Tetracaine Hydrochloride: A Comprehensive Overview
Jul 12,2024
Introduction
Tetracaine hydrochloride, commonly known as amethocaine, is a potent local anesthetic widely used in medical practice. As a member of the ester-type local anesthetics, Tetracaine hydrochloride is known for its high potency and long duration of action, making it invaluable in various clinical applications.

Figure 1 Characteristics of Tetracaine hydrochloride
Properties
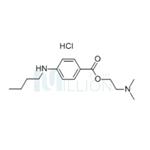
Tetracaine hydrochloride (C15H24N2O2·HCl) is an off-white crystalline powder that is highly soluble in water and alcohol. It has a molecular weight of 300.82 g/mol. The compound exhibits strong local anesthetic properties due to its ability to block sodium ion channels in nerve cells, thereby preventing the initiation and conduction of nerve impulses. This action results in a reversible loss of sensation in the applied area.
Tetracaine hydrochloride's melting point ranges from 147 to 150 degrees Celsius, and it has a pKa of 8.5, indicating it is predominantly ionized at physiological pH. Its chemical stability is relatively high, though it should be protected from light and moisture to prevent degradation. In solution, Tetracaine hydrochloride is typically used at concentrations ranging from 0.05% to 0.5% depending on the intended use and required depth of anesthesia.
Main Components
The main active ingredient in Tetracaine hydrochloride formulations is Tetracaine itself. This compound is synthesized through a series of chemical reactions involving the esterification of p-aminobenzoic acid with 2-dimethylaminoethanol. The resulting ester is then reacted with hydrochloric acid to yield the hydrochloride salt, enhancing its solubility and stability for pharmaceutical use.
Additionally, Tetracaine hydrochloride formulations may contain excipients such as preservatives, pH adjusters, and isotonic agents to maintain the solution’s efficacy and safety. Common additives include sodium chloride, to adjust osmolarity, and benzalkonium chloride, to prevent microbial contamination. The presence of these excipients ensures the preparation is suitable for various routes of administration, including topical, ophthalmic, and spinal.
Applications
Tetracaine hydrochloride is utilized in a wide range of medical applications due to its potent anesthetic effects. It is most commonly used in:
Topical Anesthesia: Tetracaine hydrochloride is often applied to mucous membranes, such as the eyes, nose, throat, and urinary tract, to provide localized pain relief during diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Its rapid onset and prolonged duration make it ideal for minor surgical interventions, dental procedures, and the management of superficial skin conditions.
Spinal Anesthesia: In spinal anesthesia, Tetracaine hydrochloride is injected into the subarachnoid space of the spinal cord. This application is particularly useful for surgeries involving the lower abdomen, pelvis, and lower extremities. The drug provides profound anesthesia with minimal systemic absorption, reducing the risk of systemic toxicity.
Ophthalmology: Tetracaine hydrochloride is extensively used in eye surgeries and procedures. Its rapid onset of action and significant numbing effect facilitate procedures such as cataract extraction, corneal scraping, and intraocular pressure measurement. It also aids in the alleviation of discomfort during contact lens fittings and other diagnostic tests.
Dermatology: In dermatological practices, Tetracaine hydrochloride is applied to the skin to relieve pain from conditions such as sunburn, insect bites, and minor cuts. It is also used in combination with other anesthetics in formulations designed for more invasive procedures, like laser treatments and biopsies.
Storage Methods
Proper storage of Tetracaine hydrochloride is crucial to maintain its efficacy and safety. The drug should be stored at controlled room temperature, typically between 20 to 25 degrees Celsius. It must be kept in a tightly closed container to protect it from moisture and light, both of which can degrade the active compound.
For solutions, refrigeration at 2 to 8 degrees Celsius can help extend the shelf life, but the solution should not be frozen as this can cause precipitation of the active ingredient. It is also important to ensure that the solution is clear and free from particulate matter before use. Any discolored or precipitated solution should be discarded.
Tetracaine hydrochloride in its powdered form should be stored in a desiccator to prevent moisture absorption. When preparing solutions, it is recommended to use sterile techniques to avoid contamination. Solutions should be used within a specified time frame, typically within 24 hours, to ensure maximum potency and safety.
![]() References
References
[1] Changez M, Chander J, Dinda A K. Transdermal permeation of tetracaine hydrochloride by lecithin microemulsion: in vivo[J]. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 2006, 48(1): 58-66.
[2] Srivastava A, Dey J, Ismail K. Interaction of tetracaine hydrochloride with sodium deoxycholate in aqueous micellar phase and at the surface[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2015, 466: 181-188.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Tetracaine hydrochloride: mechanism of action and activity Jun 21, 2023
Tetracaine hydrochloride is a versatile compound that exhibits multiple pharmacological activities, including potent antitumor effects, antibacterial properties, and long-acting local anesthetic.
- What is Tetracaine Hydrochloride used for? Sep 28, 2020
Tetracaine hydrochloride is also known as ropivacaine hydrochloride, pantocaine, pantocaine and four ropivacaine hydrochloride. It is easily soluble in water and ethanol, but insoluble in ether, benzene.
- Tetracaine hydrochloride – a local anesthetic widely used in clinic Dec 30, 2019
Tetracaine hydrochloride is a local anesthetic used to numb the eyes, nose, or throat. It may also be used before starting an intravenous to decrease pain from the procedure. Typically it is applied as a liquid to the area.
1-Methylimidazole, also known as N-methylimidazole, is a heterocyclic organic compound with the molecular formula C4H6N2.....
Jul 12,2024APIFerrocene, one of the most iconic compounds in the field of organometallic chemistry, has fascinated chemists since its discovery in the early 1950s.....
Jul 12,2024APITetracaine hydrochloride
136-47-0You may like
Tetracaine hydrochloride manufacturers
- Tetracaine hydrochloride
-
- $1.00 / 1kg
- 2024-08-08
- CAS:136-47-0
- Min. Order: 0.10000000kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 200KG
- Tetracaine hydrochloride
-

- $40.00 / 1box
- 2024-08-07
- CAS:136-47-0
- Min. Order: 1box
- Purity: 99.9+
- Supply Ability: 2000box
- Tetracaine hydrochloride
-

- $40.00 / 1box
- 2024-08-07
- CAS:136-47-0
- Min. Order: 1box
- Purity: 99.9+
- Supply Ability: 2000box




