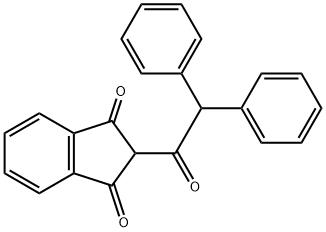
DIPHACINONE
- CAS No.
- 82-66-6
- Chemical Name:
- DIPHACINONE
- Synonyms
- pcq;Ramik;u1363;Didion;Diphac;p.c.q.;Promar;Solvan;u 1363;u-1363
- CBNumber:
- CB0324612
- Molecular Formula:
- C23H16O3
- Molecular Weight:
- 340.37
- MOL File:
- 82-66-6.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2024/12/18 13:37:16
| Melting point | 146-147° |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 436.18°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.1454 (rough estimate) |
| vapor pressure | 1.37 x l0-8 Pa (25 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.6700 (estimate) |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| Water Solubility | 0.3 mg l-1 |
| pka | 2.79±0.10(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| color | Light Yellow to Yellow |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 82-66-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Diphacinone (82-66-6) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS06,GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H300+H310-H332-H372 |
| Precautionary statements | P264-P280-P301+P310-P302+P350-P310 |
| Hazard Codes | T+ |
| Risk Statements | 28-48/23/24/25-24-20 |
| Safety Statements | 36/37-45 |
| RIDADR | 2811 |
| RTECS | NK5600000 |
| HazardClass | 6.1(a) |
| PackingGroup | I |
| HS Code | 29143990 |
| Hazardous Substances Data | 82-66-6(Hazardous Substances Data) |
| Toxicity | LD50 orally (mg/kg): 3 in rats; 340 in mice; 35 in rabbits (Correll) |
DIPHACINONE Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Diphacinone is also called 2-(diphenylacetyl)indan-1,3-dione, is a yellow powder which is practically insoluble in water, readily soluble in chloroform, toluene, xylene, acetone, ethanol, heptane, alkalis [9, p. 431].
Uses
Diphacinone is an anticoagulant rodenticide widely used to control rodent infestations.
Production Methods
Diphacinone is produced by condensation of 1,1-diphenyl acetone with dimethyl phthalate in the presence of sodium methoxide (30).
General Description
Odorless pale yellow crystals. Used as a rodenticide and anticoagulant medication.
Air & Water Reactions
Practically insoluble in water (17mg/L). Hydrolyzed by strong acid.
Reactivity Profile
DIPHACINONE is a ketone, and behaves as a weak acid. Forms water soluble alkali metal salts. Ketones are reactive with many acids and bases liberating heat and flammable gases (e.g., H2). The amount of heat may be sufficient to start a fire in the unreacted portion of the ketone. Ketones react with reducing agents such as hydrides, alkali metals, and nitrides to produce flammable gas (H2) and heat. Ketones are incompatible with isocyanates, aldehydes, cyanides, peroxides, and anhydrides. They react violently with aldehydes, HNO3, HNO3 + H2O2, and HClO4.
Health Hazard
DIPHACINONE is extremely toxic; probable oral lethal dose in humans is 5-50 mg/kg, or between 7 drops and 1 teaspoonful for a 150-lb. person. Many medical conditions will be aggravated by DIPHACINONE.
Fire Hazard
When heated to decomposition DIPHACINONE emits acrid smoke and fumes. Sensitive to light.
Agricultural Uses
Rodenticide: A U.S. EPA restricted Use Pesticide (RUP) when the formulation contains 3% or more of diphacinone. Diphacinone is an anti-coagulant rodenticide bait used for control of rats, mice, voles and other rodents. It is available in meal, pellet, wax block, and liquid bait formulations, as well as in tracking powder and concentrate formulations. It is used in general agriculture and in food-processing areas. The top five uses for diphacinone in California are on landscapes, general vertebrate pest control, around structures and right of ways, and on oranges. This material is also used as an anticoagulant medication. Not approved for use in EU countries.
Trade name
DE-PESTER®[C]; DIDANDIN®; DIPAXIN®; DITRAC®; GOLD CREST®; KILL-RO RAT KILLER®; LIQUA-TOX®, diphacinone sodium salt; ORAGULANT®; P. C. Q. ®; PID®; PROMAR®; RAMIK®; RAT KILLER®; RODENT CAKE®[C]; SOLVAN®; TOMCAT®; U 1363®
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion. Inlxbits blood clotting, leading to hemorrhages. Action similar to coumadin (warfarin). A pesticide used in rodent control. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes
Metabolic pathway
Diphacinone is a member of the indandione class of anti-coagulants. Its fate in rats and mice has been reported but no information on its degradation in soil or plants has been published. It is metabolised by hydroxylation and conjugation.
DIPHACINONE Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of3
chevron_rightPreparation Products
82-66-6(DIPHACINONE)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




