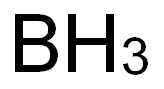Is boron nonmetal?Is it good for health?
Mar 12,2024
Boron is a trace element that is naturally present in many foods and available as a dietary supplement. It is a structural component of plant cell walls and is required for plant growth, pollination, and seed formation.

Chemical properties
Elemental boron is rare and poorly studied because the pure material is extremely difficult to prepare. Most studies of boron involve samples that contain small amounts of carbon. The chemical behavior of boron resembles that of silicon more than aluminum. Crystalline boron is chemically inert and resistant to attack by boiling hydrofluoric or hydrochloric acid. When finely divided, it is attacked slowly by hot concentrated hydrogen peroxide, hot concentrated nitric acid, hot sulfuric acid, or a hot mixture of sulfuric and chromic acids.
Boron and Health
Boron is an nonmetal. Boron has been consumed for menstrual cramps and boric acid has been used vaginally for yeast infections, but evidence is limited.
Boron seems to affect the way the body handles other minerals such as calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus. It also seems to increase estrogen levels post-menopause. Boric acid, a common form of boron, can kill yeast that causes vaginal infections. Boron may have antioxidant effects.
People commonly use boron for boron deficiency and vaginal yeast infections. It is also used for athletic performance, menstrual cramps, osteoarthritis, osteoporosis, and many other conditions, but there is no good scientific evidence to support many of these uses.
Preparation
The earliest routes to elemental boron involved the reduction of boric oxide with metals such as magnesium or aluminum. However, the product is almost always contaminated with borides of those metals. Pure boron can be prepared by reducing volatile boron halides with hydrogen at high temperatures. Ultrapure boron for use in the semiconductor industry is produced by the decomposition of diborane at high temperatures and then further purified by the zone melting or Czochralski processes.
The production of boron compounds does not involve the formation of elemental boron but exploits the convenient availability of borates.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Boron: Chemical information, Major minerals, Chemical reactions and Major uses May 27, 2024
Boron exist as two natural stable isotopes, 11B (80.1%) and 10B (19.9%).
- Boron: An Element with Exceptional Chemistry Apr 7, 2024
Unlike its group 13 neighbors, boron exhibits behaviors and forms compounds that are not quite metallic and yet not fully nonmetallic.
- How many valence electrons does boron have? Mar 12, 2024
Boron has 3 valence electrons. The number of electrons in the outermost (or) valence shell layer of an atom is called valence electrons.
1,7-Dimethylxanthine is a naturally occurring alkaloid compound that can enhance alertness and reduce drowsiness.....
Feb 27,2025APIYes, the current study suggests that ursolic acid (UA) significantly ameliorates the progression of obesity.....
Mar 12,2024Plant extracts