N,N-Dimethylethylenediamine: A Key Chemical Compound in Modern Applications
Sep 2,2024
Introduction
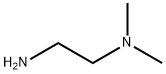
N, N-Dimethylethylenediamine, often abbreviated as N, N-DIMETHYLETHYLENEDIAMINE, is an organic compound that belongs to the class of aliphatic amines. Its chemical formula is C4H12N2, and its structural formula is represented as (CH3)2NCH2CH2NH2. This colorless liquid has a distinctive amine-like odor and is soluble in water, alcohol, and others, making it a versatile compound in various chemical reactions.
N, N-DIMETHYLETHYLENEDIAMINE has gained prominence due to its dual functionality: it acts as a ligand in coordination chemistry and as a catalyst or reagent in organic transformations. Its use is widespread in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and polymer industries, making it a compound of significant interest to chemists and chemical engineers.

Figure 1 Characteristics of N, N-Dimethylethylenediamine
Properties of N, N-Dimethylethylenediamine
Solubility: Soluble in water, alcohols, and most organic solvents
Vapor Pressure: 33.2 mmHg at 25°C
N, N-DIMETHYLETHYLENEDIAMINE's low boiling point and high vapor pressure indicate that it is volatile and should be handled with care, especially in poorly ventilated areas. Its solubility in various solvents enhances its utility in diverse chemical reactions, particularly in those involving polar solvents.
Chemical Composition and Structure
The chemical structure of N, N-DIMETHYLETHYLENEDIAMINE features two amine groups attached to an ethylene backbone. One of the nitrogen atoms is secondary, as it is bonded to two methyl groups (dimethyl), while the other nitrogen atom remains primary, connected to two hydrogen atoms. This bifunctional nature makes N, N-DIMETHYLETHYLENEDIAMINE an excellent ligand in coordination chemistry, as it can donate lone pairs from both nitrogen atoms to metal centers.
In addition to its role as a ligand, N, N-DIMETHYLETHYLENEDIAMINE's chemical composition allows it to act as a nucleophile in various organic reactions, such as alkylation, acylation, and Michael additions. Its reactivity stems from the electron-donating properties of the methyl groups attached to the nitrogen atom, which enhance the nucleophilicity of the amine.
Applications of N, N-Dimethylethylenediamine
N, N-DIMETHYLETHYLENEDIAMINE's unique structure and reactivity make it a valuable compound in numerous chemical processes. Some of the primary applications of N, N-DIMETHYLETHYLENEDIAMINE include:
Ligand in Coordination Chemistry: N, N-DIMETHYLETHYLENEDIAMINE is frequently used as a bidentate ligand in coordination complexes, particularly with transition metals. Its ability to form stable chelates makes it a popular choice in catalytic processes, such as cross-coupling reactions (e.g., Suzuki, Heck, and Sonogashira reactions).
Catalyst in Organic Synthesis: N, N-DIMETHYLETHYLENEDIAMINE serves as a catalyst or co-catalyst in various organic transformations, including C-H activation, cycloadditions, and asymmetric synthesis. Its dual amine functionality allows it to facilitate reactions that require base catalysis or nucleophilic activation.
Pharmaceutical Industry: In drug discovery and development, N, N-DIMETHYLETHYLENEDIAMINE is utilized in the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Its ability to act as a ligand in metal-catalyzed reactions and as a reagent in organic synthesis makes it a versatile tool for medicinal chemists.
Agrochemicals: N, N-DIMETHYLETHYLENEDIAMINE is employed in the production of agrochemicals, such as herbicides, fungicides, and insecticides. Its role as a building block in the synthesis of biologically active compounds contributes to the development of new and effective agricultural products.
Polymer Chemistry: In polymer chemistry, N, N-DIMETHYLETHYLENEDIAMINE is used as a chain extender or cross-linking agent in the production of polyurethane foams, coatings, and adhesives. Its reactivity with isocyanates and other electrophiles allows for the formation of durable and flexible polymer networks.
Water Treatment: N, N-DIMETHYLETHYLENEDIAMINE is also used in water treatment processes as a chelating agent to remove heavy metals from wastewater. Its ability to form stable complexes with metal ions helps in the purification of industrial effluents.
Storage and Handling of N, N-Dimethylethylenediamine
Given its volatile nature and strong odor, N, N-DIMETHYLETHYLENEDIAMINE requires careful handling and storage to ensure safety and maintain its stability. The following guidelines are recommended for the proper storage and handling of N, N-DIMETHYLETHYLENEDIAMINE:
Storage Conditions: N, N-DIMETHYLETHYLENEDIAMINE should be stored in a cool, well-ventilated area, away from sources of ignition, heat, and direct sunlight. It should be kept in tightly sealed containers made of materials resistant to amines, such as stainless steel or high-density polyethylene (HDPE). Storing N, N-DIMETHYLETHYLENEDIAMINE at temperatures below its boiling point is recommended to minimize evaporation and reduce the risk of vapor buildup.
Handling Precautions: When handling N, N-DIMETHYLETHYLENEDIAMINE, appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) should be worn, including gloves, safety goggles, and lab coats. In poorly ventilated areas, a respirator may be necessary to avoid inhalation of vapors. Any spills or leaks should be addressed immediately, as N, N-DIMETHYLETHYLENEDIAMINE's volatility can lead to rapid vaporization and potential inhalation hazards.
Disposal: Waste N, N-DIMETHYLETHYLENEDIAMINE should be disposed of by local environmental regulations. It should not be released into the environment, as it may pose a risk to aquatic life. Chemical waste disposal companies can guide the appropriate methods for handling N, N-DIMETHYLETHYLENEDIAMINE waste.
Conclusion
N, N-Dimethylethylenediamine is a versatile and valuable compound in the field of chemistry, with applications ranging from organic synthesis to industrial catalysis. Its dual functionality as a ligand and nucleophile makes it a powerful tool for chemists working in various disciplines, including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and polymer science. However, due to its volatile nature and strong odor, proper storage and handling practices are essential to ensure safety and maintain its efficacy in chemical processes.
![]() Reference
Reference
[1] Nikitina V M, Nesterova O V, Kokozay V N, et al. N, N-Dimethylethylenediamine in direct and direct template syntheses of Cu (II)/Cr (III) complexes[J]. Polyhedron, 2009, 28(7): 1265-1272.
[2] McDonald T M, D'Alessandro D M, Krishna R, et al. Enhanced carbon dioxide capture upon incorporation of N, N′-dimethylethylenediamine in the metal–organic framework CuBTTri[J]. Chemical Science, 2011, 2(10): 2022-2028.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
P-Toluenesulfonamide (p-TSA) is a vital chemical compound widely used across various industries, particularly in the chemical and pharmaceutical sectors.....
Sep 2,2024APIAfatinib dimaleate is very soluble in water and aqueous buffers with a pH of 1 to 6 (> 50 mg/ mL). The free base is strongly lipophilic (log P = 4.7) but is strongly pH dependent.....
Sep 2,2024DrugsN,N-Dimethylethylenediamine
108-00-9You may like
N,N-Dimethylethylenediamine manufacturers
- 2-Dimethylaminoethylami
-

- $10.00 / 1KG
- 2024-08-21
- CAS:108-00-9
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 10 ton
- 1,1-Dimethylethylenediamine
-

- $1.00 / 1KG
- 2024-04-19
- CAS:108-00-9
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99.91%
- Supply Ability: 200000
- 2-dimethylaminoethylami
-

- $0.00 / 1Kg
- 2024-04-08
- CAS:108-00-9
- Min. Order: 1Kg
- Purity: 99.9%
- Supply Ability: 200tons