ARSENIC(III) IODIDE
- CAS No.
- 7784-45-4
- Chemical Name:
- ARSENIC(III) IODIDE
- Synonyms
- NA 1557;Triiodoarsine;triiodoarsane;Asenic lodide;ARSENIC IODIDE;Arsenousiodide;Arsenous iodide;Arsenoustriiodide;ARSENIC TRIIODIDE;ARSENIC COMPOUNDS
- CBNumber:
- CB7192357
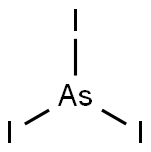
- Molecular Formula:
- AsI3
- Molecular Weight:
- 455.64
- MOL File:
- 7784-45-4.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2023/11/28 16:31:43
| Melting point | 146 °C |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 403 °C |
| Density | 4.69 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| Flash point | 424°C |
| solubility | slightly soluble in H2O, ethanol, ethyl ether; soluble in benzene. toluene |
| form | Powder |
| Specific Gravity | 4.39 |
| color | red |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in alcohol, ether, Carbon disulfide, water(6 g/100 m). |
| Sensitive | Moisture Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,803 |
| Dielectric constant | 7.0(150℃) |
| Exposure limits |
ACGIH: TWA 0.01 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 5 mg/m3; Ceiling 0.002 mg/m3 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7784-45-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Arsenous triiodide (7784-45-4) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS06,GHS09 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H301-H331-H400-H301+H331-H410 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P301+P310a-P304+P340-P311a-P405-P501a-P261-P273-P301+P310-P311-P501 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | T,N | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 23/25-50/53 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 20/21-28-45-60-61 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 1557 6.1/PG 1 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | CG1950000 | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 6.1 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | II | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
ARSENIC(III) IODIDE Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
red powder(s); enthalpy of formation ?58.2 kJ/mol; entropy 213.0 J/(mol · K); enthalpy of vaporization 59.3 kJ/mol; decomposes slowly in air at 100°C, rapidly at 200°C, to give As, I2, As2O3; made by precipitation from a hot AsCl3-HCl solution by the addition of KI [KIR78] [STR93]
Uses
Arsenic(III) iodide is useful for preparing organoarsenic compounds.
Preparation
Arsenic triiodide is prepared by treating elemental arsenic with a solution of iodine in carbon disulfide. Alternatively, it can be precipitated out from a hot solution of arsenic trioxide or arsenic trisulfide in hydrochloric acid on treatment with potassium or sodium iodide. Also, it is made by the reaction of arsenic trichloride with potassium iodide.
General Description
Orange-red rhombohedral crystals (from acetone). Density 4.69 g / cm3. Melting point 285.6°F (140.9°C). Red as a liquid.
Air & Water Reactions
Reacts slowly with oxygen from the air, liberating iodine [Merck]. Water soluble. Aqueous solutions are strongly acidic (pH of 0.1N solution about 1.1) and ultimately form HI and As2O3, although an equilibrium AsI3 + 3H2O = H3AsO3 + 3HI has been observed [Merck 1989].
Reactivity Profile
ARSENIC IODIDE gives acidic solutions in water. These solutions neutralize bases exothermically. Can react as either an oxidizing agent or reducing agent.
Hazard
Toxic and carcinogen.
Health Hazard
Highly toxic, may be fatal if inhaled, swallowed or absorbed through skin. Contact with molten substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Avoid any skin contact. Effects of contact or inhalation may be delayed. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may be corrosive and/or toxic and cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
Combustible material: may burn but does not ignite readily. Containers may explode when heated. Runoff may pollute waterways. Substance may be transported in a molten form.
Safety Profile
Inorganic compounds are confirmed human carcinogens producing tumors of the mouth, esophagus, larynx, bladder, and paranasal sinus. Recognized carcinogens of the skin, lungs, and liver. Used as insecticides, herbicides, silvicides, defoliants, desiccants, and rodenticides. Poisoning from arsenic compounds may be acute or chronic. Acute poisoning usually results from swallowing arsenic compounds; chronic poisoning from either swallowing or inhaling. Acute allergic reactions to arsenic compounds used in medical therapy have been fairly common, the type and severity of reaction depending upon the compound. Inorganic arsenicals are more toxic than organics. Trivalent is more toxic than pentavalent. Acute arsenic poisoning (from ingestion) results in marked irritation of the stomach and intestines with nausea, vomiting, and darrhea. In severe cases, the vomitus and stools are bloody and the patient goes into collapse and shock with weak, rapid pulse, cold sweats, coma, and death. Chronic arsenic poisoning, whether through ingestion or inhalation, may manifest itself in many different ways. There may be disturbances of the digestive system such as loss of appetite, cramps, nausea, constipation, or diarrhea. Liver damage may occur, resulting in jaundice. Disturbances of the blood, kidneys, and nervous system are not infrequent. Arsenic can cause a variety of skin abnormalities including itching, pigmentation, and even cancerous changes. A characteristic of arsenic poisoning is the great variety of sympt-oms that can be produced. Dangerous; when heated to decomposition, or when metallic arsenic contacts acids or acid fumes, or when water solutions of arsenicals are in contact with active metals such as Fe, Al, or Zn, highly toxic fumes of arsenic are emitted.
Purification Methods
It crystallises from acetone and sublimes below 100o. It is very slowly hydrolysed by H2O (much more slowly than the chloride). POISONOUS. [Schenk in Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry (Ed. Brauer) Academic Press Vol I p 597-598 1963.]
ARSENIC(III) IODIDE Preparation Products And Raw materials
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxford Laboratory | 91-250-2390032 | Maharashtra, India | 43 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Jyoti Chemical Centre | 09594652522 | Mumbai, India | 215 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Chongqing Chemdad Co., Ltd | +86-023-6139-8061 +86-86-13650506873 | China | 39916 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Aston Chemical | 13000000000 | United States | 1634 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Shaanxi Didu New Materials Co. Ltd | +86-89586680 +86-13289823923 | China | 9003 | 58 | Inquiry |
| LEAPCHEM CO., LTD. | +86-852-30606658 | China | 43348 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Aladdin Scientific | +1-+1(833)-552-7181 | United States | 57511 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Hebei Weibang Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +8615350571055 | China | 5251 | 58 | Inquiry |
| ABCR GmbH & CO. KG | 49 721 95061 0 | Germany | 6846 | 75 | Inquiry |
| Portail Substances Chimiques | 10 20 0000 | France | 6027 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| Oxford Laboratory | 58 |
| Jyoti Chemical Centre | 58 |
| Chongqing Chemdad Co., Ltd | 58 |
| Aston Chemical | 58 |
| Shaanxi Didu New Materials Co. Ltd | 58 |
| LEAPCHEM CO., LTD. | 58 |
| Aladdin Scientific | 58 |
| Hebei Weibang Biotechnology Co., Ltd | 58 |
| ABCR GmbH & CO. KG | 75 |
| Portail Substances Chimiques | 58 |





