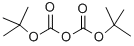
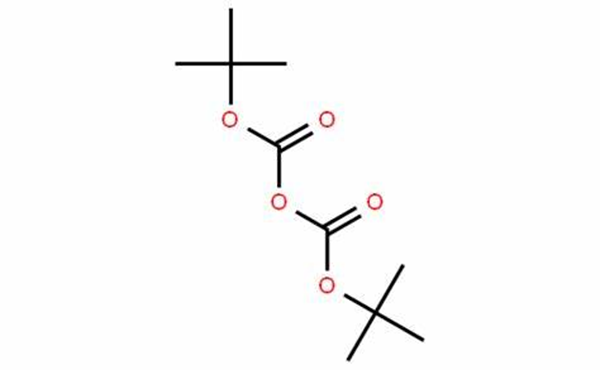
Di-tert-butyl dicarbonate: a versatile carboxylating reagent
Apr 15,2024
Di-tert-butyl dicarbonate (Boc-anhydride) is a widely used reagent in organic chemistry. It is an extremely efficient reagent to introduce the tert-butoxycarbonyl (BOC) protecting group for the amine functionality. It is also an efficient tert-butoxycarbonylating agent for alcohols and thiols. Boc-anhydride has been used for the conversion of amines to corresponding isocyanates, carbamates and urea derivatives. In some cases, it is used as an apparent dehydrating agent when it reacts with carboxylic acids, primary nitroalkanes, or with certain hydroxyl groups. It’s easy to introduce and cleave as a protecting group add to its value as a versatile reagent.
Compounds possessing tert-butyl carboxylate functionality are
useful building blocks in organic synthesis, preferably due to their
ease of de-protection to the corresponding carboxylic acid under
acidic medium. Esterification of a carboxylic acid with tert-butanol,
tert-butyl bromide or isobutylene is the most common method of
synthesis of a tert-butyl ester. As part of a research program aimed
at developing a one step organic transformation to achieve tertbutyl acetates of some nitrogen heterocycles, we decided to explore
the possibility of using Boc-anhydride as a carboxylating agent.
Hongmei Li and Jaume Balsells have demonstrated the synthesis of
tert-butyl benzoates from haloarenes bearing multiple halogen
substituents via selective metal–halogen exchange with lithium trin-butylmagnesium ate complex, followed by reacting with Bocanhydride. Interestingly the broad scope and synthetic utility of
this reagent as a carboxylating agent has not been explored for
substrates that could not produce triarenemagnesium ate complexes. Herein, we report Boc-anhydride as a mild and efficient
carboxylating reagent by demonstrating the synthesis of tert-butyl
aryl acetates, substituted di-tert-butyl malonates and tert-butyl
benzoates by trapping the carbon nucleophiles generated by a nonnucleophilic base such as LDA with Boc-anhydride.
Results and discussion
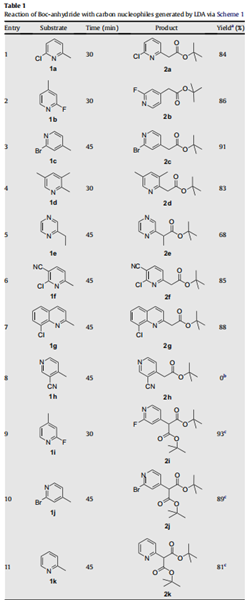
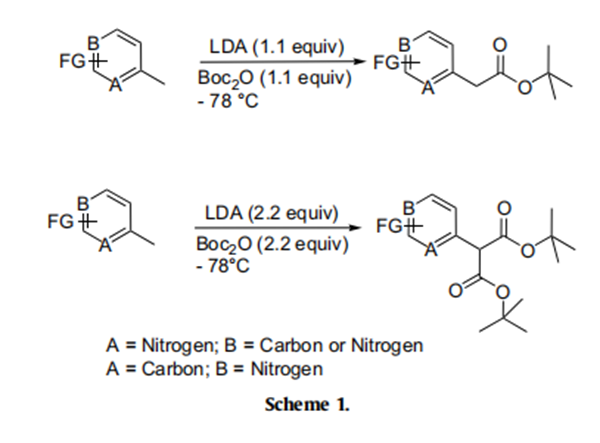
Our initial investigations were aimed at scrutinizing the feasibility of trapping Boc-anhydride with carbanions generated by LDA.
Accordingly, the nitrogen heterocycle 1a was treated with a freshly
prepared solution of LDA (1.1 equiv) in THF at - 78℃ for 0.5 h and
to the resulting solution was added Boc-anhydride (1.1 equiv). To
our satisfaction, the product formed was found to be the expected
tert-butyl acetate 2a in 84% isolated yield (entry 1, Table 1). Subsequently, we investigated the scope of this reagent as a tert-butyl
carboxylating agent on other nitrogen heterocycles (entries 2–11,
Table 1) having an active methyl group as shown in Scheme 1. This
procedure was found to exhibit excellent scope, and the reaction
condition was found to be optimal as we could obtain most of the
products in good to excellent yields as depicted in Table 1. Surprisingly, 3-cyano-4-picoline did not react with LDA under this
reaction conditions and only starting material was recovered from
the reaction mixture (entry 8, Table 1). While pyridine and quinoline substrates provided good yield of products, moderate yield was obtained for pyrazine (entry 5, Table 1). Interestingly, the use of
excess of LDA (2.2 equiv) and Boc-anhydride (2.2 equiv) led to the
formation of di-tert-butyl malonates (entries 9–11, Table 1). It further emphasizes the synthetic utility of Boc-anhydride in producing
the tert-butyl malonates of substrates possessing an active methyl
group.
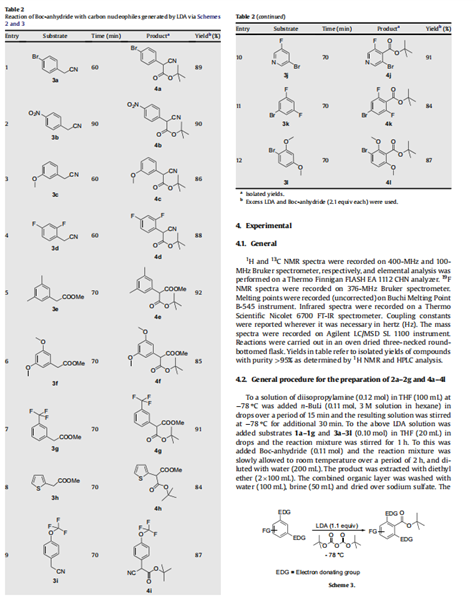
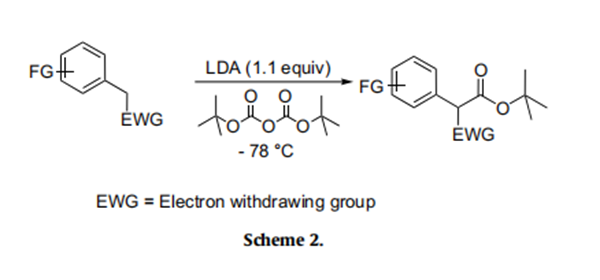
Having achieved the initial objective of tert-butyl acetate synthesis using Boc-anhydride as a carboxylating reagent, we proceeded to study the generality and efficacy of this method. With the optimal reaction conditions in hand, subsequently, we investigated the scope of this reaction on active methylene compounds (Scheme 2). A variety of active methylene compounds bearing multiple functional groups such as halo, methoxy, nitro, alkyl and tri- fluoromethoxy (entries 1–9, Table 2) participated effectively in this ester synthesis. Substrates having multiple reactive centres (entries 4 and 6, Table 2) were also studied. It is interesting to note that substrates having two reactive centers such as 3d and 3f gave exclusively 4d and 4f at - 78℃. Further, unlike in the case of active methyl substrates, the use of excess of LDA (2.2 equiv) and Bocanhydride (2.2 equiv) failed to introduce a second tert-butyl carboxylate group on substrates possessing an active methylene group. As described in Table 2, this reaction was also found to be useful for the synthesis of tert-butyl benzoates (Scheme 3). Commercially available electron rich substrates such as 3j–3k were reacted with Boc-anhydride under these conditions to provide the corresponding tert-butyl benzoates in good yields. The tolerance of functional group such as bromo under these conditions adds a synthetic advantage to this protocol (entries 10–12, Table 2).
Conclusion
In summary, carbanions generated by a non-nucleophilic base (LDA) were effectively trapped with di-tert-butyl dicarbonate to provide the corresponding tert-butyl carboxylates in high yields. This reaction represents another useful way to prepare a variety of tert-butyl aryl acetates, di-tert-butyl aryl malonates and tert-butyl benzoates and highlights the synthetic utility of di-tert-butyl dicarbonate as a versatile carboxylating reagent.
References:
[1] JOHN KALLIKAT AUGUSTINE. Di-tert-butyl dicarbonate: a versatile carboxylating reagent[J]. Tetrahedron, 2009. DOI:10.1016/j.tet.2008.10.089.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Di-tert-butyl dicarbonate: Application, synthesis and toxicity Apr 14, 2023
Di-tert-butyl dicarbonate is referred to as Boc anhydride, which can be used in the protection and deprotection of amines.
- The synergistic effect of di-tert-butyl dicarbonate Dec 20, 2019
Di-tert-butyl dicarbonate ( Boc2O) is mainly used to introduce a tert-butoxycarbonyl (Boc) protecting group to protect an amino group (especially an amino group of an amino acid), and is one of the commonly used reagents for organic synthes
Supplementation with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate monohydrate can synthesize neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin, maintaining a healthy nervous system.....
Nov 4,2025Biochemical EngineeringManganese sulfide (MnS) is semiconductor material, undergoes a transition to an antiferromagnetically (AFM) ordered phase below room temperature. This article will introduce its crystal structure.....
Apr 15,2024Inorganic chemistryDi-tert-butyl dicarbonate
24424-99-5You may like
Di-tert-butyl dicarbonate manufacturers
- Di-tert-butyl dicarbonate
-

- 2025-12-15
- CAS:24424-99-5
- Min. Order:
- Purity: 0.99
- Supply Ability:
- Di-tert-butyl dicarbonate
-

- $0.00 / 50kg
- 2025-12-15
- CAS:24424-99-5
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 1
- Di-tert-butyl dicarbonate
-

- $20.00 / 1kg
- 2025-12-11
- CAS:24424-99-5
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 100 mt