Chondroitin Sulfate: Structure and Biological Functions in Central Nervous System
Jul 4,2024
General Description
Chondroitin sulfate, a glycosaminoglycan found in connective tissues, plays diverse roles within the central nervous system (CNS). It is crucial during neuronal development, myelination, and nodal matrix assembly, enhancing signal transmission and supporting synaptic stability through perineuronal nets. In CNS injuries, chondroitin sulfate's upregulation leads to inhibitory glial scar formation, hindering axonal regrowth and plasticity. Through interactions with growth factors, receptors, and integrins, chondroitin sulfate influences cellular signaling, calcium availability, and neural regeneration. Targeted treatments like Chondroitinase ABC show promise in degrading chondroitin sulfate chains to promote recovery post-injury, highlighting its pivotal role in CNS integrity, development, and recovery processes.

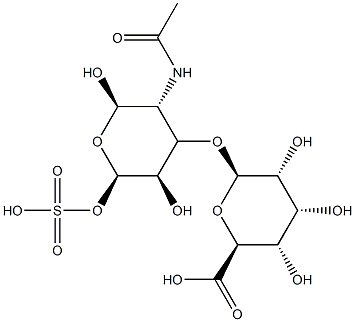
Figure 1. Chondroitin Sulfate
Structure
Dissecting the Molecular Makeup
Chondroitin sulfate is a complex molecule predominantly found in the extracellular matrix of connective tissues. Structurally, chondroitin sulfate consists of long chains of repeating disaccharide units. Each disaccharide unit is formed by two sugars: N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) and glucuronic acid (GlcA). These sugars are linked together through a specific glycosidic linkage, where glucuronic acid is bonded to N-acetylgalactosamine via a β(1 → 3) linkage followed by a β(1 → 4) linkage. This structure forms an unbranched polysaccharide chain. Chondroitin sulfate is categorized as a glycosaminoglycan (GAG), and its chains can include up to 50 disaccharide subunits. A notable feature of chondroitin sulfate is the presence of sulfation, a modification that enhances its functional properties. Sulfate groups are commonly added at specific positions on the GalNAc, particularly the C-4 or C-6 position, and less frequently on the glucuronic acid at the C-3 position.
Functional Enhancements through Sulfation and Attachment to Core Proteins
In the formation of larger structural compounds, chondroitin sulfate chains are attached to core proteins through a linkage tetrasaccharide. This linker consists of xylose, followed by two galactose molecules, and ends with glucuronic acid. The attachment occurs at the serine residues of the core protein, contributing to the formation of proteoglycans such as aggrecan. The size and molecular weight of these proteoglycans can vary significantly, with some reaching a molecular weight of up to 3000 kDa, depending on the number of chondroitin sulfate chains and the length of these chains attached to the core proteins. This structural diversity allows chondroitin sulfate to fulfill various roles in biological processes, particularly in providing structural support and facilitating cellular signaling in connective tissues. 1
Biological Functions in Central Nervous System
Vital Role in CNS Development
Chondroitin sulfate is integral to a wide array of biological functions, particularly within the central nervous system. Its involvement is critical during various stages of development and in response to neural injuries. Chondroitin sulfate forms a major component of proteoglycans, which are known to interact with growth factors, chemokines, and guidance molecules. These interactions influence neuronal growth, support neural plasticity, and control the availability of bioactive molecules to cells, underlining the functional importance of chondroitin sulfate in the CNS. During CNS development, chondroitin sulfate plays a pivotal role in the myelination of axons. This process is essential for proper neuronal function as it enhances the speed and reliability of electrical signal transmission across nerve fibers. Moreover, chondroitin sulfate is involved in assembling the nodal matrix, a crucial component that ensures effective signal conduction. In the adult brain, chondroitin sulfate contributes to the structure and function of perineuronal nets (PNNs). These nets are specialized extracellular matrix structures that envelope neurons and regulate synaptic stability and plasticity, further illustrating the versatility of chondroitin sulfate in neuronal regulation and protection.
Adaptive Functions in Response to Injury
In instances of CNS injury, such as trauma or disease-induced damage, chondroitin sulfate's role shifts towards an inhibitory function. The upregulation of chondroitin sulfate-rich proteoglycans forms glial scars, which can obstruct axonal regrowth, hinder plasticity, and inhibit overall neural regeneration. This response, while initially protective, can lead to long-term deficits. Chondroitin sulfate-targeting treatments, such as with Chondroitinase ABC, aim to degrade these glycosaminoglycan chains, showing promise in reducing scar formation and promoting recovery and functional regeneration post-injury. Chondroitin sulfate's influence extends to molecular interactions that regulate cellular responses crucial for neural function. It potentially affects calcium availability, which is vital for neuron signaling. Chondroitin sulfate may also interact with specific receptors like contactin-1 and receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase σ, and modulate integrin activation, all of which are important for cell adhesion and signaling pathways. These interactions underscore chondroitin sulfate's comprehensive role in modulating neural cell behavior, guiding neuronal growth, and influencing synaptic plasticity.
Overall, chondroitin sulfate is indispensable in maintaining CNS integrity, facilitating development, and enabling recovery processes. 2
Reference
1. Mikami T, Kitagawa H. Biosynthesis and function of chondroitin sulfate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013; 1830(10): 4719-4733.
2. Kwok JC, Warren P, Fawcett JW. Chondroitin sulfate: a key molecule in the brain matrix. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012; 44(4): 582-586.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Biomedical applications of chondroitin sulfate-based composites Jun 26, 2023
Chondroitin sulfate-based composites have several potential biomedical applications due to their inherent properties such as biocompatibility, biodegradability, and ability to mimic the matrix.
- Pharmacological effects of chondroitin sulfate Jul 1, 2021
Chondroitin sulfate (CS, hereinafter referred to as CS) is a type of sulfated glycosaminoglycan, which exists in the connective tissues of humans and animals, mainly distributed in cartilage, bone, tendon, muscle membrane.
- Uses and Safety concerns of Chondroitin sulfate Oct 16, 2019
Chondroitin sulfate is a chemical that is normally found in cartilage around joints in the body. Chondroitin sulfate is usually manufactured from animal sources, such as shark and cow cartilage.
Lithium tetrafluoroborate improves solid-state battery performance and safety, but its toxicity necessitates careful handling and compliance to mitigate health risks.....
Jul 4,2024APIChondroitin sulfate
9007-28-7You may like
Chondroitin sulfate manufacturers
- Chondroitin Sulfate / CS
-

- $0.00 / 1Kg/Bag
- 2024-07-03
- CAS:9007-28-7
- Min. Order: 1Kg/Bag
- Purity: 99% up, High Density
- Supply Ability: 20 tons
- Chondroitin sulfate
-

- $0.00 / 1kg
- 2024-06-18
- CAS:9007-28-7
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 0.99
- Supply Ability: 50000kg
- Chondroitin Sulfate
-

- $0.00 / 1KG
- 2024-06-17
- CAS:9007-28-7
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%, USP
- Supply Ability: 5,000KG