HEXACHLOROBENZENE
- CAS No.
- 118-74-1
- Chemical Name:
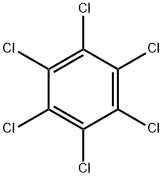
- HEXACHLOROBENZENE
- Synonyms
- Hexachlorocyclohexane;HCB;Hexachlorbenzene;PERCHLOROBENZENE;Hexachlorbenzol;BENZENE HEXACHLORIDE;Benzene, hexachloro-;granox;hexacb;Amatin
- CBNumber:
- CB4149734
- Molecular Formula:
- C6Cl6
- Molecular Weight:
- 284.78
- MOL File:
- 118-74-1.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/3/14 15:18:26
| Melting point | 227-229 °C(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 323-326 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.5691 |
| vapor pressure | 1.45 x l0-3 Pa (20 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.5691 (estimate) |
| Flash point | 11 °C |
| storage temp. | APPROX 4°C |
| solubility | Chloroform, Hexanes (Slightly) |
| Water Solubility | Practically insoluble in water |
| Merck | 13,4696 |
| BRN | 1912585 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 6.11 at 25 °C (continuous flow sparger, Sproule et al., 1991) |
| Exposure limits | No exposure limit has been set for this com pound. Carcinogenicity: Animal Sufficient Evidence, Human Limited Evidence (IARC). |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| InChIKey | CKAPSXZOOQJIBF-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 118-74-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 2B (Vol. Sup 7, 79) 2001 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Hexachlorobenzene (118-74-1) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS08,GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H350-H372-H410 |
| Precautionary statements | P202-P260-P264-P270-P273-P308+P313 |
| Hazard Codes | T,N,Xn,F,Xi |
| Risk Statements | 45-48/25-50/53-67-65-62-51/53-48/20-38-11-39/23/24/25-23/24/25-66-36/38-36 |
| Safety Statements | 53-45-60-61-62-36/37-33-29-16-9-26 |
| RIDADR | UN 2729 6.1/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | DA2975000 |
| HazardClass | 6.1(b) |
| PackingGroup | III |
| HS Code | 2903920000 |
| Toxicity | LC50 for ?ve freshwater species 0.05-0.2 mg/L (Hartley and Kidd, 1987); acute oral LD50 for rats 10,000 mg/kg (RTECS, 1985). |
HEXACHLOROBENZENE price More Price(3)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 40008 | Hexachlorobenzene solution certified reference material, 1000?μg/mL in acetone | 118-74-1 | 1ML | ₹5226.9 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| ottokemi | H 1305 | Hexachlorobenzene, crystalline | 118-74-1 | 5gm | ₹6093 | 2022-05-26 | Buy |
| ottokemi | H 1305 | Hexachlorobenzene, crystalline | 118-74-1 | 25gm | ₹29007 | 2022-05-26 | Buy |
HEXACHLOROBENZENE Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Hexachlorobenzene is a white crystalline solid. This compound does not occur naturally. It is formed as a by-product during the manufacture of chemicals used as solvents (substances used to dissolve other substances), other chlorine-containing compounds, and pesticides. Small amounts of hexachlorobenzene can also be produced during combustion processes such as burning of city wastes. It may also be produced as a by-product in waste streams of chlor-alkali and wood-preserving plants. Hexachlorobenzene was widely used as a pesticide until 1965. It was also used to make fireworks, ammunition, and synthetic rubber.
Chemical Properties
Hexachlorobenzene is a solid, crystallizing in nee dles.
Uses
Hexachlorobenzene is used as a fungicideand as an intermediate in organic synthesis.
Definition
hexachlorobenzene: A colourlesscrystalline compound, C6Cl6; m.p.227°C. It is made by the chlorinationof benzene with an iron(III) chloridecatalyst or by treating hexachlorocyclohexanewith chlorine in hexachloroethane.It is used to preservewood and dress seeds, and in themanufacture of hexafluorobenzene.
General Description
A white crystalline substance. Insoluble in water and denser than water. Contact may irritate skin, eyes and mucous membranes. May be toxic by ingestion. Used to make other chemicals.
Air & Water Reactions
HEXACHLOROBENZENE is sensitive to moisture. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
HEXACHLOROBENZENE reacts violently with dimethylformamide. .
Hazard
Possible carcinogen. Toxic by ingestion. Combustible.
Health Hazard
The acute oral and inhalation toxicity ofhexachlorobenzene is low in test animals.Repeated ingestion of this compound mayproduce porphyria hepatica (increased for mation and excretion of porphyrin) causedby disturbances in liver metabolism. The oralLD50 value in rabbits is 2600 mg/kg; theinhalation LC50 value from a single exposureis 1800 mg/m3 (NIOSH 1986). The occupa tional health hazard from inhalation shouldbe very low because of its very low vaporpressure (0.00001 torr).
Hexachlorobenzene causes cancer in ani mals. Oral administration of this compoundfor 18 weeks to 2 years caused tumors inthe liver, kidney, thyroid, and blood in rats,mice, and hamsters. It is a suspected humancarcinogen, evidence of which occurs to alimited extent.
Fire Hazard
Noncombustible solid; very low reactiv ity. Reaction with dimethyl formamide is reported to be violent at temperatures above 65°C (149°F) (NFPA 1997).
Potential Exposure
Hexachlorobenzene was used as a fun gicide; an additive for pyrotechnic compositions; and as wood preservative. It was used widely as a pesticide to pro tect seeds of onions and sorghum, wheat, and other grains against fungus until 1965. This material was used to make fireworks; ammunition for military uses; synthetic rubber; as a porosity controller in the manufacture of electrodes; as an intermediate in dye manufacture; in organic synthesis. It is formed as a by-product of making other chemicals; in the waste streams of chloralkali and wood-preserving plants; and when burning municipal waste. Currently, there are no commercial uses of hexachlorobenzene in the United States.
Carcinogenicity
Hexachlorobenzene is reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen based on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity from studies in experimental animals.
Metabolic pathway
With the incubation of rat liver microsomes, hexachlorobenzene is metabolized to give pentachlorophenol and tetrachlorohydroquinone, and, in addition, a considerable amount of covalent binding to protein is detected (250 pM pentachlorophenol, 17 pM tetrachlorohydroquinone, and 11 pM tetrachlorobenzoquinone covalent binding in an incubation containing 50 μM hexachlorobenzene).
Metabolism
Sensitized photolysis of HCB at wavelengths greater
than 285 nm in acetonitrile/water containing acetone gave
dechlorinated products: pentachlorobenzene (78) (71%),
1,2,3,4-tetrachlorobenzene (79) (0.6%), 1,2,3,5-tetrachlorobenzene
(80) (2.2%), and 1,2,4,5- tetrachlorobenzene
(81) (3.7%). Without acetone, products included
pentachlorobenzene (78) (76.8%), 1,2,3,5-tetrachlorobenzene
(80) (1.2%), 1,2,4,5- tetrachlorobenzene (81) (1.7%),
and 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene (82) (0.2%) (105).
Irradiation of hexachlorobenzene in methanol solution
at wavelengths greater than 260 nm gave a
mixture of reductively dechlorinated products (pentachlorobenzene
and a tetrachlorobenzene, probably 80)
and pentachlorobenzyl alcohol 83, and also a tetrachlorodi(
hydroxymethyl)benzene (106). A similar product
mixture was obtained by exposing a methanolic solution of
hexachlorobenzene inmethanol to sunlight outdoors. After
15 days, only 30% of hexachlorobenzene was recovered.
Photolysis rates were enhanced by the addition of sensitizers
(diphenylamine, tryptophane, and naturally occurring
organic substances), but no products were identified.
In an anaerobic sewage sludge, hexachlorobenzene was
reductively dechlorinated and the principal product was
1,3,5-trichlorobenzene (84). Pentachlorobenzene, 1,2,3,5-
tetrachlorobenzene, and dichlorobenzenes were also identified
(107). In activated sludge, 1.5% of hexachlorobenzene
was mineralized as carbon dioxide after 5 days.
Shipping
UN2729 Hexachlorobenzene, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.
Purification Methods
Crystallise hexachlorobenzene repeatedly from *benzene. Dry it under vacuum over P2O5. [Beilstein 5 H 205, 5 IV 670.]
Incompatibilities
Reacts violently with oxidizers; dimethyl formamide above 65 ℃.
Waste Disposal
Incineration is most effective @ 1300 ℃ and 0.25 seconds. Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform to EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal.
HEXACHLOROBENZENE Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
1of2
chevron_right| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Otto Chemie Pvt. Ltd. | +91 9820041841 | Mumbai, India | 5873 | 58 | Inquiry |
| CLEARSYNTH LABS LTD. | +91-22-45045900 | Hyderabad, India | 6351 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Central Drug House(P) Ltd. | 91-11-49404040 | New Delhi, India | 6160 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Triveni chemicals | 08048762458 | New Delhi, India | 6093 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Henan Tianfu Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-0371-55170693 +86-19937530512 | China | 21663 | 55 | Inquiry |
| CONIER CHEM AND PHARMA LIMITED | +8618523575427 | China | 49403 | 58 | Inquiry |
| career henan chemical co | +86-0371-86658258 +8613203830695 | China | 29821 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co.,Ltd. | +86-0551-65418671 +8618949823763 | China | 34571 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Sinoway Industrial co., ltd. | 0592-5800732; +8613806035118 | China | 988 | 58 | Inquiry |
| SUZHOU SENFEIDA CHEMICAL CO.,LTD | +86-0512-83500002 +8615195660023 | China | 23048 | 58 | Inquiry |
118-74-1(HEXACHLOROBENZENE)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




