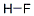불산
|
|
불산 속성
- 녹는점
- -35°C
- 끓는 점
- 105°C
- 밀도
- 1.15 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
- 증기 밀도
- 1.27 (vs air)
- 증기압
- 25 mm Hg ( 20 °C)
- 인화점
- 112°C
- 저장 조건
- Store at +5°C to +30°C.
- 용해도
- very soluble in H2O, ethanol; soluble in ethyl ether
- 산도 계수 (pKa)
- 3.17(at 25℃)
- 물리적 상태
- 액체, 이중 하위 끓는점 석영 증류
- Specific Gravity
- 1.15
- 냄새
- 매콤하고 자극적인 냄새
- pH 범위
- 1
- 수소이온지수(pH)
- 3.27(1 mM solution);2.65(10 mM solution);2.12(100 mM solution)
- 수용성
- 녹는
- 감도
- Hygroscopic
- Merck
- 14,4790
- 노출 한도
- Ceiling limit 3 ppm (~2.5 mg/m3) as F (ACGIH); TWA 3 ppm (MSHA and OSHA).
- Dielectric constant
- 17.0(-73℃)
- 안정성
- 안정적인. 흡습성. 유리, 알칼리 금속, 경금속, 알칼리 토금속과 호환되지 않습니다.
- LogP
- 0.1 at 20℃
- CAS 데이터베이스
- 7664-39-3(CAS DataBase Reference)
안전
- 위험 및 안전 성명
- 위험 및 사전주의 사항 (GHS)
| 위험품 표기 | T+,C,T,Xn | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 위험 카페고리 넘버 | 26/27/28-35-36/37/38-20/21/22 | ||
| 안전지침서 | 26-36/37/39-45-7/9-36/37-28-36 | ||
| 유엔번호(UN No.) | UN 1790 8/PG 2 | ||
| WGK 독일 | 2 | ||
| RTECS 번호 | MW7875000 | ||
| 위험 참고 사항 | Corrosive | ||
| TSCA | Yes | ||
| DOT ClassificationII | 8, Hazard Zone C (Corrosive material) | ||
| 위험 등급 | 8 | ||
| 포장분류 | II | ||
| HS 번호 | 28111100 | ||
| 유해 물질 데이터 | 7664-39-3(Hazardous Substances Data) | ||
| 독성 | LC50 (15 min.) in rats, guinea pigs: 2689, 4327 ppm (Rosenholtz) | ||
| IDLA | 30 ppm | ||
| 기존화학 물질 | KE-20198 | ||
| 유해화학물질 필터링 | 97-1-382 | ||
| 사고대비 물질 필터링 | 43 | ||
| 함량 및 규제정보 | 물질구분: 유독물질; 혼합물(제품)함량정보: 플루오르화 수소 및 이를 1% 이상 함유한 혼합물 |
불산 C화학적 특성, 용도, 생산
개요
Hydrofluoric acid is a solution of hydrogen fluoride in water. Hydrofluoric acid is highly corrosive inorganic acid. It is utilized widely in the manufacture of ceramics and graphite, in the electropolishing and pickling of metals, in the etching and frosting of glass, in the semiconductor industry as etchant and cleaning agent, in the chemical and oil-refining industries, and in cleaning solutions, laundry powder and pesticides. Hydrofluoric acid is also widely used in the preparation of many useful fluorine compounds, such as Teflon, Freon, fluorocarbons, and many medications such as fluoxetine (Prozac).화학적 성질
colourless gas with a pungent odour용도
Hydrofluoric acid is used as a fluorinatingagent, as a catalyst, and in uranium refining.It is also used for etching glass and forpickling stainless steel. Hydrogen fluoridegas is produced when an inorganic fluoride is distilled with concentrated sulfuricacid.정의
A colorless liquid produced by dissolving hydrogen fluoride in water. It is a weak acid, but will dissolve most silicates and hence can be used to etch glass. As the interatomic distance in HF is relatively small, the H–F bond energy is very high and hydrogen fluoride is not a good proton donor. It does, however, form hydrogen bonds.생산 방법
Anhydrous hydrogen fluoride is manufactured by the action of sulfuric on calcium fluoride. Powdered acid-grade fluorspar (≥97% CaF2) is distilled with concentrated sulfuric acid; the gaseous hydrogen fluoride that leaves the reactor is condensed and purified by distillation.Anhydrous hydrogen fluoride is manufactured by treating fluorspar (fluorite, CaF2) with concentrated sulfuric acid in heated kilns. The gaseous HF evolved is purified by distillation, condensed as liquid anhydrous HF, and stored in steel tanks and cylinders.
일반 설명
HF is a colorless inorganic acid. Hydrogen fluoride may be formed by reacting calcium fluoride and sulfuric acid at 200oC. The fluoride in the acid has very high affinity to silicon, making it useful in etching or removal of silicon.공기와 물의 반응
Fumes in air. Fumes are highly irritating, corrosive, and poisonous. Generates much heat on dissolution [Merck, 11th ed., 1989]. Heat can cause spattering, fuming, etc.반응 프로필
Hydrofluoric acid attacks glass and any other silica containing material. May react with common metals (iron, steel) to generate flammable hydrogen gas if diluted below 65% with water. Reacts exothermically with chemical bases (examples: amines, amides, inorganic hydroxides). Can initiate polymerization in certain alkenes. Reacts with cyanide salts and compounds to release gaseous hydrogen cyanide. May generate flammable and/or toxic gases with dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, nitriles, sulfides. Additional gas-generating reactions may occur with sulfites, nitrites, thiosulfates (to give H2S and SO3), dithionites (SO2), and carbonates. Can catalyze (increase the rate of) chemical reactions. Reacts explosively with cyanogen fluoride, methanesulfonic acid or glycerol mixed with nitric acid. Reacts violently with arsenic trioxide, phosphorus pentachloride, acetic anhydride, alkali metals, ammonium hydroxide, chlorosulfonic acid, ethylenediamine, fluorine, potassium permanganate, oleum, propylene oxide, vinyl acetate, mercury(II) oxide. Emits highly corrosive fumes of hydrogen fluoride gas when heated [Sax, 9th ed., 1996, p. 1839]. Contact with many silicon compounds and metal silicides causes violent evolution of gaseous silicon tetrafluoride [Mellor, 1956, Vol. 2, suppl. 1, p. 121].위험도
Toxic by ingestion and inhalation, highly corrosive to skin and mucous membranes.건강위험
Hydrofluoric acid and hydrogen fluoride gasare extremely corrosive to body tissues, causing severe burns. The acid can penetrate theskin and destroy the tissues beneath and evenaffect the bones. Contact with dilute acid cancause burns, which may be perceptible hoursafter the exposure. The healing is slow. Contact with the eyes can result in impairment ofvision.Prolonged exposure to 10–15 ppm concentrations of the gas may cause redness ofskin and irritation of the nose and eyes inhumans. Inhalation of high concentrations ofHF may produce fluorosis and pulmonaryedema. In animals, repeated exposure toHF gas within the range 20–25 ppm hasproduced injury to the lungs, liver, andkidneys.
LC50 value, inhalation (mice): 342 ppm/h.
화재위험
When heated, Hydrofluoric acid emits highly corrosive fumes of fluorides. Its corrosive action on metals can result in formation of hydrogen in containers and piping to create fire hazard. Toxic and irritating vapors are generated when heated. Will attack glass, concrete, and certain metals, especially those containing silica, such as cast iron. Will attack natural rubber, leather, and many organic materials. May generate flammable hydrogen gas in contact with some metals.인화성 및 폭발성
Hydrogen fluoride is not a combustible substance공업 용도
Hydrofluoric acid (HF) is a colorless liquid with a characteristic odor. It releases fumes when in contact with moist air. Hydrofluoric acid is manufactured from fluorite containing 96–97% CaF2 by reacting it with concentrated sulfuric acid:CaF2+H2SO4 = 2HF+CaSO4 The acid is sold as a 40% solution. The hydrofluoric acid is used as an activator and depressant, mostly during flotation of industrial minerals (i.e. columbite, tantalite, silica, feldspars).
Materials Uses
Carbon steel (without nonmetallic inclusions) is acceptable for handling hydrogen fluoride up to approximately 150°F (65.6°C). Aluminum- silicon-bronze, stainless steel, or nickel are suitable for cylinder valves. For higher temperatures, Monel, Inconel, nickel, or copper should be used. Cast iron or malleable fittings should be avoided. Polyethylene, lead, soft copper, Kel-F, and Teflon are acceptable gasket materials. Polyethylene, Kel-F, and Teflon are acceptable packing materials.Carcinogenicity
NTP conducted two chronic oral bioassays of fluoride administered as sodium fluoride (0, 25, 100, or 175 ppm) in drinking water for 103 weeks in rats and mice.The first study was compromised, so it was used to determine doses for the second study. NTP concluded that there was no evidence that fluoride was carcinogenic at doses up to 4.73 mg/kg/day in female rats or at doses up to 17.8 and 19.9 mg/kg/day in male and female mice, respectively.환경귀착
Hydrogen fluoride is a colorless, fuming liquid with a strong, irritating odor. The density is 1.002 at 0 ℃ and the boiling point is 19.51 ℃. Hydrogen Fluoride is naturally released into the environment, primarily from volcanoes, ranging from 0.6 to 6 million metric tons per year. The majority of artificial pollutants come from electrical utilities.Hydrogen fluoride is removed from air by wet deposition as fluoride salts with an atmospheric lifetime of 1–5 days.
저장
All work with HF should be conducted in a fume hood to prevent exposure by inhalation, and splash goggles and neoprene gloves should be worn at all times to prevent eye and skin contact. Containers of HF should be stored in secondary containers made of polyethylene in areas separate from incompatible materials. Work with anhydrous HF should be undertaken using special equipment and only by well-trained personnel familiar with first aid procedures.Purification Methods
It can be purified by trap-to-trap distillation, followed by drying over CoF2 at room temperature and further distillation. Alternatively, it can be absorbed on NaF to form NaHF2 which is then heated under vacuum at 150o to remove volatile impurities. The HF is regenerated by heating at 300o and is stored with CoF3 in a nickel vessel, being distilled as required. (Water content should be ca 0.01%.) To avoid contact with base metal, use can be made of nickel, polychlorotrifluoroethylene and gold-lined fittings [Hyman et al. J Am Chem Soc 79 3668 1957]. An aqueous solution is hydrofluoric acid (see above). It is HIGHLY TOXIC and attacks glass.비 호환성
HF reacts with glass, ceramics, and some metals. Reactions with metals may generate potentially explosive hydrogen gas.폐기물 처리
Excess hydrogen fluoride and waste material containing this substance should be placed in an appropriate container, clearly labeled, and handled according to your institution's waste disposal guidelines. For more information on disposal procedures, see Chapter 7 of this volume.참고 문헌
[1] David J. Monk, and David S. Soane, A review of the chemical reaction mechanism and kinetics for hydrofluoric acid etching of silicon dioxide for surface micromachining applications, Thin Solid Films, 1993, vol. 232, 1-12[2] P. Sanz-Gallen, S. Nogue, P. Munne and A. Faraldo, Hybocalcaemia and hypomagnesaemia due to hydrofluoric acid, Occup Med (Lond), 2001, vol. 51, 294-295
불산 준비 용품 및 원자재
원자재
발연황산
염화칼슘
HYDROGEN FLUORIDE GAS
Fluorite powder
플루오르화칼슘
Microvoid filter film
Electronic grade hydrofluoric acid
칼슘 염화물, 헥사수화물
황산
준비 용품
구리 플루오린붕산(구리 플루오르붕산)
6,9-Difluoropregn-4-ene-11,17,21-triol-3,20-dione17,21-diacetate
아연 테트라플루오로붕산염
9-Fluoropregna-1,4-diene-11,17,21-triol-3,20-dione17,21-diacetate
2-클로로-6-플로로톨루엔
탄탈 오산화물
란타넘 플루오라이드(란탄 플루오라이드)
세보플루란
3-TRIFLUOROMETHYL BENZOTRICHLORIDE
2,4-Dichlorobenzotrifluoride
플루오린화 이트륨(플루오르화 이트륨)
emulsifier acid
Boron trifluoride acetonitrile complex
1,1,1,2,3,3,3-헵타플루오로프로판
1,3-비스(플리프루오로메틸)벤젠
테트라플루오린화 타이타늄(테트라플루오르화 티타늄)
5-(trifluoromethyl)thiazol-2-amine
트리플루오로메탄술폰산 나트륨
플루오르화리튬
불가화 바륨
클로로트리플루오르메탄
Potassium fluoroaluminate
1-CHLORO-3-FLUOROISOPROPANOL
불화 스트론슘
2-메틸부틸산에틸
네오디뮴 플루오르화물
리튬 포스포헥사플루오르화
6alpha,9-difluoro-11beta,17,21-trihydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione 17,21-di(acetate)
9-fluoro-11beta,21-dihydroxypregna-1,4,16-triene-3,20-dione 21-acetate
디플루오르모노클로로에탄
트라이플루오린화 크로뮴
자료없음
ZINC TETRAFLUOROBORATE HYDRATE
독시싸이클린
불화 마그네슘
다이클로로모노플루오로메테인(디클로로모노플루오로메탄)
1,1,1-트라이클로로-2,2,2-트라이플루오로에테인
Chromium(III) fluoride tetrahydrate
Triamcinolone 21-acetate
칼륨 1,1,2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5,6,6,7,7,8,8,8-헵타데카플루오로-1- 옥탄술폰산
불산 공급 업체
글로벌( 456)공급 업체
| 공급자 | 전화 | 이메일 | 국가 | 제품 수 | 이점 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hebei Mojin Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +8613288715578 |
sales@hbmojin.com | China | 12470 | 58 |
| Hebei Yanxi Chemical Co., Ltd. | +8617531190177 |
peter@yan-xi.com | China | 6001 | 58 |
| Henan Tianfu Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-0371-55170693 +86-19937530512 |
info@tianfuchem.com | China | 21689 | 55 |
| Shanxi Naipu Import and Export Co.,Ltd | +86-13734021967 +8613734021967 |
kaia@neputrading.com | China | 1011 | 58 |
| career henan chemical co | +86-0371-86658258 |
sales@coreychem.com | China | 29914 | 58 |
| Hubei Jusheng Technology Co.,Ltd. | 18871490254 |
linda@hubeijusheng.com | CHINA | 28180 | 58 |
| Cangzhou Wanyou New Material Technology Co.,Ltd | 18631714998 |
sales@czwytech.com | CHINA | 906 | 58 |
| Hubei xin bonus chemical co. LTD | 86-13657291602 |
linda@hubeijusheng.com | CHINA | 22968 | 58 |
| Chongqing Chemdad Co., Ltd | +86-023-61398051 +8613650506873 |
sales@chemdad.com | China | 39916 | 58 |
| CONIER CHEM AND PHARMA LIMITED | +8618523575427 |
sales@conier.com | China | 49391 | 58 |
불산 관련 검색:
아세트산 엽산 글리신 시트르산 플루오린(불소) 불화소다 불화 트리에틸암모늄 수소 헥사플루오로지르콘산염(IV) 불산
Ascoric Acid
CETYLAMINE FLUORIDE
Melamine hydrogen flouride
Hydrofluoric acid, homopolymer, compd. with pyridine
Diisopropylethylamine trihydrofluoride
HYDROFLUORIC ACID ANTIDOTE GEL
hydrofluoric acid mixture,ammonium fluoride - hydrofluoric acid mixture
Hydrofluoric acid-d
Mixed acid