piperazine (1-BOC-Piperazine) belongs to the monosubstituted piperazine compounds.
- Different applications of 1-tert-Butoxycarbonylpiperazine Jun 15, 2022
1-tert-Butoxycarbonylpiperazine is an important chemical product.
1-BOC-Piperazine
57260-71-6You may like
1-BOC-Piperazine manufacturers
- tert-Butyl 1-piperazinecarboxylate
-

- $19.90 / 25kg
- 2025-10-21
- CAS:57260-71-6
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 10 mt
- N-Boc-piperazine
-
- $5.00 / 1KG
- 2025-09-25
- CAS:57260-71-6
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: g-kg-tons, free sample is available
- tert-Butyl 1-piperazinecarboxylate
-

- $0.00 / 25KG
- 2025-08-08
- CAS:57260-71-6
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 50000KG/month