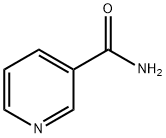
Uses and Correlational research of Niacinamide
Oct 24,2019
There are two forms of vitamin B3. One form is niacin, the other is niacinamide. Niacinamide is found in many foods including yeast, meat, fish, milk, eggs, green vegetables, beans, and cereal grains. Niacinamide is also found in many vitamin B complex supplements with other B vitamins. Niacinamide can also be formed in the body from dietary niacin.

Uses
Niacinamide is taken by mouth for preventing vitamin B3 deficiency and related conditions such as pellagra. It is also taken by mouth for acne, diabetes, oral cancer, osteoarthritis, and many other conditions. However, there is no good scientific evidence to support these uses.
Niacinamide is also applied to the skin for acne, eczema, and other skin conditions. There is also no good evidence to support these uses.
A disease cause by niacin deficiency (pellagra). Niacinamide is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for these uses. Niacinamide is sometimes preferred over niacin because it does not cause "flushing," (redness, itching and tingling), a side effect of niacin treatment.
Correlational research
Acne. Early research shows that taking tablets containing niacinamide and other ingredients for 8 weeks improves skin appearance in people with acne. Other research shows that applying a cream containing niacinamide improves the appearance of skin in people with acne.
Diabetes. Some research shows that taking niacinamide might help prevent the loss of insulin production in children and adults at risk for type 1 diabetes. It might also prevent the loss of insulin production and reduce the dose of insulin needed by children recently diagnosed with type 1 diabetes. However, niacinamide does not seem to prevent the development of type 1 diabetes in at-risk children. In people with type 2 diabetes, niacinamide seems to help protect insulin production and improve blood sugar control.
High levels of phosphate in the blood (hyperphosphatemia). High blood levels of phosphate can be caused by reduced kidney function. In people with kidney failure who are on hemodialysis and have high levels of blood phosphate, taking niacinamide seems to help decrease phosphate levels when taken with or without phosphate binders.
Head and neck cancer. Research shows that taking niacinamide while receiving radiotherapy and a type of treatment called carbogen might help control tumor growth and increase survival in some people with cancer of the larynx. Taking niacinamide while receiving radiotherapy and carbogen seems to benefit people with cancer of the larynx who are also anemic. It also seems to help people who have tumors that are deprived of oxygen.
Skin cancer. Taking niacinamide seems to help prevent new skin cancer or precancerous spots (actinic keratosis) from forming in people with a history of skin cancer or actinic keratosis.
Osteoarthritis. Taking niacinamide seems to improve joint flexibility and reduce pain and swelling in people with osteoarthritis. Also, some people with osteoarthritis who take niacinamide might need to take fewer pain medications.
Pharmacologic action
Niacinamide can be made from niacin in the body. Niacin is converted to niacinamide when it is taken in amounts greater than what is needed by the body. Niacinamide is easily dissolved in water and is well-absorbed when taken by mouth.
Niacinamide is required for the proper function of fats and sugars in the body and to maintain healthy cells.Unlike niacin, niacinamide has no beneficial effects on fats and should not be used for treating high cholesterol or high fat levels in the blood.
Safety concerns
When taken by mouth: Niacinamide is LIKELY SAFE for most adults. Unlike niacin, niacinamide does not cause flushing. However, niacinamide might cause minor side effects such as stomach upset, gas, dizziness, rash, itching, and other problems.
When doses of over 3 grams per day of niacinamide are taken, more serious side effects can happen. These include liver problems or high blood sugar.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- How to synthesize Nicotinamide? Feb 28, 2024
The steps are to dissolve 3-cyanopyridine in alcohol, add water and a catalyst to perform a hydrolysis reaction and obtain nicotinamide through post-processing of the reaction product.
- Topical Pharmacology and Uses in Skin of Nicotinamide Mar 9, 2022
Aging is caused by many different factors such as the loss of deep bone structure and subcutaneous fat, in addition to oxidative skin damage caused by cumulative sun exposure.
- Nicotinamide - Medical Applications and Role in Skin Diseases Mar 9, 2022
Niacinamide, also known as nicotinamide, is an increasingly popular component of topical cosmeceuticals. It has shown a wide variety of benefits such as improving epidermal barrier function and therefore inflammatory dermatoses.
Manganese is a chemical element with the symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is not found as a free element in nature; it is often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of indus....
Oct 24,2019Inorganic chemistryTo elucidate possible reasons for the recalcitrance of 2-chlorotoluene, the metabolism of chloromethylcatechols, formed after dioxygenation and dehydrogenation by Ralstonia sp. strain PS12 tetrachlorobenzene dioxygenase and chlorobenzene di....
Oct 24,2019Organic ChemistryNicotinamide
98-92-0You may like
- Nicotinamide
-

- $10.00 / 1g
- 2024-07-23
- CAS:98-92-0
- Min. Order: 10g
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 10000kg
- Nicotinamide
-
- $22.00 / 1kg
- 2024-07-22
- CAS:98-92-0
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 0.99
- Supply Ability: 100kg
- Nicotinamide
-

- $0.00 / 1kg
- 2024-07-22
- CAS:98-92-0
- Min. Order: 0.10000000149011612kg
- Purity: ≥99%
- Supply Ability: 20tons