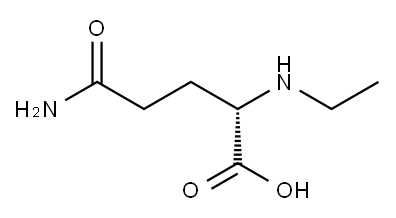
L-Theanine: Food Sources, Effects and Benefits, Side Effects
Apr 12,2024
L-Theanine is a natural non-protein amino acid extracted from green tea. It has a wide range of pharmacological effects including: antioxidant, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, hypolipidemic, promotes sedation and soothing, regulates human brain function and immunity, and anti-tumour. Due to its multiple functional health properties, it is widely used in the food supplement, pharmaceutical, nutraceutical and cosmetic industries.
Food Sources of L-Theanine
The main source of L-Theanine is found in tea plants, such as black and green tea. L-Theanine is also found in certain types of mushrooms. In the tea plant, L-theanine is the major amino acid, occurring
in every organ except the fruit. The L-theanine content changes
with tea cultivar and location. The root is the chief site of L-theanine synthesis, from which it is translocated to the leaf in
the xylem sap. L-Theanine is biosynthesized by the ligation of
theanine synthetase (EC 6.3.1.6) from ethylamine and L-glutamic acid in the tea plant (step 8 in Figure 1). In
addition, L-theanine can be hydrolyzed by theanine amidohydrolase (EC 3.5.1.65), producing L-glutamic acid and ethylamine (step 9 in Figure 1), which is similar to that catalyzed by
glutamine amidohydrolase (EC 3.5.1.2).
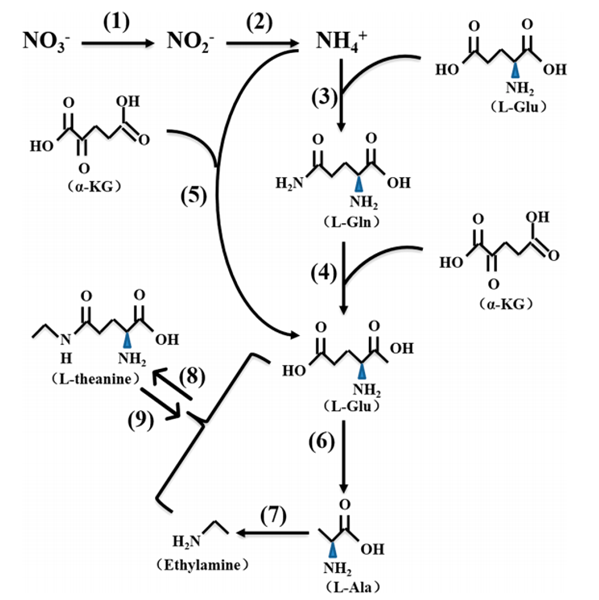
Enzymes involved are (1) nitrate reductase, (2) nitrite reductase, (3) glutamine synthetase, (4) glutamate synthase, (5) glutamate dehydrogenase, (6) alanine transaminase, (7) alanine decarboxylase, (8) theanine synthetase, and (9) theanine amidohydrolase. L-Ala, L-alanine; L-Glu, L-glutamic acid; L-Gln, L-glutamine; α- KG, 2-oxoglutarate.
Effects and Benefits
L-Theanine has the unique flavour and potential health benefits of tea. It enhances relaxation, relieves anxiety and stress, improves concentration and learning ability, among other effects related. In addition, it may prevent certain cancers and cardiovascular diseases, promote weight loss and enhance the performance of the immune system. Specific effects are seen in the following areas:
Antioxidant
L-Theanine is an amino acid analogue of glutamic acid, while (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) in tea has an extremely strong oxidative effect similar to dopamine. Studies have shown that l-theanine not only has an antioxidant effect by itself, but it also effectively inhibits copper-promoted EGCG oxidation, hydroxyl radical generation, and DNA damage; and reduces the formation of quinone-protein (i.e., quinone-protein) adducts associated with EGCG oxidation. In mice treated with EGCG, l-theanine significantly increased hepatic EGCG levels and reduced hepatic quinone protein levels and liver damage. Therefore, it is also used in cosmetic formulations for improving skin condition and alleviating skin aging.
Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory
L-Theanine regulates immune function in vivo by inhibiting the expression of inflammatory factors. Studies have shown that L-Theanine regulates immune function and glutamine metabolism by competitively binding to cannabinoid receptor 1. In E44813 stressed rats, L-Theanine promotes the nuclear translocation of p-ERK1/2 and ultimately GS by inhibiting the activity of cannabinoid receptor 1. At the same time, it reduces the expression of pro-inflammatory factor TNF-alpha and produces an anti-inflammatory effect in rats.
Antibacterial
It was found that different concentrations of L-Theanine had a significant inhibitory effect on the growth and sporulation ability of TEA grey blight disease. It inhibits pathogen of tea grey blight disease mainly by affecting amino acid metabolism, carbohydrate metabolism and biosynthetic processes related to cell structure of pathogenic fungi .
Improving obesity
L-Theanine has a potential role in combating diet-induced obesity in mice, the study found. Intraperitoneal injection of L-Theanine improved obesity, glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity, and reduced plasma triglycerides, total cholesterol and free fatty acids in high-fat diet-fed mice, which may be associated with induced WAT browning.
Relieving stress and anxiety
Tea is thought to have the ability to promote feelings of calm and soothing, which has been linked to the fact that L-Theanine competes with glutamate for receptors and exerts a relaxing effect across the blood-brain barrier. In addition, it significantly increases activity in the alpha band, which can relax the mind without causing drowsiness. Studies reporting suffering from generalised anxiety disorder and taking antidepressants reported higher sleep satisfaction after taking 450-900 mg of L-Theanine daily for 8 weeks.
Neuroprotection
Treatment of Parkinson's model mice with L-Theanine showed that it was effective in reducing the immunohistochemical features of Parkinson's disease, particularly Lewy bodies and alpha-synuclein, and increased the number of tyrosine hydroxylase-positive cells. L-Theanine also ameliorated MPTP-induced motor dysfunction in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease, as evidenced by the transthyrette test.L-Theanine treatment resulted in a reduction in the levels of several pro-inflammatory mediators overexpressed in Parkinson's disease (i.e., TNF-alpha, IL-6, COX-2, and MAC-1), and significant reductions in the levels of the pro-apoptotic proteins Bcl-2, caspase-3, p53, and PARP-1 were significantly reduced. L-theanine targets several proteins associated with WNT/β-catenin signalling, namely β-catenin, WNT-3a, WNT-5a, TCF1/TCF7 and LEF1, via the MAPK pathway (p-JNK, p-ERK and p-p38), thereby modulating the oxidative stress-related factors SOD-1, GST and NOX-4.This suggests that L-Theanine has neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects and can be used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease.
Side Effects
There have been no definite reports of side effects or toxicity associated with L-Theanine. L-Theanine is derived from natural sources and is well tolerated orally and safe for short-term use. Doses of up to 900 mg per day have been used safely for 8 weeks. It is not known if L-theanine is safe for prolonged use. It may cause mild side effects such as headache, dizziness, stomach upset, excitability or rapid heartbeat, which may be related to the caffeine in the tea consumed.
References:
[1] LIJIE JIA, JINSONG ZHANG*; l-Theanine Inhibits (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate Oxidation via Chelating Copper[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2022. DOI:10.1021/acs.jafc.2c01379.
[2] LIU A, LIN L, XU W, et al. l-Theanine regulates glutamine metabolism and immune function by binding to cannabinoid receptor 1†[J]. Food & Function, 2021. DOI:10.1039/D1FO00505G.
[3] ZHEN CHEN. From Tea Leaves to Factories: A Review of Research Progress in l-Theanine Biosynthesis and Production[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2021. DOI:10.1021/acs.jafc.0c06694.
[4] ZHANG Y, WANG F, WANG L, et al. The Response of Growth and Transcriptome Profiles of Tea Grey Blight Disease Pathogen Pestalotiopsis theae to the Variation of Exogenous L-Theanine[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2024. DOI:10.3390/ijms25063493.
[5] WAN-QIU PENG. l-Theanine Activates the Browning of White Adipose Tissue Through the AMPK/α-Ketoglutarate/Prdm16 Axis and Ameliorates Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice.[J]. Diabetes, 2021. DOI:10.2337/db20-1210.
[6] LIWEN WANG . How does the tea L-theanine buffer stress and anxiety[J]. Food Science and Human Wellness, 2022. DOI:10.1016/j.fshw.2021.12.004.
[7] KHOIRUNNISA RATIH . L-Theanine alleviates MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease by targeting Wnt/β-catenin signaling mediated by the MAPK signaling pathway[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2023. DOI:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.12.030.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Effectiveness of L-Theaninede Sep 27, 2022
L-Theanine is the major amino acid found in Camellia sinensis, the source of green tea. L-theanine is reported to increase brain levels of dopamine, serotonin, GABA, nerve growth factor, and brain-derived neurotrophic factor.
- What is L-theanine good for?Benefits And Use,Dosage Sep 17, 2020
L-theanine is an amino acid. The human body does not produce this compound, and it is not essential for humans. Green tea, black tea, and certain types of mushroom naturally contain L-theanine.
- What are the benefits of L-theanine? Oct 15, 2019
L-theanine is an amino acid found most commonly in tea leaves and in small amounts in Bay Bolete mushrooms. It can be found in both green and black tea.
1,7-Dimethylxanthine is a naturally occurring alkaloid compound that can enhance alertness and reduce drowsiness.....
Feb 27,2025APIAntimony (III) telluride (Sb2Te3) is a well-studied and experimentally confirmed typical 3D layered topological insulators. This article will show its crystal structure.....
Apr 12,2024Inorganic chemistryL-Theanine
3081-61-6You may like
- L-theanine
-

- $0.00 / 25Kg/Bag
- 2025-04-27
- CAS:3081-61-6
- Min. Order: 2Kg/Bag
- Purity: 99% up, High Density
- Supply Ability: 20 tons
- L-Theanine
-

- $0.00 / 1KG
- 2025-04-27
- CAS:3081-61-6
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: ≥98% HPLC
- Supply Ability: 1000KG
- L-Theanine
-

- $0.00 / 1Kg/Bag
- 2025-04-25
- CAS:3081-61-6
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 98%-102%
- Supply Ability: 10 TONS