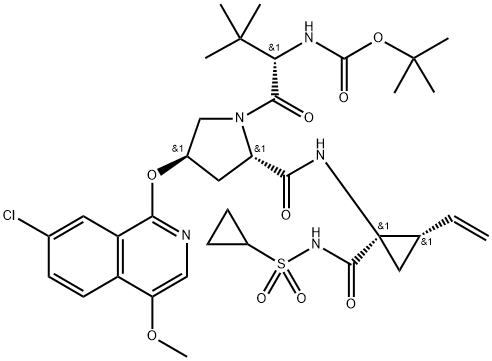
Asunaprevir synthesis
- Product Name:Asunaprevir
- CAS Number:630420-16-5
- Molecular formula:C35H46ClN5O9S
- Molecular Weight:748.29

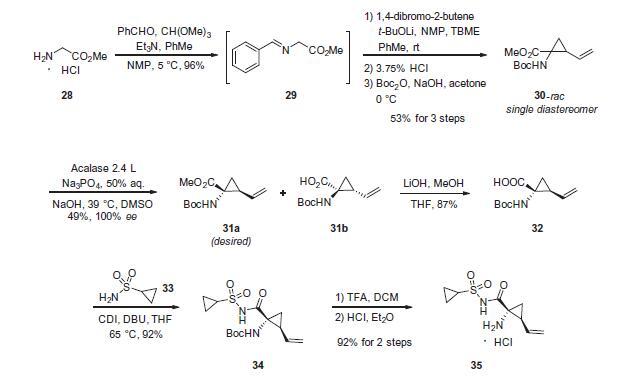
Although the synthesis of asunaprevir vinyl cyclopropane subunit 35 has been described by researchers at BMS, it is interesting to note that this subunit, or structural derivatives of 35, have been found within a number of other antiviral drugs, particularly those which target inhibition of NS3 protease as its mechanism of action. For example, researchers at Boehringer-Ingelheim have described a scale synthesis of (1R,2S)-1-amino-2-vinylcyclopropane carboxylic acid (des-N-tert-butoxycarbonyl (Boc) 32; also referred to as ‘vinyl-ACCA’) as a means to incorporate this subunit into that company’s antiviral agent BILN 2061. A macrocyclic version of this same cyclopropane-containing system is found in the antiviral agents paritaprevir hydrate (XXVII) developed by Enanta and Abbvie, and a saturated version in vaniprevir (XXXVII) developed by Merck and described later in this review (vide infra). The preparation of 32 described by Beaulieu and co-workers was performed on pilot-plant scale and the details surrounding the conversion of 32 to 35 are described by the BMS patent. Beginning with commercially available methyl glycine HCl (28), condensation with benzaldehyde in the presence of a dehydrating reagent (trimethyl orthoformate) and base led to the transient imine 29. This underwent a highly diastereoselective alkylation reaction whereby treatment with lithium t-butoxide followed by subjection to 1,4- dibromo-2-butene facilitated an SN2–SN20 reaction. Subsequent acidification and Boc protection resulted in 30-rac as a racemate that existed as a single diastereomer having the vinyl and the ester groups in a cis configuration. The authors postulate that the lithium enolate intermediate which forms upon the initial alkylation binds the proximal bromine atom which accounts for the stereoselectivity of the reaction. Next, selective saponification of the undesired enantiomer 31b took place via treatment with acalase 2.4 L, which is a remarkably versatile and relatively inexpensive enzyme capable of resolving a wide variety of racemic esters,49 under basic conditions. This enzymatic resolution returned a 49% yield of the desired ester 31a (theoretical 50%), and a simple aqueous workup removed the undesired acid 31b. Methyl ester 31a was then saponified using methanolic lithium hydroxide to give 32, which was subsequently coupled with cyclopropanesulfonamide 33 to deliver 34 in excellent yield. Next, removal of the Boc group using TFA followed by salt formation with ethereal HCl delivered the key cyclopropane subunit 35.
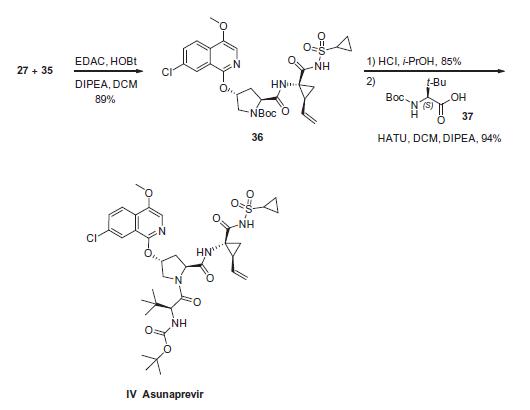
Cyclopropyl amine 35 was subjected to proline derivative 27 under conventional amide bond-forming conditions. This was followed by removal of the pyrrolidine nitrogen Boc group with acid and subsequent coupling with N-Boc-3-methyl valine (37) to deliver asunaprevir (IV) in good yield for each of these steps.
1169846-35-8
4 suppliers
inquiry
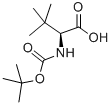
62965-35-9
443 suppliers
$6.00/5g

630420-16-5
144 suppliers
$60.00/1mg
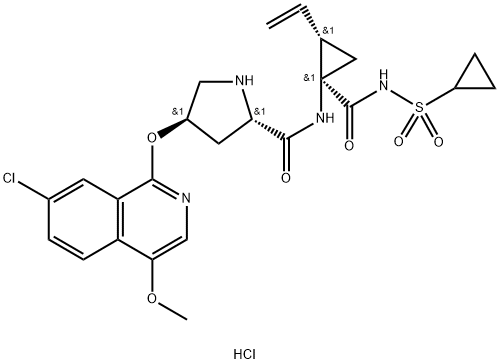
![(2S,4R)-4-[(7-Chloro-4-methoxy-1-isoquinolinyl)oxy]-N-[(1R,2S)-1-[[(cyclopropylsulfonyl)amino]carbonyl]-2-ethenylcyclopropyl]-2-pyrrolidinecarboxamide HCl](/CAS/20210111/GIF/1028252-93-8.gif)
1028252-93-8
1 suppliers
inquiry

62965-35-9
443 suppliers
$6.00/5g

630420-16-5
144 suppliers
$60.00/1mg