Lurasidone Hydrochloride: Pharmacodynamics, Clinical Effectiveness and Adverse Effects
Apr 10,2024
General Description
Lurasidone Hydrochloride, a second-generation antipsychotic, exerts its pharmacodynamic effects through complex interactions with multiple receptors in the central nervous system. It acts as an antagonist for dopamine D2L, 5-HT2A, 5-HT7, and noradrenergic α2C receptors, and a partial agonist for 5-HT1A receptors. Clinical studies show inconclusive results on QT interval changes, indicating a favorable cardiac safety profile. In terms of clinical effectiveness, lurasidone demonstrates significant improvement in depressive symptoms, overall severity, response rate, and remission compared to certain antipsychotics. Adverse effects include common AEs like nausea and somnolence, with lower weight gain compared to some antipsychotics. Monitoring adverse effects is crucial for patient safety.

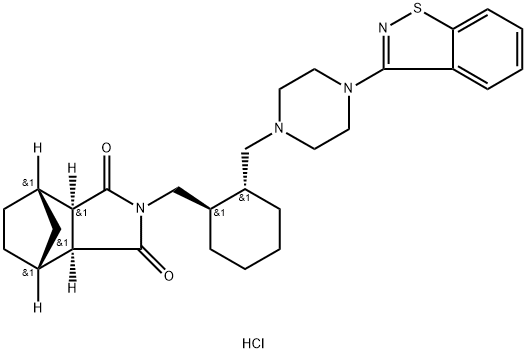
Figure 1. Lurasidone hydrochloride
Pharmacodynamics
Lurasidone Hydrochloride, a second-generation antipsychotic, exerts its pharmacodynamic effects primarily through its interaction with various receptors in the central nervous system. In assay systems using rat, guinea pig, and human recombinant cells, Lurasidone Hydrochloride has been found to act as an antagonist with high affinity for dopamine D2L, 5-HT2A, 5-HT7, and noradrenergic α2C receptors, as well as a partial agonist with high affinity for 5-HT1A receptors. Additionally, Lurasidone Hydrochloride exhibits somewhat lower binding affinity for noradrenergic α1 and α2A receptors, dopamine D3 and D4.4 receptors, and low affinity for dopamine D1, serotonin 5-HT2C, L-type Ca2+ channel, and voltage-gated Na+ channel. In functional studies and animal behavioral models, these receptor-binding affinities have been supported by evidence of corresponding functional activities. Notably, Lurasidone Hydrochloride inhibits the hERG channel current, with implications for QTc prolongation in conscious dogs at certain dosing levels. However, clinical studies in patients with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder showed inconclusive results regarding QT interval changes, with no apparent dose–response relationship observed. Importantly, no patients experienced clinically significant QT interval absolute values or changes from baseline, providing reassurance about the drug's cardiac safety profile. Furthermore, the active metabolites of Lurasidone Hydrochloride, ID-14283 and ID14326, exhibit similar receptor-binding affinities to the parent compound, indicating potential contributions to its overall pharmacodynamic profile. In conclusion, lurasidone hydrochloride's pharmacodynamics are characterized by its complex interaction with multiple receptors, highlighting its unique mechanism of action and potential implications for both therapeutic efficacy and safety in the treatment of psychiatric conditions. 1
Clinical Effectiveness
Lurasidone hydrochloride has been the subject of extensive research to assess its clinical effectiveness in treating depressive symptoms and overall severity, as well as its impact on response rate, remission, adherence, psychiatric hospitalization, all-cause hospitalization, and all-cause discontinuation. In terms of depressive symptoms measured by MADRS score, a network meta-analysis (NMA) revealed that lurasidone demonstrated statistically significant improvement compared to aripiprazole and ziprasidone. However, it showed no significant difference compared to olanzapine and quetiapine. Similarly, in assessing overall severity using CGI-BP-S score, Lurasidone hydrochloride exhibited statistically significant improvement compared to aripiprazole and ziprasidone, with no significant difference compared to olanzapine and quetiapine. Moreover, Lurasidone hydrochloride was associated with a statistically significant improvement in response rate and remission rate compared to aripiprazole and ziprasidone, and it showed no significant difference compared to olanzapine and quetiapine. Additionally, Lurasidone hydrochloride was found to have a significantly higher adherence rate compared with olanzapine, risperidone, and quetiapine. It was also associated with significantly lower psychiatric and all-cause hospitalization rates compared to certain antipsychotics. Notably, the differences in all-cause discontinuation rates between Lurasidone hydrochloride and other atypical antipsychotics were not statistically significant. However, it’s important to consider these findings in the context of specific patient populations and individual treatment responses when considering the use of lurasidone hydrochloride in clinical practice. 2
Adverse Effects
Adverse effects of Lurasidone Hydrochloride are an important consideration in clinical practice. Common adverse events (AEs) with an incidence of 5% or more during lurasidone therapy include nausea, somnolence, headache, dizziness, akathisia, fatigue, insomnia, tremor, Parkinsonism, nasopharyngitis, anxiety, depression, and extrapyramidal symptoms. Notably, lurasidone was associated with less weight gain compared to olanzapine and quetiapine, but not significantly different from aripiprazole. In terms of specific adverse effects, lurasidone showed a significantly lower incidence of somnolence compared to quetiapine and ziprasidone, but similar rates to aripiprazole and olanzapine. Differences in extrapyramidal symptoms between lurasidone and aripiprazole or quetiapine were not statistically significant. Regarding severe AEs, the proportion of patients reporting at least one severe AE was around 10.9% in monotherapy and ranged from 4.9% to 10.5% in adjunctive lurasidone therapy. These findings underscore the importance of monitoring and managing adverse effects when prescribing Lurasidone Hydrochloride to ensure patient safety and treatment efficacy. 2
Reference
1. Greenberg WM, Citrome L. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Lurasidone Hydrochloride, a Second-Generation Antipsychotic: A Systematic Review of the Published Literature. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2017;56(5):493-503.
2. Tran K, Ford C. Lurasidone Hydrochloride for Bipolar Disorder: A Review of Clinical Effectiveness, Cost-Effectiveness, and Guidelines. Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; February 20, 2020.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- The application of Lurasidone hydrochloride Jan 10, 2023
The lurasidone hydrochloride, with the CAS No: 367514-88-3, is also known as Lurasidonhydrochloride. This chemical’s molecular formula is C28H36N4O2S and molecular weight is 492.684. It is an atypical
Carboxin, a key fungicide in agriculture, inhibits fungal growth effectively while Delftia sp. HFL-1 degrades it and its metabolite, offering sustainable solutions.....
Apr 10,2024APIThe molecular backbone of lactoferrin is characterized by its ability to tightly bind iron ions, a property central to many of its biological functions.....
Apr 10,2024APILurasidone hydrochloride
367514-88-3You may like
Lurasidone hydrochloride manufacturers
- Lurasidone hydrochloride
-
- $2.00 / 1kg
- 2024-07-22
- CAS:367514-88-3
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 200KG/M
- Luracidon hydrochloride
-
- $2.00 / 1kg
- 2024-07-22
- CAS:367514-88-3
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 200KG
- Lurasidone hydrochloride
-

- $6.00 / 1kg
- 2024-07-10
- CAS:367514-88-3
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: More than 99%
- Supply Ability: 2000KG/Month