Cephalexin: Pharmacology and Side Effects
Jul 26,2024
General Description
Cephalexin is a widely used antibiotic known for its broad antimicrobial spectrum targeting various infections. Its high oral doses are effective against respiratory, skin, and genitourinary tract infections. Rapid absorption from the upper intestine enhances systemic distribution without penetrating host tissues. Renally cleared, cephalexin maintains therapeutic urine concentrations efficiently. Dosage adjustments are vital for patients with reduced renal function to avoid toxicity. While common side effects like diarrhea can occur, serious effects such as skin blistering, abdominal pain, or allergic reactions necessitate immediate medical attention. Monitoring side effects and consulting healthcare providers for management is essential during cephalexin treatment.

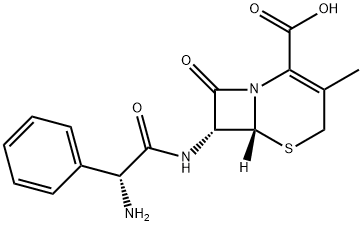
Figure 1. Cephalexin
Pharmacology
Pharmacological Properties
Cephalexin is a highly utilized antibiotic within clinical settings, primarily due to its broad antimicrobial spectrum that effectively targets common pathogens. It is particularly effective against infections in the upper and lower respiratory tracts, skin and soft tissues, and the genitourinary tract. The efficacy of cephalexin stems from its ability to be administered in high oral doses which are not only effective but also minimize gastrointestinal irritation. This aspect of cephalexin's pharmacology makes it a preferred choice for treating a variety of bacterial infections. Additionally, cephalexin is absorbed high in the intestinal tract, ensuring effective systemic distribution while preserving the lower bowel flora, which is crucial for maintaining gastrointestinal health. 1
Absorption and Distribution
The pharmacokinetic profile of cephalexin is notable for its absorption characteristics; it is not absorbed from the stomach but rather efficiently and rapidly from the upper intestine. This rapid absorption contributes to its effectiveness in systemic infections. Once absorbed, cephalexin does not penetrate host tissue cells, a factor which likely contributes to its low incidence of side effects. Furthermore, cephalexin's distribution to tissues is swift, reaching significant concentrations in various tissues except in the spinal fluid and aqueous humour. The drug's low binding affinity to human serum proteins enhances its bioavailability, ensuring that its therapeutic concentrations are maintained in the body fluids without significant degradation or metabolism. 1
Excretion and Dosage Considerations
Cephalexin is characterized by its rapid clearance from the body, predominantly through renal pathways. Approximately 70 to 100% of the administered dose of cephalexin can be recovered in the urine within 6 to 8 hours, indicating efficient renal excretion. The concentrations in the urine significantly exceed the minimum inhibitory concentrations necessary for most urinary tract pathogens, highlighting cephalexin's potency. However, dosage adjustments are crucial for patients with reduced renal function, particularly those with creatinine clearances below 30 ml/min. These adjustments are proportional to the degree of renal impairment, and careful monitoring of renal function is recommended to optimize cephalexin therapy and minimize potential toxicity. 1
Side Effects
Serious Side Effects
Cephalexin, while effective in treating bacterial infections, can also lead to various serious side effects that require immediate medical attention. The most commonly reported side effect is diarrhea, which can sometimes be severe. Rare but critical side effects include abdominal or stomach pain, fever, and vomiting of blood. Skin-related issues such as blistering, peeling, or loosening of the skin are also serious and demand prompt medical evaluation. Other severe reactions encompass yellowing of the eyes or skin, difficulty breathing or swallowing, and unexplained bleeding or bruising. Patients experiencing chest pain, swelling, or paralysis should seek urgent medical care as these symptoms could indicate severe allergic reactions or other complications. 2
Other Side Effects
In addition to its serious effects, cephalexin may induce less severe side effects that typically do not necessitate immediate medical intervention. These can include acid or sour stomach, dry mouth, and heartburn. Some patients may experience muscle pain or stiffness, nervousness, or irregular heartbeats. Itching of the vagina or genital area and pain during sexual intercourse are less common but should be discussed with a healthcare provider if persistent or bothersome. It's important to note that while these side effects are generally manageable and often diminish as the body adjusts to the medication, any concerns should be addressed with a healthcare professional. If you encounter any side effects not listed here or have questions about your medication, consulting your doctor or pharmacist is advisable for proper management and guidance. 2
Reference
1. Griffith RS. The pharmacology of cephalexin. Postgrad Med J. 1983; 59 Suppl 5: 16-27.
2. Cephalexin Side Effects. Drugs. 2023.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Cephalexin: Antimicrobial Activity, Susceptibility, Administration and Dosage, Clinical Uses etc. Mar 22, 2022
Cephalexin (also spelt cefalexin) is a semisynthetic first-generation cephalosporin antibiotic intended for oral administration. Cephalexin was the first oral cephalosporin introduced for clinical use in 1969.
Sodium tert-butoxide is pivotal in organic synthesis for its strong base properties, enhancing non-precious metal catalyst efficiency for sustainable chemistry advancements globally.....
Jul 26,2024APIClindamycin hydrochloride inhibits bacterial protein synthesis, reduces virulence, enhances neutrophil function, but requires careful management due to potential severe adverse effects.....
Jul 26,2024APICephalexin
15686-71-2You may like
- Cephalexin
-

- $0.00 / 1Kg/Bag
- 2024-07-25
- CAS:15686-71-2
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 95%-102%;BP
- Supply Ability: 1000 KG
- Cefalexin
-

- $1.00 / 1g
- 2024-07-16
- CAS:15686-71-2
- Min. Order: 1g
- Purity: 99
- Supply Ability: 20tons
- Cephalexin monohydrate
-

- $10.00 / 1kg
- 2024-06-06
- CAS:15686-71-2
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 98%
- Supply Ability: 20tons