Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (API), popularly speaking, are the raw materials of medicines, only pharmaceutical raw materials are processed into pharmaceutical preparations , can they become medicines available for clinical use, so drugs we usually eat are the finished drugs through processing. Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients based on its sources can be divided into two major categories ,including chemical synthetic drugs and natural chemical drugs. Chemical synthetic drugs can be divided into organic synthetic drugs and inorganic synthetic drugs. Inorganic synthetic drugs are inorganic compounds ( very few is element), such as aluminum hydroxide, magnesium trisilicate which are used for the treatment of gastric and duodenal ulcers ; organic synthetic drugs are mainly composed of drugs made by basic organic chemical raw materials, through a series of organic chemical reactions (such as aspirin, chloramphenicol, caffeine, etc.). Natural chemical drugs ,based on its sources,can be divided into two categories including biochemical drugs and plant chemical drugs. Antibiotics are generally made by the microbial fermentation, which belongs to the biochemistry category. A variety of semi-synthetic antibiotics occurs in recent years,which are biosynthesis and chemical synthesis combining products.Among active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, the organic synthetic drugs varieties, yields and values have the largest proportion,which are the main pillars of the chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The quality of active Pharmaceutical Ingredients decides whether the formulation is good or bad , so its quality standards are very strict ,countries in the world have developed national pharmacopoeia standards and strict quality control methods for its widely used active Pharmaceutical ingredients.
2-Iodobenzoic Acid: Applications in Medicinal Chemistry and its Preparation Method
2-Iodobenzoic acid enables synthesis of crucial compounds for medical advancement, enhancing diagnostic techniques and potential treatments in medicinal chemistry.
May 11,2024 APIDicyclohexylamine: Overview, Antibacterial Activity and Detection Method
Dicyclohexylamine inhibits bacterial growth via spermidine synthase, showing sensitivity in Streptococcus uberis, with potential therapeutic applications and LC-MS/MS detection in honey.
May 11,2024 API4-Chloro-7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine: Applications in Medicinal Chemistry and its Improved Synthesis
Recent synthesis advancements of 4-Chloro-7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine enhance kinase inhibitor development, offering high yields and accessibility for researchers.
May 11,2024 APICetearyl Alcohol: Overview, Benefits in Skincare and Origin
Cetearyl alcohol, derived from plants, serves as a versatile ingredient in skincare, providing moisturizing, emulsifying, and stabilizing benefits.
May 11,2024 APITris Hydrochloride: Preparation Method, Precautions, Advantages and Limitations
Tris Hydrochloride is widely used in biochemistry for its versatile pH range and compatibility. Precautions include pH control and avoiding interference, despite limitations.
May 10,2024 APIPyromellitic Dianhydride: Applications in Wastewater Treatment and its Preparation Method
Pyromellitic Dianhydride, synthesized from 1,2,4,5-Benzenetetracarboxylic Acid, plays a crucial role wastewater treatment.
May 10,2024 APIp-Coumaric acid: Mechanisms for Antimelanogenic Effects, Skin and Cell Membrane Permeability
p-Coumaric acid's diverse bioactivities include antioxidant and antimicrobial effects. Despite limited permeability, it shows promise in melanin inhibition and transdermal delivery.
May 10,2024 API4-Formylbenzoic acid: Chemical Characteristics, Applications in Medicinal Chemistry and Preparation Method
4-Formylbenzoic acid, prepared through oxidation of aldehydes, is a stable compound used in antiviral and diabetes drug development due to its role in synthesizing potent inhibitors.
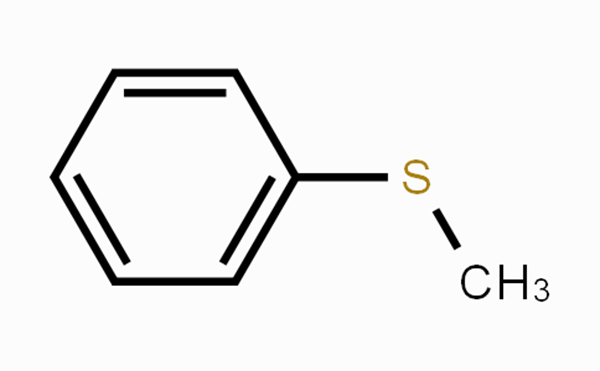
May 10,2024 APIWhat is Thioanisole used for as a scavenger?
Thioanisole is a commonly used scavenger in peptide synthesis to trap released nucleophiles during the global deprotection step of the peptide side chain.
May 10,2024 APIWhat are the chemical reactions involved in N-Iodosuccinimide?
N-Iodosuccinimide (NIS) is an electrophilic iodide.
May 9,2024 API