Pregabalin vs. Gabapentin: similarities and differences
Jun 7,2024
Similarities of Pregabalin vs. Gabapentin
Pregabalin and Gabapentin are both classified as anticonvulsants or antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) and are both used to treat partial seizures. Pregabalin and Gabapentin are also both approved for the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia in adults. They are also considered first-line medications for the treatment of neuropathic pain following spinal cord injury, and there was no difference in efficacy between the two medications for pain, anxiety, or sleep.
Differences of Pregabalin vs. Gabapentin
However, Pregabalin and Gabapentin are different in terms of indications, dosage used, clinical efficacy and side effects. Below is a brief list about the differences between the two:
Indications
Pregabalin is approved for the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia in adults, neuralgia due to diabetic peripheral neuropathy, neuralgia due to spinal cord injury, fibromyalgia and partial seizures in adults and children as young as 1 month old.
Gabapentin, in addition to being approved for the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia in adults, is also approved for the treatment of partial seizures in adults and children 3 years of age and older, and is often used as an add-on medication for epilepsy. In addition, it is sometimes used off-label for treatments such as prevention of pain conditions (trigeminal neuralgia and neuropathy) and treatment of restless leg syndrome.
Dosage
The table below compares the forms and strengths available for pregabalin and gabapentin:

Pregabalin Dosages
Below are examples of the typical dosages for pregabalin in adults:
Postherpetic neuralgia: 75–150 mg two times daily or 50–100 mg three times daily; maximum dosage of 600 mg daily
Nerve pain due to diabetic neuropathy: 50–100 mg three times daily; maximum dosage of 600 mg daily
Fibromyalgia: 75–150 mg twice daily; maximum 450 mg daily
Nerve pain due to spinal cord injury: 75–300 mg two times daily; maximum 600 mg daily
Adjunct treatment of partial seizures: 150–600 mg, divided into two or three doses throughout the day
Gabapentin Doses
Here are some examples of the typical doses for gabapentin in adults:
Postherpetic neuralgia: 300–600 mg three times a day; maximum dosage of 1,800 mg daily
Adjunct treatment of partial seizures: 300–1,200 mg three times daily; maximum dosage of 3,600 mg daily
Clinical Efficacy
Clinical studies have shown Pregabalin to be more effective than Gabapentin in treating partial seizures in patients with epilepsy. However, it was not better than Gabapentin at reducing seizure frequency. Yet another study found Gabapentin to be superior to Pregabalin in the treatment of chronic sciatica. Pregabalin was found to be more effective in reducing pain in a small clinical trial, while Gabapentin was more effective in reducing symptoms of anxiety, insomnia and fatigue in adults suffering from low back pain.
Side Effects
Common side effects of Pregabalin and Gabapentin include dizziness, dry mouth, eye problems, nausea, drowsiness and oedema. However, Pregabalin is more likely to cause weight gain. And both have symptoms of serious adverse reactions that may produce suicidal thoughts or behaviour, respiratory depression, heart problems and severe allergic reactions.
References:
[1] JACQUELINE FRENCH. Adjunctive pregabalin vs gabapentin for focal seizures: Interpretation of comparative outcomes.[J]. Neurology, 2016. DOI:10.1212/WNL.0000000000003118.
[2] YILMAZ B, GOKTEPE A, TAN A. Gabapentin vs. Pregabalin for the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain in Patients with Spinal Cord Injury: A Crossover Study Spinal Kord Yarali Hastalarin Nöropatik Ağri Tedavisinde Gabapentin ve Pregabalin Etkinliğinin Karşilaştirilmasi: Çapraz Çalişma[C]. 1900. DOI:10.5152/tftrd.2015.79069.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Is Pregabalin a painkiller? What types of pain can it be used to treat? Jan 14, 2025
Pregabalin is a novel central nervous system modulator that is used to treat peripheral and central neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia, knee OA pain, and to relieve acute postoperative pain.
- Side effects of taking pregabalin Feb 18, 2024
Pregabalin is a drug that has been approved for different indications across the world, including the treatment of pain syndromes.
- Uses and Preparation of Pregabalin Jul 5, 2022
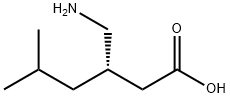
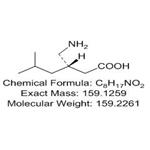
Pregabalin is a 3-isobutyl derivative of gamma-amino butyric acid (GABA) with anti-convulsant, anti-epileptic, anxiolytic, and analgesic activities
Supplementation with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate monohydrate can synthesize neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin, maintaining a healthy nervous system.....
Nov 4,2025Biochemical Engineeringβ-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) is an electron carrier as it carries electrons from hydride from one region of the cell to another.....
Jun 7,2024APIPregabalin
148553-50-8You may like
- Pregabalin
-
- $0.00 / 10mg
- 2025-12-16
- CAS:148553-50-8
- Min. Order: 10mg
- Purity: 90%+
- Supply Ability: 10g
- Pregabalin
-

- $100.00 / 50kg
- 2025-12-16
- CAS:148553-50-8
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 5000Ton
- Pregabalin
-

- $1.00 / 1kg
- 2025-12-16
- CAS:148553-50-8
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 0.99
- Supply Ability: 1000 kg