ARSENIC(III) CHLORIDE
- CAS No.
- 7784-34-1
- Chemical Name:
- ARSENIC(III) CHLORIDE
- Synonyms
- AsCl3;arsenicbutter;Arsenic butter;butterofarsenic;Trichloroarsine;trichloroarsane;ARSENIC CHLORIDE;arsenouschloride;arseniouschloride;Arsenous chloride
- CBNumber:
- CB4161860
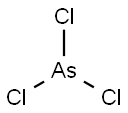
- Molecular Formula:
- AsCl3
- Molecular Weight:
- 181.28
- MOL File:
- 7784-34-1.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2024/3/14 15:18:26
| Melting point | −16 °C(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 130.2 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 2.15 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 6.25 |
| refractive index | 1.6006 (589.3 nm 20℃) |
| Flash point | 130.2°C |
| solubility | reacts with H2O; very soluble in chloroform,ctc, ethyl ether |
| form | Liquid |
| color | Colorless to yellow-brown |
| Water Solubility | Decomposes in water with formation of As(OH)<sub>3</sub> and HCl. Increasing dilutions in water result in As<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub> precipitation |
| Sensitive | Moisture Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,801 |
| Dielectric constant | 12.4(21℃) |
| Stability | Stability Reacts with water. Corrodes many metals. Reacts violently on contact with potassium, sodium and aluminium. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7784-34-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Arsenic(III) chloride (7784-34-1) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS06,GHS09 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H300+H310-H331-H410 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P262-P273-P280-P301+P310-P302+P352+P310-P304+P340+P311 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | T,N | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 23/25-50/53 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 20/21-28-45-60-61 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 1560 6.1/PG 1 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | CG1750000 | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 6.1 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | I | |||||||||
| HS Code | 28121044 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | cyt-hmn:leu 600 nmol/L MUREAV 88,73,81 | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
ARSENIC(III) CHLORIDE price More Price(2)
ARSENIC(III) CHLORIDE Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
colourless oily liquid
Physical properties
Colorless oily liquid; fumes in air; density 2.163 g/ml at 20°C; refractive index 1.621 at 14°C; melts at 0.16°C; boils at 130.2°C; vapor pressure 9.75 torr at 25°C; decomposes in water; soluble in alcohol, ether, HCl and HBr.
Uses
Arsenic Trichloride is an highly toxic inorganic compounds and is an intermediate in the manufacture of organoarsenic compounds.
Preparation
The compound is generally made from arsenic trioxide by (i) passing chlorine over it or (ii) treating the trioxide with sulfur monochloride, S2Cl2. Alternatively it is prepared from arsenic trioxide by distillation with either concentrated hydrochloric acid or a mixture of sulfuric acid and a metal chloride. Arsenic trichloride may also be prepared by combination of arsenic and chlorine.
Definition
A poisonous oily liquid. It fumesin moist air due to hydrolysis with water
vapor:AsCl3 + 3H2O = As2O3 + 6HCl
Arsenic(III) chloride is covalent and exhibits nonmetallic properties.
General Description
A colorless to yellow oily fuming liquid. ARSENIC(III) CHLORIDE is irritating to the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. Very toxic by inhalation and ingestion.
Air & Water Reactions
Fumes in air. Reacts with water to form hydrochloric acid and As(OH)3.
Reactivity Profile
When ARSENIC CHLORIDE is heated to decomposition or on contact with mineral acids, ARSENIC(III) CHLORIDE emits highly toxic fumes of hydrogen chloride and of metallic arsenic. Explodes with Na, K, and Al on impact [Sax, 9th ed., 1996, p. 275]. The interaction of hexafluoroisopropylideneaminolithium with a range of chlorinated and /or fluorinated derivatives of arsenic, boron, phosphorus, silicon, and sulfur yielded a violently exothermic reaction.
Hazard
Strong irritant to eyes and skin.
Health Hazard
ARSENIC(III) CHLORIDE can cause death. In acute exposures, it is extremely toxic and caustic, owing not only to the poisonous nature of arsenic, but also to the release of hydrochloric acid in the presence of water. Exposure to the skin causes local irritation and blisters. Inhalation or ingestion causes hemorrhagic gastroenteritis resulting in loss of fluids and electrolytes, collapse, shock and death. Chronic poisoning can lead to peripheral nerve damage, skin conditions, liver damage and it has been implicated in the induction of skin and lung cancer. The fatal human dose is 70-180 mg depending on the weight of the victim.
Fire Hazard
When in contact with active metals such as arsenic, iron, aluminum, zinc, or when heated to decomposition, ARSENIC(III) CHLORIDE emits highly toxic fumes of arsenic. Upon contact with water hydrogen chloride is produced. Water causes ARSENIC(III) CHLORIDE to decompose to yield arsenic acid and hydrochloric acid. Avoid active metals such as arsenic, iron, aluminum, zinc, decomposed by water to form arsenic hydroxide and hydrogen chloride. Avoid air, ultraviolet light. Hazardous polymerization may not occur.
Safety Profile
Confirmed human carcinogen. A poison via inhalation. See also ARSENIC COMPOUNDS and CHLORIDES. Very poisonous; fumes in air. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of As and Cl-. Highly reactive. Explodes with Na, K, and Al on impact.
Synthesis
The direct synthesis of AsCl3 is uneconom ical. An old commercial production method is the Glauber process using arsenic trioxide:
As2O3 +6NaCl+3H2SO4?→ 2AsCl3+3Na2SO4+3H2O
However, AsCl3 is easier to produce by react ing As2O3 with gaseous hydrogen chloride at 180–200℃.
Potential Exposure
Arsenic chloride is used in the ceramics industry; in the synthesis of chlorine-containing arsenicals; as a chemical intermediate for arsenic insecticides, pharmaceuticals; and has been used in chemical warfare agents.
Shipping
UN1560 Arsenic trichloride, Hazard class 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poison Inhalation Hazard, Inhalation Hazard Zone B.
Purification Methods
Reflux the trichloride with arsenic for 4hours, then fractionally distil it. The middle fraction is stored with sodium wire for two days, then again distilled [Lewis & Sowerby J Chem Soc 336 1957]. It fumes in moist air forming the solid hydroxy-chloride [AsCl(OH)2] and is readily hydrolysed by H2O to form arsenious acid. POISONOUS. [Schenk in Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry (Ed. Brauer) Academic Press Vol I p 596 1963.]
Incompatibilities
Contact with sodium, potassium, or powdered aluminum may cause a violent reaction. It is decomposed in water, forming arsenic hydroxide and hydrogen chloride. Exposure to light forms toxic gas. Violent reaction with anhydrous ammonia, strong acids; strong oxidizers and halogens. Incompatible with alkali metals; active metals, such as arsenic, iron, aluminum, zinc. Corrodes metals in the presence of moisture and forms flammable and explosive hydrogen gas.
Waste Disposal
Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal. Dissolve in a minimum of concentrated hydrochloric acid. Dilute with water until white precipitate forms. Add HCl to dissolve. Saturate with H2S; filter and wash precipitate and return to supplier. Alternatively, precipitate with heavy metals, such as lime or ferric hydroxide in lieu of H2S.If needed, seek professional environmental engineering assistance from the United States Environmental Protection Agency Environmental Response Team at (908) 548-8730 (24-hour response line). In accordance with 40CFR165, follow recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Must be disposed properly by following package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office.
ARSENIC(III) CHLORIDE Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
7784-34-1(ARSENIC(III) CHLORIDE)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




