Clindamycin Hydrochloride: Mechanisms of Action and Adverse Effects
Oct 22,2024
Clindamycin is an antibiotic that fights bacteria in the body. Clindamycin is used to treat serious infections caused by bacteria.
Clindamycin is usually available as one of three salts: clindamycin phosphate, clindamycin hydrochloride, or clindamycin nicotinamide. These salt forms are all prodrugs of clindamycin but once inside the body or applied to the skin, they are rapidly converted to active clindamycin by hydrolysis. All three salt forms of clindamycin: clindamycin phosphate, clindamycin hydrochloride, and clindamycin nicotinamide have the same antimicrobial spectrum and effectiveness.

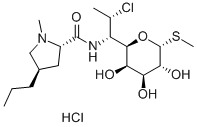
Figure 1. Clindamycin hydrochloride
What is clindamycin hydrochloride?
Clindamycin hydrochloride is a salt of clindamycin that is usually used for oral formulations of clindamycin.
Clindamycin hydrochloride is a prodrug of clindamycin that is rapidly converted to active clindamycin once inside the body.
Clindamycin hydrochloride has the same antimicrobial spectrum and effectiveness as clindamycin phosphate, clindamycin nicotinamide, and clindamycin.
What is Clindamycin Hydrochloride used to treat?
Clindamycin Hydrochloride may be used to treat a wide range of infections, although it should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria to reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and to maintain its effectiveness.
Infections Clindamycin Hydrochloride treats in adults and children include serious:
Infections caused by susceptible anaerobic bacteria
Infections due to susceptible isolates of streptococci, pneumococci, and staphylococci, if a less toxic alternative (such as erythromycin) is not suitable
Lower respiratory tract infections including pneumonia, empyema, and lung abscess caused by susceptible isolates of anaerobes, Streptococcus pneumoniae, other streptococci (except Enterococcus faecalis), and Staphylococcus aureus in adults and children
Skin and skin structure infections caused by susceptible isolates of Streptococcus pyogenes, Staphylococcus aureus, and anaerobes in adults and children
Gynecological infections including endometritis, nongonococcal tubo-ovarian abscess, pelvic cellulitis, and postsurgical vaginal cuff infection caused by susceptible anaerobes in adults and children
Intra-abdominal infections including peritonitis and intra-abdominal abscesses caused by susceptible anaerobic organisms in adults and children
Septicemia caused by susceptible isolates of Staphylococcus aureus, streptococci (except E. faecalis), and susceptible anaerobes in adults and children
Bone and joint infections including acute hematogenous osteomyelitis caused by susceptible isolates of S. aureus and as adjunctive therapy in the surgical treatment of chronic bone and joint infections due to susceptible organisms in adults and children.
Clindamycin Hydrochloride does not adequately penetrate the cerebrospinal fluid and should NOT be used to treat meningitis.
Clindamycin Hydrochloride side effects
The most common clindamycin side effects include:
nausea or vomiting
stomach (abdominal) pain
mild skin rash
vaginal itching or discharge.
Clindamycin Hydrochloride may also cause a metallic taste in your mouth.
Serious side effects and warnings
Clindamycin Hydrochloride carries a Boxed Warning for Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD).
Clindamycin can cause diarrhea, which may range in severity from mild to fatal colitis. Diarrhea associated with clindamycin use is sometimes caused by an overgrowth of dangerous Clostridium difficile bacteria in the large intestine. Seniors especially should be monitored for diarrhea. If you have diarrhea that is watery or bloody, stop using clindamycin and call your doctor. Do not use anti-diarrhea medicine unless your doctor tells you to. Seek urgent medical attention.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Properties, pharmacological effects and clinical applications of clindamycin hydrochloride Jul 25, 2022
Clindamycin inhibits protein synthesis by acting on the 50S ribosomal subunits of bacteria. The colitis resulting from the use of clindamycin has been extensively studied and is now easily manageable.
Supplementation with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate monohydrate can synthesize neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin, maintaining a healthy nervous system.....
Nov 4,2025Biochemical EngineeringTri-tert-butylphosphine tetrafluoroborate catalyzes reactions, like α-arylation and Sonogashira coupling, with stability and sterically controlled precision, crucial for complex molecule synthesis.....
Oct 22,2024APIClindamycin hydrochloride
21462-39-5You may like
Clindamycin hydrochloride manufacturers
- Clindamycin Hydrochloride
-

- $1.00 / 500g
- 2025-12-16
- CAS:21462-39-5
- Min. Order: 300g
- Purity: 99.8%
- Supply Ability: 20 TONS
- Clindamycin hydrochloride
-

- $0.00 / 25KG
- 2025-12-16
- CAS:21462-39-5
- Min. Order: 25KG
- Purity: ≥830μg/mg; USP43
- Supply Ability: 10tons/moonth
- Clindamycin hydrochloride
-

- 2025-12-15
- CAS:21462-39-5
- Min. Order:
- Purity: 0.99
- Supply Ability: